7 Ways to Solve Genetics Problems Easily
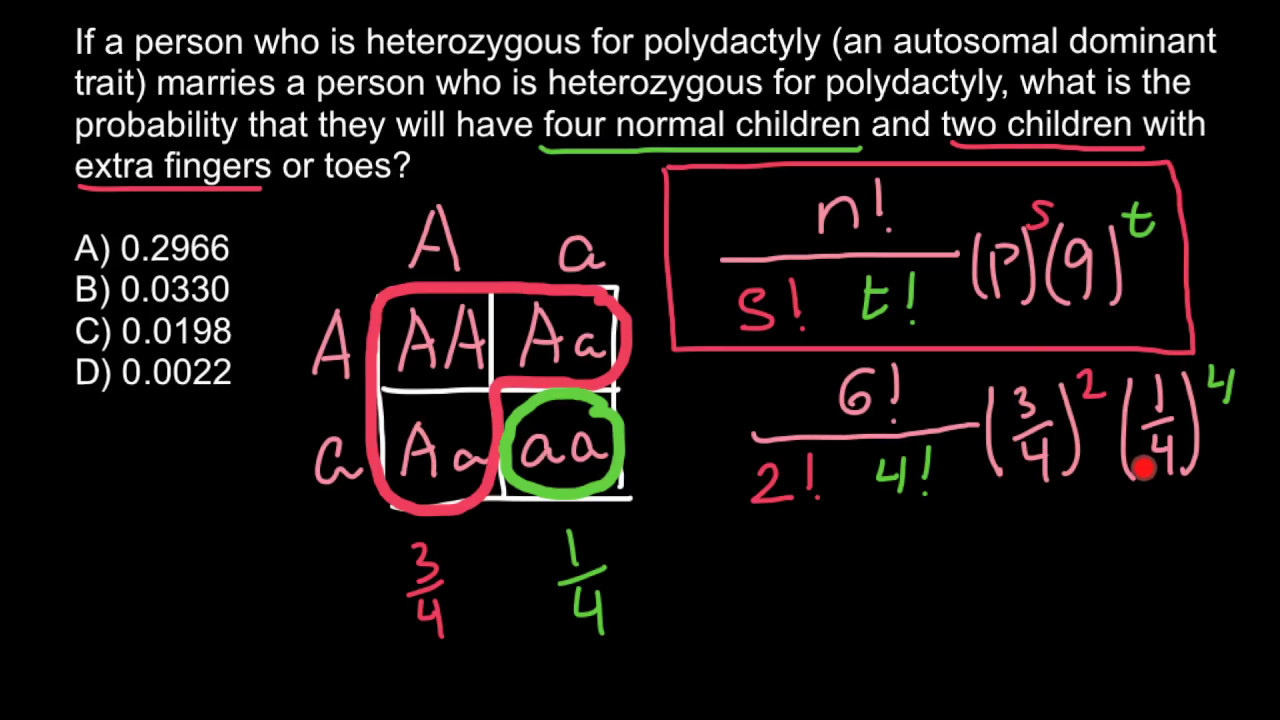
Introduction to Genetics Problems
Genetics problems can be intimidating, especially for students who are new to the subject. However, with the right approach and techniques, solving genetics problems can become easier and more manageable. In this article, we will discuss 7 ways to solve genetics problems easily, including understanding the basics, using Punnett squares, and analyzing pedigree charts.
1. Understand the Basics of Genetics
Before diving into solving genetics problems, it’s essential to understand the basics of genetics. This includes knowing the difference between genotype and phenotype, understanding the laws of Mendel, and being familiar with genetic terminology. Make sure you understand the following key concepts:
- Genotype: The genetic makeup of an individual, including the specific genes and alleles they possess.
- Phenotype: The physical expression of an individual’s genotype, such as their eye color or height.
- Mendel’s laws: The fundamental principles of inheritance, including the law of segregation and the law of independent assortment.
📝 Note: Reviewing the basics of genetics is crucial to solving genetics problems. Take the time to study and understand these concepts before moving on to more complex problems.
2. Use Punnett Squares to Predict Genotypes and Phenotypes
Punnett squares are a powerful tool for predicting the genotypes and phenotypes of offspring. A Punnett square is a diagram that shows the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a cross between two parents. To use a Punnett square, follow these steps:
- Determine the genotypes of the parents.
- Identify the possible alleles that can be inherited by the offspring.
- Draw a Punnett square and fill in the possible genotypes of the offspring.
- Determine the probability of each genotype and phenotype.

| Parent 1 | Parent 2 | Offspring Genotype | Offspring Phenotype |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bb | Bb | BB, Bb, bb | Brown eyes, blue eyes |
| BB | bb | Bb | Brown eyes |
3. Analyze Pedigree Charts to Determine Genetic Relationships
Pedigree charts are diagrams that show the genetic relationships between individuals in a family. To analyze a pedigree chart, follow these steps:
- Identify the individuals in the pedigree chart and their relationships to each other.
- Determine the genotypes of the individuals in the pedigree chart.
- Look for patterns of inheritance, such as autosomal dominant or recessive traits.
📝 Note: Pedigree charts can be complex, so take the time to carefully analyze the relationships between individuals and the patterns of inheritance.
4. Use Hardy-Weinberg Equations to Calculate Allele Frequencies
The Hardy-Weinberg equation is a mathematical formula that describes the frequency of alleles in a population. The equation is:
p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1
Where:
- p is the frequency of the dominant allele
- q is the frequency of the recessive allele
To use the Hardy-Weinberg equation, follow these steps:
- Determine the frequency of the dominant and recessive alleles in the population.
- Plug the frequencies into the equation and solve for p and q.
- Use the frequencies to calculate the probability of each genotype and phenotype.
5. Practice, Practice, Practice
Solving genetics problems requires practice and repetition. The more you practice, the more comfortable you’ll become with the concepts and techniques. Try solving different types of genetics problems, such as:
- Monohybrid crosses: Crosses between two parents that differ in only one trait.
- Dihybrid crosses: Crosses between two parents that differ in two traits.
- Pedigree analysis: Analyzing pedigree charts to determine genetic relationships.
6. Use Online Resources and Tools
There are many online resources and tools available to help you solve genetics problems. Some popular resources include:
- Genetics simulators: Online tools that allow you to simulate genetic crosses and analyze the results.
- Genetics calculators: Online calculators that can help you calculate allele frequencies and probabilities.
- Genetics tutorials: Online tutorials that provide step-by-step instructions for solving genetics problems.
7. Join a Study Group or Find a Study Partner
Solving genetics problems can be challenging, but it’s more fun and effective with a study group or partner. Join a study group or find a study partner who is also interested in genetics. You can work together to solve problems, discuss concepts, and share resources.
In conclusion, solving genetics problems requires a combination of understanding the basics, using tools and techniques, and practicing regularly. By following these 7 ways to solve genetics problems easily, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a genetics master.
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
+Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an individual, including the specific genes and alleles they possess. Phenotype refers to the physical expression of an individual’s genotype, such as their eye color or height.
How do I use a Punnett square to predict genotypes and phenotypes?
+To use a Punnett square, determine the genotypes of the parents, identify the possible alleles that can be inherited by the offspring, draw a Punnett square and fill in the possible genotypes of the offspring, and determine the probability of each genotype and phenotype.
What is the Hardy-Weinberg equation and how do I use it?
+The Hardy-Weinberg equation is a mathematical formula that describes the frequency of alleles in a population. To use the equation, determine the frequency of the dominant and recessive alleles in the population, plug the frequencies into the equation and solve for p and q, and use the frequencies to calculate the probability of each genotype and phenotype.