Ionic Bonding Worksheet Answers
Understanding Ionic Bonding: A Comprehensive Guide
Ionic bonding is a fundamental concept in chemistry that involves the formation of ions and their subsequent combination to form a stable molecule. In this article, we will delve into the world of ionic bonding, exploring its definition, types, and examples. We will also provide a comprehensive worksheet with answers to help reinforce your understanding of this crucial topic.
What is Ionic Bonding?
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that occurs between two atoms with significantly different electronegativities. This results in the transfer of one or more electrons from the less electronegative atom (typically a metal) to the more electronegative atom (usually a nonmetal). The resulting ions have opposite charges, which attract each other to form a strong ionic bond.
Types of Ionic Bonds
There are two primary types of ionic bonds:
- Monatomic ions: These are formed when a single atom gains or loses electrons to achieve a stable noble gas configuration. Examples include sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl-).
- Polyatomic ions: These are formed when multiple atoms share electrons to achieve a stable noble gas configuration. Examples include ammonium (NH4+) and carbonate (CO32-).
How Ionic Bonds are Formed
The formation of ionic bonds involves the following steps:
- Electron transfer: One or more electrons are transferred from the less electronegative atom to the more electronegative atom.
- Ion formation: The resulting ions have opposite charges, which attract each other.
- Bond formation: The ions combine to form a stable molecule, with the positively charged ion (cation) attracted to the negatively charged ion (anion).
Examples of Ionic Bonds
Some common examples of ionic bonds include:
- Sodium chloride (NaCl): Formed between sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl-) ions.
- Calcium carbonate (CaCO3): Formed between calcium (Ca2+) and carbonate (CO32-) ions.
- Ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3): Formed between ammonium (NH4+) and nitrate (NO3-) ions.
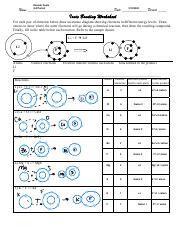
Worksheet Answers
Below are the answers to a comprehensive ionic bonding worksheet:
Section 1: Multiple Choice
- What is the primary driving force behind ionic bonding? a) Electron transfer b) Electrostatic attraction c) Covalent sharing d) Hydrogen bonding
Answer: b) Electrostatic attraction
- Which of the following is an example of a polyatomic ion? a) Sodium (Na+) b) Chloride (Cl-) c) Ammonium (NH4+) d) Calcium (Ca2+)
Answer: c) Ammonium (NH4+)
Section 2: Short Answer
- Describe the difference between monatomic and polyatomic ions.
Answer: Monatomic ions are formed when a single atom gains or loses electrons to achieve a stable noble gas configuration. Polyatomic ions, on the other hand, are formed when multiple atoms share electrons to achieve a stable noble gas configuration.
- What is the role of electron transfer in ionic bonding?
Answer: Electron transfer is the primary mechanism by which ionic bonds are formed. One or more electrons are transferred from the less electronegative atom to the more electronegative atom, resulting in the formation of ions with opposite charges.
Section 3: Essay Question
Describe the formation of an ionic bond between sodium (Na) and chloride (Cl). Be sure to include the role of electron transfer and electrostatic attraction.
Answer: The formation of an ionic bond between sodium (Na) and chloride (Cl) involves the transfer of one electron from the sodium atom to the chloride atom. This results in the formation of a positively charged sodium ion (Na+) and a negatively charged chloride ion (Cl-). The oppositely charged ions are then attracted to each other through electrostatic forces, resulting in the formation of a strong ionic bond.
👍 Note: Ionic bonds are typically stronger than covalent bonds due to the electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions.
Section 4: Fill-in-the-Blank
- The resulting ions in an ionic bond have ______________________ charges.
Answer: opposite
- The primary mechanism by which ionic bonds are formed is through ______________________.
Answer: electron transfer
Conclusion
In conclusion, ionic bonding is a fundamental concept in chemistry that involves the formation of ions and their subsequent combination to form a stable molecule. Understanding the different types of ionic bonds, how they are formed, and the role of electron transfer and electrostatic attraction is crucial for any student of chemistry. We hope this comprehensive guide and worksheet answers have helped reinforce your understanding of ionic bonding.
What is the main difference between ionic and covalent bonds?
+
The main difference between ionic and covalent bonds is the way in which the atoms share electrons. In ionic bonds, electrons are transferred from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of ions with opposite charges. In covalent bonds, electrons are shared between atoms to form a stable molecule.
What is an example of a polyatomic ion?
+
An example of a polyatomic ion is the ammonium ion (NH4+), which is formed when multiple atoms share electrons to achieve a stable noble gas configuration.
What is the role of electron transfer in ionic bonding?
+
Electron transfer is the primary mechanism by which ionic bonds are formed. One or more electrons are transferred from the less electronegative atom to the more electronegative atom, resulting in the formation of ions with opposite charges.