Mastering Heating Curves: Worksheet with Answers Inside
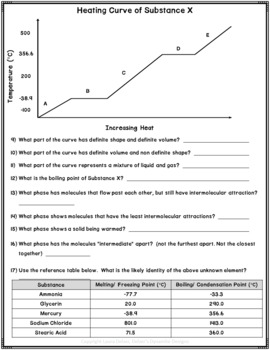
Heating Curves: A Comprehensive Guide
A heating curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the temperature of a substance and the amount of heat energy added to it. Understanding heating curves is crucial in various fields, including chemistry, physics, and engineering. In this article, we will delve into the world of heating curves, exploring their significance, types, and applications.
What is a Heating Curve?
A heating curve is a plot of temperature against heat energy added to a substance. The curve illustrates how the temperature of a substance changes as it absorbs heat energy. The shape of the curve depends on the physical properties of the substance, such as its specific heat capacity, melting point, and boiling point.
Types of Heating Curves
There are several types of heating curves, each representing a different phase transition or physical process. Some of the most common types of heating curves include:
- Solid-Liquid Phase Transition Curve: This curve represents the melting of a solid as it absorbs heat energy. The temperature remains constant until the solid is completely melted.
- Liquid-Vapor Phase Transition Curve: This curve represents the vaporization of a liquid as it absorbs heat energy. The temperature remains constant until the liquid is completely vaporized.
- Linear Heating Curve: This curve represents the heating of a substance that does not undergo a phase transition. The temperature increases linearly with the addition of heat energy.
Key Features of Heating Curves
Heating curves have several key features that are essential to understand:
- Melting Point: The temperature at which a solid begins to melt.
- Boiling Point: The temperature at which a liquid begins to vaporize.
- Specific Heat Capacity: The amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a substance by 1°C.
- Heat of Fusion: The amount of heat energy required to melt a solid.
- Heat of Vaporization: The amount of heat energy required to vaporize a liquid.
Applications of Heating Curves
Heating curves have numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Chemical Engineering: Heating curves are used to design and optimize heat transfer systems, such as heat exchangers and reactors.
- Materials Science: Heating curves are used to study the thermal properties of materials, such as their melting points and specific heat capacities.
- Food Processing: Heating curves are used to optimize food processing techniques, such as cooking and sterilization.
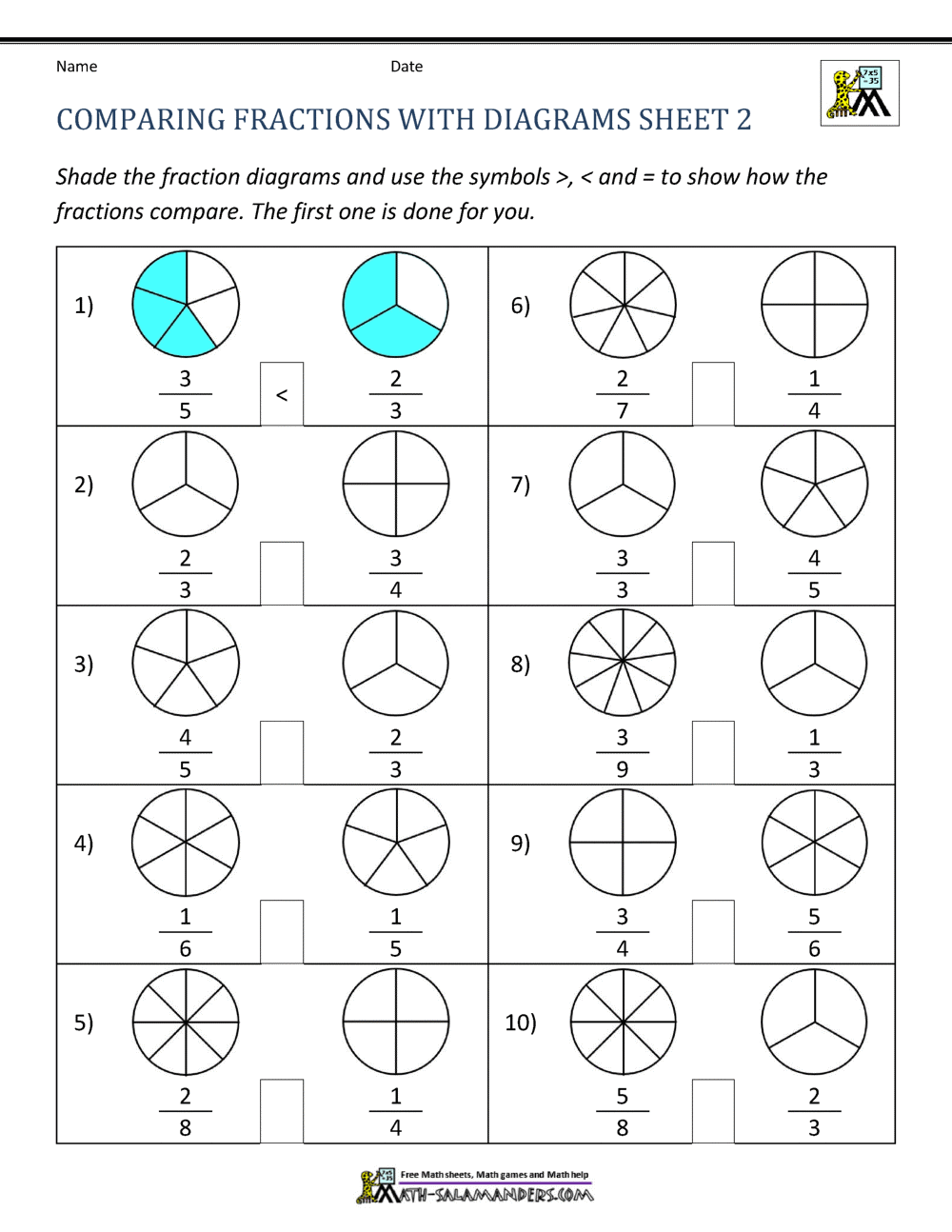
Worksheet with Answers
Now that we have covered the basics of heating curves, let’s practice with a worksheet. Please answer the following questions:
- What is the melting point of ice?
- What is the boiling point of water?
- What is the specific heat capacity of copper?
- What is the heat of fusion of ice?
- What is the heat of vaporization of water?
Answers
- 0°C
- 100°C
- 0.385 J/g°C
- 334 J/g
- 2250 J/g
🔍 Note: The answers are based on standard values and may vary slightly depending on the specific conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, heating curves are a powerful tool for understanding the thermal properties of substances. By analyzing heating curves, we can gain insights into the physical processes that occur during phase transitions and heat transfer. With this knowledge, we can design and optimize systems, materials, and processes that are more efficient, safe, and sustainable.
What is the significance of heating curves in chemical engineering?
+Heating curves are used to design and optimize heat transfer systems, such as heat exchangers and reactors, which are crucial in chemical engineering.
What is the difference between heat of fusion and heat of vaporization?
+Heat of fusion is the amount of heat energy required to melt a solid, while heat of vaporization is the amount of heat energy required to vaporize a liquid.
How are heating curves used in food processing?
+Heating curves are used to optimize food processing techniques, such as cooking and sterilization, to ensure that food is cooked evenly and safely.