Forecasting Weather Map Worksheet #3 Made Easy
Mastering Weather Map Forecasting: A Step-by-Step Guide
As a meteorologist or weather enthusiast, being able to accurately forecast the weather is crucial. One of the most important tools in weather forecasting is the weather map. In this article, we will break down the complexities of weather map forecasting and provide a step-by-step guide on how to read and interpret these maps.
Understanding the Basics of Weather Maps
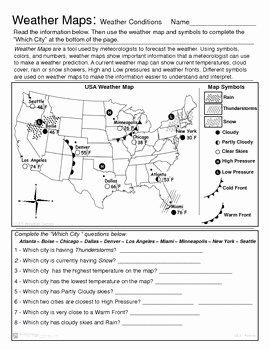
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty of weather map forecasting, it’s essential to understand the basics. Weather maps, also known as surface weather maps, are graphical representations of the current weather conditions over a specific area. These maps show various weather phenomena, such as high and low-pressure systems, fronts, and precipitation patterns.
🌡️ Note: Weather maps are typically drawn at the surface level, which is approximately 2 meters above the ground.
Identifying Key Features on a Weather Map
To accurately forecast the weather, you need to be able to identify the key features on a weather map. These features include:
- High and Low-Pressure Systems: These are indicated by large H’s and L’s on the map. High-pressure systems are typically associated with fair weather, while low-pressure systems are associated with inclement weather.
- Fronts: Fronts are boundaries between two air masses of different temperatures and humidity levels. There are four types of fronts: cold fronts, warm fronts, stationary fronts, and occluded fronts.
- Isobars: Isobars are lines that connect points of equal pressure on the map. They help identify high and low-pressure systems and can indicate wind direction and speed.
- Wind Direction and Speed: Wind direction is indicated by arrows on the map, while wind speed is indicated by the length of the arrow.
Interpreting Weather Maps: A Step-by-Step Guide
Now that you know the key features of a weather map, let’s move on to interpreting these maps. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Identify the location: Start by identifying the location of the weather map. Look for the latitude and longitude lines to determine the area covered by the map.
- Locate high and low-pressure systems: Identify the high and low-pressure systems on the map. Note their location, size, and shape.
- Identify fronts: Look for fronts on the map and note their location and type (cold, warm, stationary, or occluded).
- Analyze isobars: Analyze the isobars to identify areas of high and low pressure. Note the shape and orientation of the isobars to determine wind direction and speed.
- Determine wind direction and speed: Use the wind direction arrows to determine the direction and speed of the wind.

| Weather Map Feature | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| High-Pressure System | Associated with fair weather, light winds, and clear skies |
| Low-Pressure System | Associated with inclement weather, strong winds, and precipitation |
| Cold Front | Associated with rain, thunderstorms, and a drop in temperature |
| Warm Front | Associated with rain, fog, and a rise in temperature |
Common Weather Map Symbols
Weather maps use a variety of symbols to represent different weather phenomena. Here are some common symbols you’ll encounter:
- Cloud Symbols: Cloud symbols indicate the type and amount of cloud cover. The most common cloud symbols are:
- Cirrus clouds: Thin, wispy clouds
- Cumulus clouds: Puffy, white clouds
- Stratus clouds: Low-lying, layered clouds
- Precipitation Symbols: Precipitation symbols indicate the type and intensity of precipitation. The most common precipitation symbols are:
- Rain: Blue dots or lines
- Snow: White dots or lines
- Sleet: White dots or lines with a slash through them
- Other Symbols: Other symbols on a weather map include:
- Wind direction and speed arrows
- Front symbols (cold, warm, stationary, and occluded)
- High and low-pressure system symbols (H and L)
By following these steps and understanding the key features and symbols on a weather map, you’ll be able to accurately forecast the weather like a pro!
In this article, we’ve covered the basics of weather map forecasting and provided a step-by-step guide on how to read and interpret these maps. Remember to practice reading weather maps regularly to improve your forecasting skills.
As we conclude this article, we hope you’ve gained a better understanding of weather map forecasting. Keep in mind that practice makes perfect, so be sure to practice reading weather maps regularly to improve your forecasting skills.
What is the purpose of a weather map?
+A weather map is a graphical representation of the current weather conditions over a specific area. Its purpose is to help meteorologists and weather enthusiasts forecast the weather.
What are the key features of a weather map?
+The key features of a weather map include high and low-pressure systems, fronts, isobars, wind direction and speed arrows, and precipitation symbols.
How do I interpret a weather map?
+To interpret a weather map, start by identifying the location, high and low-pressure systems, fronts, isobars, and wind direction and speed arrows. Use these features to determine the current weather conditions and forecast the weather.