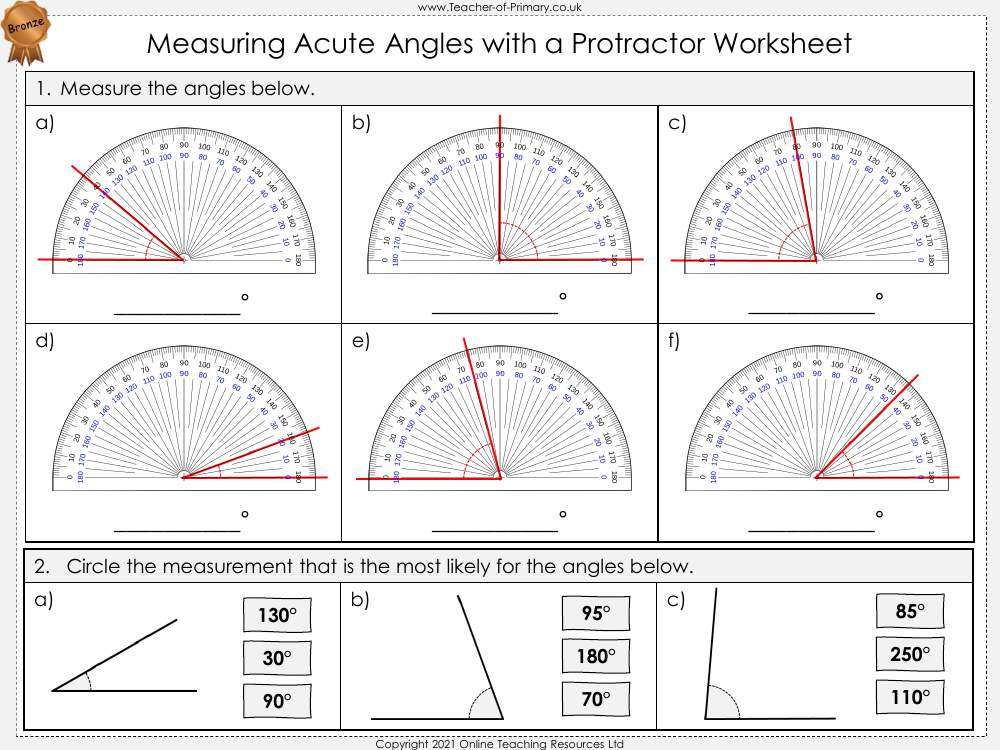
Top 7 Isotopes Worksheet Answers for Students
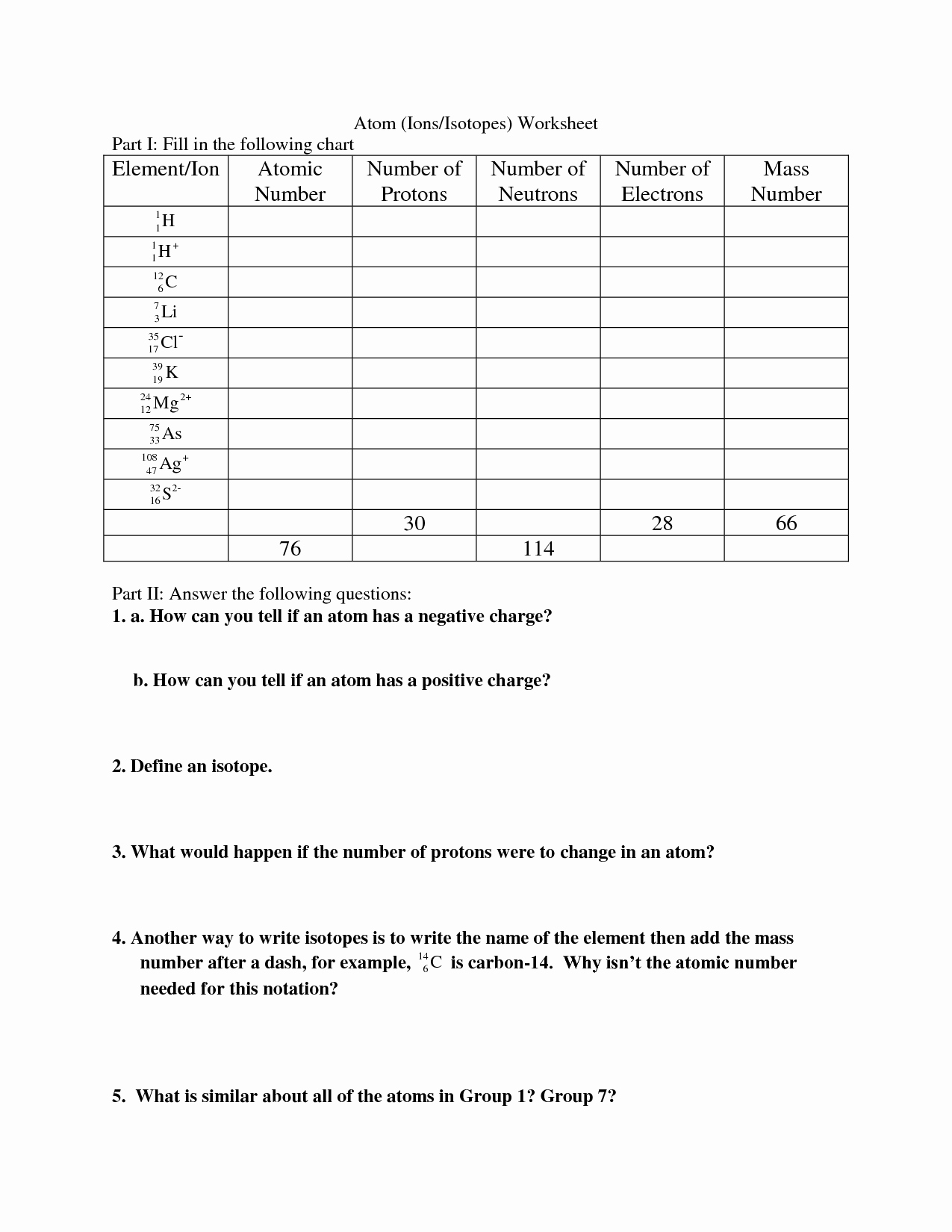
Understanding Isotopes: A Comprehensive Guide for Students
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons in their atomic nuclei. This variation in neutron number leads to differences in physical properties, such as mass and radioactivity. As a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics, understanding isotopes is crucial for students. This article will provide a detailed explanation of isotopes, their types, and applications, along with a worksheet to help students reinforce their knowledge.
What are Isotopes?
Isotopes are atoms of the same chemical element that have the same number of protons (atomic number) but differ in the number of neutrons in their nuclei. This difference in neutron number affects the atomic mass of the isotope but not its chemical properties. Isotopes can be classified into two main categories: stable isotopes and radioactive isotopes.
Stable Isotopes
Stable isotopes are non-radioactive and have a stable nucleus. They do not undergo spontaneous radioactive decay and are abundant in nature. Examples of stable isotopes include carbon-12, oxygen-16, and nitrogen-14.
Radioactive Isotopes
Radioactive isotopes, on the other hand, have an unstable nucleus and undergo radioactive decay, emitting radiation to become more stable. These isotopes have a limited lifespan and are used in various applications, including medicine, industry, and scientific research. Examples of radioactive isotopes include carbon-14, uranium-238, and potassium-40.
Types of Isotopes
Isotopes can be classified based on their neutron number and stability. Here are the main types of isotopes:
- Protium: Isotopes with one proton and no neutrons in their nucleus.
- Deuterium: Isotopes with one proton and one neutron in their nucleus.
- Tritium: Isotopes with one proton and two neutrons in their nucleus.
- Radioisotopes: Isotopes that undergo radioactive decay.
Applications of Isotopes
Isotopes have numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Medicine: Radioisotopes are used in medical imaging, cancer treatment, and diagnostics.
- Industry: Isotopes are used in oil and gas exploration, food irradiation, and sterilization of medical instruments.
- Scientific Research: Isotopes are used in dating rocks and fossils, studying climate change, and analyzing environmental samples.
Top 7 Isotopes Worksheet Answers
Here are the answers to a worksheet on isotopes:
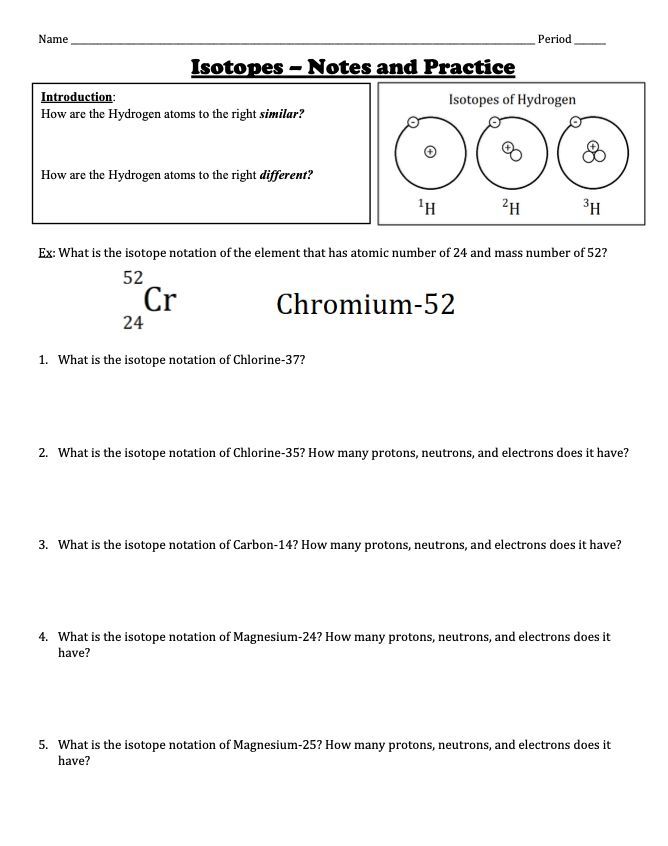
| Isotope | Atomic Number | Neutron Number | Stability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon-12 | 6 | 6 | Stable |
| Carbon-14 | 6 | 8 | Radioactive |
| Oxygen-16 | 8 | 8 | Stable |
| Uranium-238 | 92 | 146 | Radioactive |
| Potassium-40 | 19 | 21 | Radioactive |
| Nitrogen-14 | 7 | 7 | Stable |
| Hydrogen-1 (Protium) | 1 | 0 | Stable |
📝 Note: The atomic number and neutron number of an isotope can be used to determine its stability and type.
In conclusion, isotopes are an essential concept in chemistry and physics, and understanding their types, properties, and applications is crucial for students. The worksheet answers provided above will help students reinforce their knowledge and prepare for exams.
What is the difference between stable and radioactive isotopes?
+Stable isotopes have a stable nucleus and do not undergo radioactive decay, while radioactive isotopes have an unstable nucleus and undergo radioactive decay.
What are some common applications of isotopes?
+Isotopes are used in medicine, industry, and scientific research, including medical imaging, cancer treatment, and dating rocks and fossils.
How can isotopes be classified?
+Isotopes can be classified based on their neutron number and stability, including protium, deuterium, tritium, and radioisotopes.