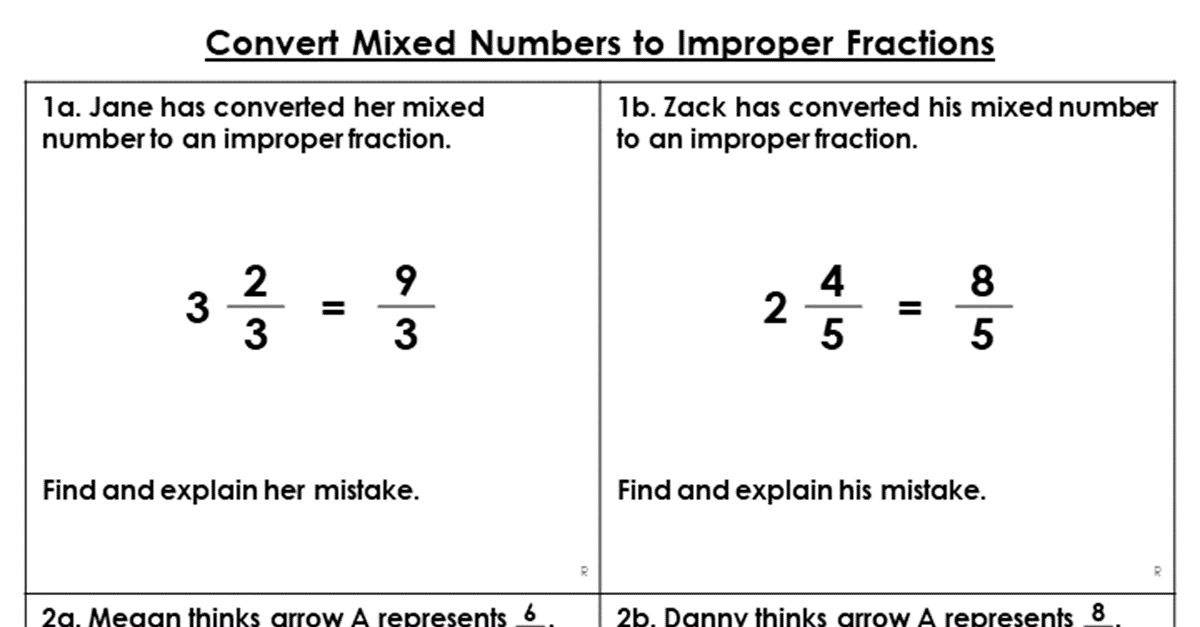
Cell Size Limitations: Surface Area to Volume Ratio Explained

Cell Size Limitations: The Importance of Surface Area to Volume Ratio
The size of a cell is a critical factor in determining its function and survival. While larger cells may seem more efficient, there are limitations to cell size due to the surface area to volume ratio. In this article, we will explore the importance of this ratio and how it affects cell function.
What is the Surface Area to Volume Ratio?
The surface area to volume ratio is a mathematical concept that describes the relationship between the surface area of a cell and its volume. The surface area is the total area of the cell membrane, while the volume is the total amount of space inside the cell. As cells grow in size, their volume increases faster than their surface area. This means that the surface area to volume ratio decreases as the cell size increases.
Why is the Surface Area to Volume Ratio Important?
The surface area to volume ratio is important because it affects the rate of diffusion, the efficiency of nutrient uptake, and the cell’s ability to regulate its internal environment. A smaller surface area to volume ratio means that the cell has less surface area available for diffusion, making it more difficult for nutrients to enter and waste to leave. This can lead to a decrease in cellular function and potentially even cell death.
Consequences of a Large Cell Size
As cells grow in size, the surface area to volume ratio decreases, leading to several consequences:
- Reduced diffusion rates: With a smaller surface area to volume ratio, the rate of diffusion decreases, making it more difficult for nutrients to enter the cell.
- Decreased efficiency of nutrient uptake: A smaller surface area to volume ratio means that the cell has less surface area available for nutrient uptake, making it less efficient.
- Impaired regulation of internal environment: A larger cell size makes it more difficult for the cell to regulate its internal environment, leading to potential problems with ion balance and pH regulation.
- Increased energy expenditure: Larger cells require more energy to maintain their internal environment and support their increased size.
Examples of Cell Size Limitations
Several examples illustrate the limitations of cell size due to the surface area to volume ratio:
- Bacteria: While some bacteria can grow to be quite large, most are small in size. This is because larger bacteria would have a smaller surface area to volume ratio, making it more difficult for them to regulate their internal environment.
- Cells in the human body: Cells in the human body, such as muscle cells and nerve cells, have a limited size range. This is because larger cells would have a smaller surface area to volume ratio, leading to decreased efficiency and potentially even cell death.
Evolutionary Adaptations to Overcome Cell Size Limitations
Several evolutionary adaptations have emerged to overcome the limitations of cell size:
- Increased surface area: Some cells, such as those in the lungs, have increased surface area to improve gas exchange.
- Microvilli: Microvilli are small projections on the surface of cells that increase the surface area to volume ratio.
- Folds and invaginations: Some cells have folds and invaginations that increase the surface area to volume ratio.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the surface area to volume ratio is a critical factor in determining cell function and survival. As cells grow in size, their volume increases faster than their surface area, leading to a decrease in the surface area to volume ratio. This can lead to decreased diffusion rates, decreased efficiency of nutrient uptake, impaired regulation of internal environment, and increased energy expenditure. Understanding the limitations of cell size due to the surface area to volume ratio is essential for understanding cellular function and the evolution of life on Earth.
What is the surface area to volume ratio?
+The surface area to volume ratio is a mathematical concept that describes the relationship between the surface area of a cell and its volume.
Why is the surface area to volume ratio important?
+The surface area to volume ratio is important because it affects the rate of diffusion, the efficiency of nutrient uptake, and the cell’s ability to regulate its internal environment.
What are some examples of cell size limitations?
+Examples of cell size limitations include bacteria, cells in the human body, and cells in other organisms that have evolved to overcome these limitations.