5 Ways to Master Stoichiometry

Mastering Stoichiometry: The Key to Unlocking Chemical Reactions
Stoichiometry is a fundamental concept in chemistry that deals with the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions. It’s a crucial tool for chemists, engineers, and scientists to balance equations, predict yields, and optimize reaction conditions. However, many students struggle to grasp the concepts of stoichiometry, leading to frustration and confusion. In this article, we’ll explore five ways to master stoichiometry and make it a breeze to work with.
1. Understand the Basics: Mole Ratios and Conversion Factors
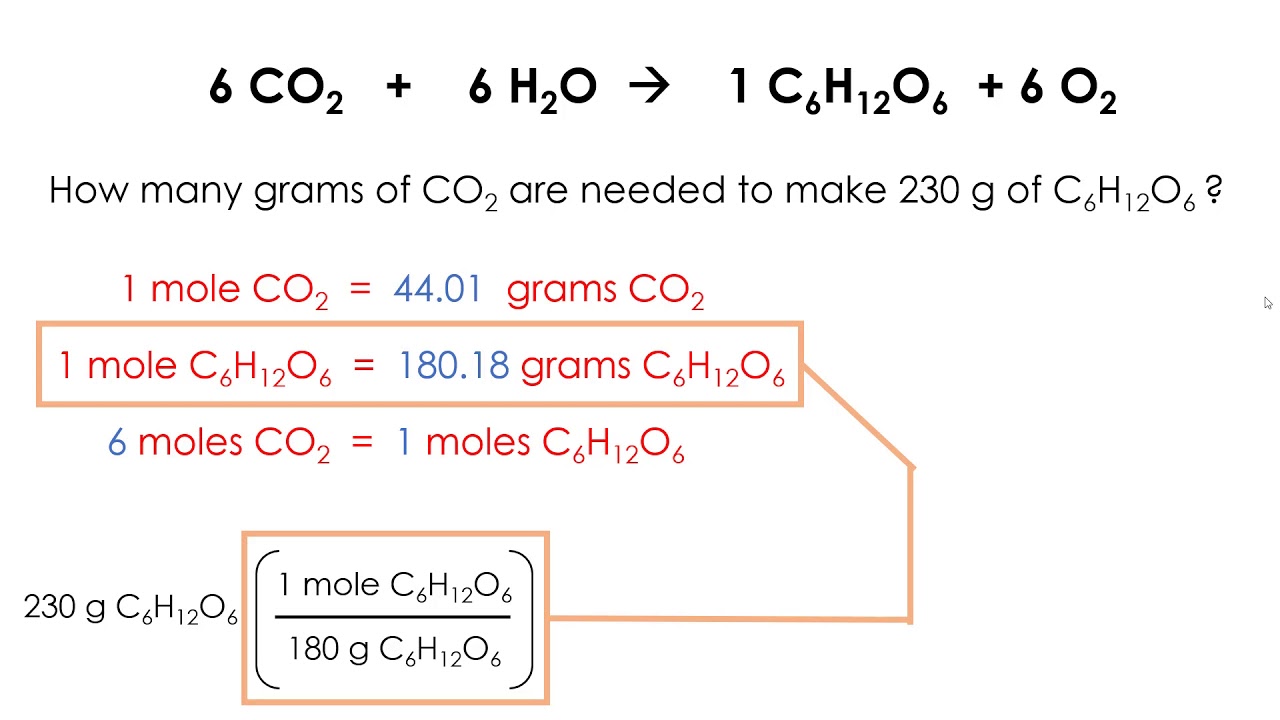
Stoichiometry is all about mole ratios and conversion factors. To start, you need to understand the concept of a mole and how to calculate mole ratios. A mole is a unit of measurement that represents 6.022 x 10^23 particles (atoms or molecules). Mole ratios are used to describe the proportions of reactants and products in a balanced equation.
To work with mole ratios, you need to be familiar with conversion factors. Conversion factors are used to convert between different units, such as grams to moles or moles to liters. Here are some common conversion factors:
- 1 mole = 6.022 x 10^23 particles
- 1 mole = 22.4 liters (at STP)
- 1 gram = 1 mole x molar mass
By understanding mole ratios and conversion factors, you’ll be able to balance equations and calculate the amounts of reactants and products.
2. Practice Balancing Equations
Balancing equations is an essential skill in stoichiometry. It involves making sure that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both the reactant and product sides of the equation. Here are some tips for balancing equations:
- Start by counting the number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation.
- Use coefficients (numbers in front of the formulas of reactants or products) to balance the equation.
- Balance the equation one element at a time, starting with elements that appear only once on each side.
- Use the “half-reaction” method to balance equations that involve oxidation and reduction reactions.
Practice balancing equations with different types of reactions, such as synthesis, decomposition, and replacement reactions.
3. Use Stoichiometry Tables
Stoichiometry tables are a powerful tool for solving stoichiometry problems. A stoichiometry table is a table that lists the number of moles of each reactant and product in a balanced equation. By using a stoichiometry table, you can easily calculate the amounts of reactants and products.
Here’s an example of a stoichiometry table for the reaction between hydrogen and oxygen to form water:
| Reactant/Product | Moles |
|---|---|
| H2 | 2 |
| O2 | 1 |
| H2O | 2 |
By using a stoichiometry table, you can calculate the number of moles of each reactant and product, making it easier to solve stoichiometry problems.
4. Learn to Calculate Percent Yield
Percent yield is a measure of the efficiency of a reaction. It’s calculated by dividing the actual yield of a product by the theoretical yield and multiplying by 100.
Percent Yield = (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) x 100
To calculate percent yield, you need to know the actual yield of the product and the theoretical yield. The actual yield is the amount of product that’s actually obtained, while the theoretical yield is the amount of product that’s predicted by the balanced equation.
Here’s an example of calculating percent yield:
- Theoretical yield = 100 g
- Actual yield = 80 g
- Percent yield = (80 g / 100 g) x 100 = 80%
By learning to calculate percent yield, you can evaluate the efficiency of a reaction and optimize reaction conditions.
5. Practice, Practice, Practice
Practice is key to mastering stoichiometry. Try solving different types of stoichiometry problems, such as:
- Limiting reagent problems
- Percent yield problems
- Stoichiometry tables
Use online resources, such as Khan Academy or MIT OpenCourseWare, to practice solving stoichiometry problems. You can also use stoichiometry worksheets or practice problems from textbooks.
By following these five tips, you’ll be well on your way to mastering stoichiometry and becoming a proficient chemist.
What is stoichiometry?
+Stoichiometry is the branch of chemistry that deals with the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions.
What is the importance of mole ratios in stoichiometry?
+Mole ratios are essential in stoichiometry because they describe the proportions of reactants and products in a balanced equation.
How do I calculate percent yield?
+Percent yield is calculated by dividing the actual yield of a product by the theoretical yield and multiplying by 100.
By mastering stoichiometry, you’ll be able to solve complex chemical problems and become a proficient chemist. Remember to practice regularly and use online resources to reinforce your learning.
Related Terms:
- Gram to Gram stoichiometry formula
- Grams to grams stoichiometry calculator