Long Division Worksheet with Answers and Examples
Understanding Long Division: A Comprehensive Guide
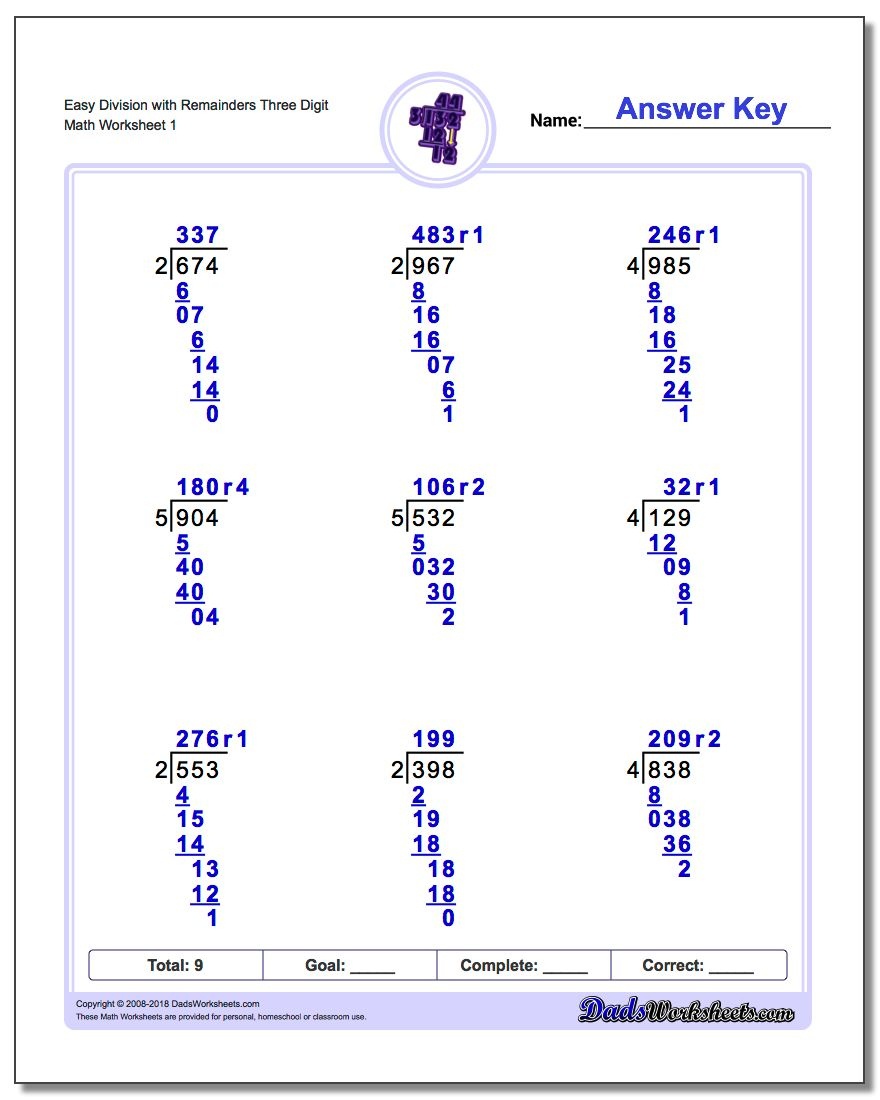
Long division is a method used to divide a large number (dividend) by a smaller number (divisor) to find the quotient and remainder. It is a crucial concept in mathematics, and mastering it can help you solve various mathematical problems. In this article, we will provide a detailed explanation of long division, including examples, worksheets, and answers.
Step-by-Step Guide to Long Division
To perform long division, follow these steps:
- Write the dividend and divisor: Write the dividend (the number being divided) on top of a line, and the divisor (the number by which we are dividing) below it.
- Divide the first digit: Divide the first digit of the dividend by the divisor, and write the result below the line.
- Multiply and subtract: Multiply the result from step 2 by the divisor, and subtract the product from the dividend.
- Bring down the next digit: Bring down the next digit of the dividend, and repeat steps 2 and 3.
- Repeat the process: Continue repeating steps 2-4 until you have processed all the digits of the dividend.
- Write the remainder: The final result is the quotient (result of the division) and the remainder (the amount left over).
Examples of Long Division
Example 1: Dividing a 2-Digit Number by a 1-Digit Number

| 12 | ÷ | 3 |
| _____ | ||
| 4 | 0 | 0 |
To divide 12 by 3, we follow the steps:
- Write the dividend (12) and divisor (3).
- Divide the first digit (1) by 3, which gives us 0.
- Multiply 0 by 3, and subtract the product from 12, which gives us 12.
- Bring down the next digit (2), and divide 12 by 3, which gives us 4.
- Write the remainder, which is 0.
The final answer is: 4 R 0
Example 2: Dividing a 3-Digit Number by a 2-Digit Number
| 432 | ÷ | 12 |
| _____ | ||
| 36 | 0 | 0 |
To divide 432 by 12, we follow the steps:
- Write the dividend (432) and divisor (12).
- Divide the first digit (4) by 12, which gives us 0.
- Multiply 0 by 12, and subtract the product from 432, which gives us 432.
- Bring down the next digit (3), and divide 43 by 12, which gives us 3.
- Multiply 3 by 12, and subtract the product from 43, which gives us 7.
- Bring down the next digit (2), and divide 72 by 12, which gives us 6.
- Write the remainder, which is 0.
The final answer is: 36 R 0
Long Division Worksheet
Here is a worksheet with 5 long division problems for you to practice:
| 1. 945 ÷ 15 = | _____ |
| 2. 216 ÷ 12 = | _____ |
| 3. 753 ÷ 9 = | _____ |
| 4. 945 ÷ 20 = | _____ |
| 5. 1234 ÷ 34 = | _____ |
Answers to the Worksheet
Here are the answers to the worksheet:
| 1. 945 ÷ 15 = 63 R 0 |
| 2. 216 ÷ 12 = 18 R 0 |
| 3. 753 ÷ 9 = 83 R 6 |
| 4. 945 ÷ 20 = 47 R 5 |
| 5. 1234 ÷ 34 = 36 R 10 |
Conclusion
Long division is a fundamental concept in mathematics, and mastering it can help you solve various mathematical problems. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can become proficient in long division. Remember to practice regularly to improve your skills. With practice, you will become more confident and proficient in your ability to perform long division.
What is the purpose of long division?
+Long division is used to divide a large number (dividend) by a smaller number (divisor) to find the quotient and remainder.
How do I perform long division?
+To perform long division, follow these steps: write the dividend and divisor, divide the first digit, multiply and subtract, bring down the next digit, and repeat the process until you have processed all the digits of the dividend.
What is the remainder in long division?
+The remainder is the amount left over after dividing the dividend by the divisor.
Related Terms:
- Worksheet division Grade 3
- Division Worksheet Grade 4
- Division without regrouping worksheets
- Division Worksheet grade 2
- Division drill worksheets pdf