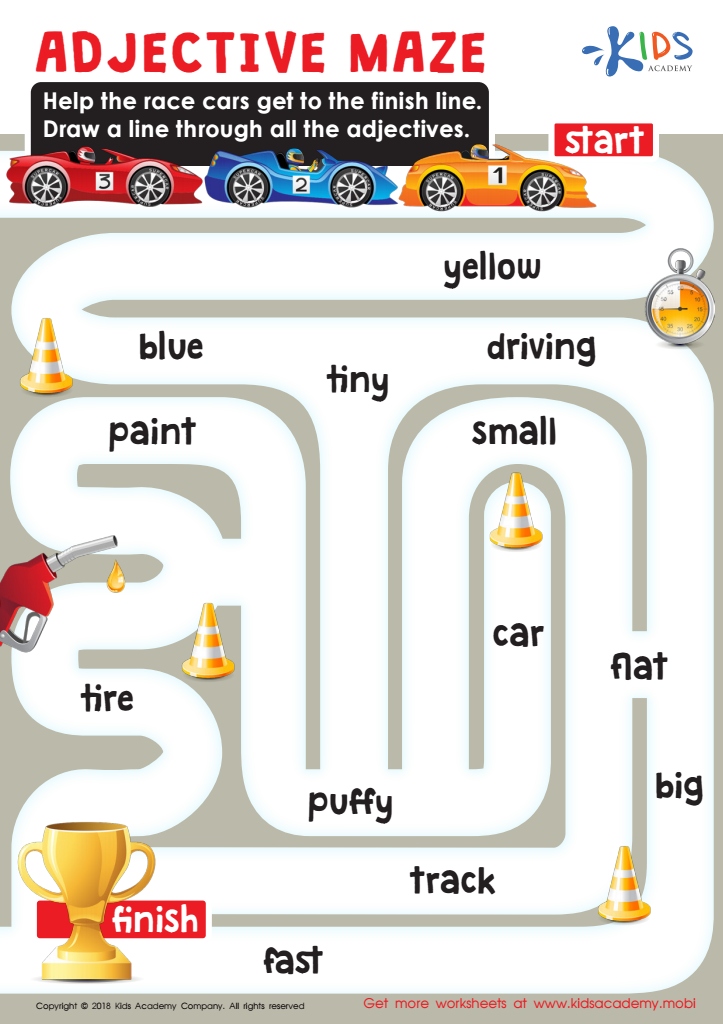
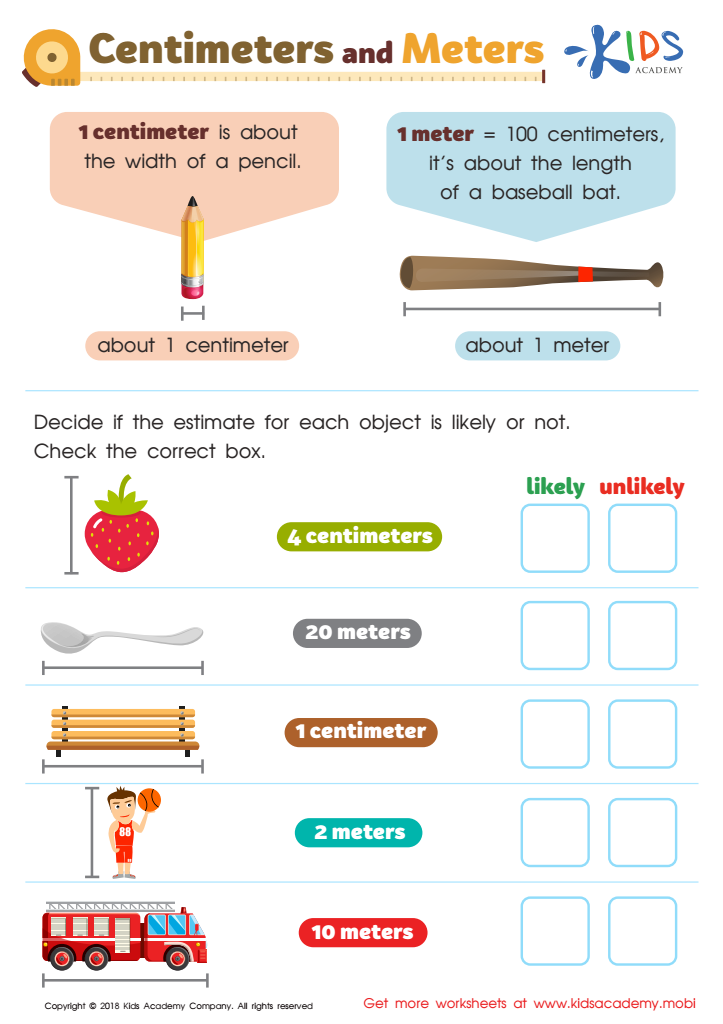
Protestant Reformation Worksheet

Understanding the Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a significant event in Christian history that took place in the 16th century. It was a time of great change and upheaval, marked by the emergence of new Christian denominations and the decline of the Catholic Church’s authority.
Causes of the Protestant Reformation
There were several factors that contributed to the Protestant Reformation, including:
- Disillusionment with the Catholic Church: Many people were dissatisfied with the Catholic Church’s corruption, abuses of power, and emphasis on rituals and traditions.
- The Rise of Humanism: Humanism emphasized the importance of individualism, reason, and intellectual curiosity, which led to a desire for reform within the Church.
- The Influence of the Printing Press: The invention of the printing press allowed for the widespread dissemination of ideas and contributed to the growth of literacy, which helped to spread Protestant ideas.
- The Church’s Response to the Black Death: The Church’s handling of the Black Death, which killed millions of people in Europe, led to widespread criticism and disillusionment with the Church.
Key Figures of the Protestant Reformation
Some of the key figures of the Protestant Reformation include:
- Martin Luther: A German theologian and monk who is often credited with starting the Protestant Reformation. He wrote the 95 Theses, which criticized the Catholic Church’s practice of selling indulgences.
- John Calvin: A French theologian who developed the doctrine of predestination and founded the Calvinist movement.
- Huldrych Zwingli: A Swiss theologian who played a key role in the Reformation in Switzerland.
- King Henry VIII: The King of England who broke away from the Catholic Church and established the Church of England.
Major Protestant Denominations
The Protestant Reformation led to the emergence of several major Protestant denominations, including:
- Lutheranism: Founded by Martin Luther, this denomination emphasizes justification by faith alone and the authority of Scripture.
- Calvinism: Founded by John Calvin, this denomination emphasizes predestination and the sovereignty of God.
- Anglicanism: Founded by King Henry VIII, this denomination emphasizes the authority of Scripture and the importance of tradition.
- Anabaptism: A movement that emphasizes adult baptism, community, and pacifism.
Impact of the Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation had a significant impact on Western society, including:
- The Decline of the Catholic Church’s Authority: The Protestant Reformation marked the beginning of the decline of the Catholic Church’s authority in Europe.
- The Emergence of New Christian Denominations: The Protestant Reformation led to the emergence of several new Christian denominations, which has contributed to the diversity of Christianity today.
- The Growth of Education and Literacy: The Protestant Reformation emphasized the importance of education and literacy, which contributed to the growth of education and literacy in Europe.
- The Development of Modern Democracy: The Protestant Reformation’s emphasis on individualism and the authority of Scripture contributed to the development of modern democracy.
📝 Note: The Protestant Reformation was a complex and multifaceted event that cannot be fully understood without considering its historical context and the diverse perspectives of those involved.
What was the main cause of the Protestant Reformation?
+The main cause of the Protestant Reformation was the widespread disillusionment with the Catholic Church's corruption, abuses of power, and emphasis on rituals and traditions.
Who was the key figure of the Protestant Reformation?
+Martin Luther is often credited with starting the Protestant Reformation. He wrote the 95 Theses, which criticized the Catholic Church's practice of selling indulgences.
What were the major Protestant denominations that emerged from the Reformation?
+The major Protestant denominations that emerged from the Reformation include Lutheranism, Calvinism, Anglicanism, and Anabaptism.
In conclusion, the Protestant Reformation was a significant event in Christian history that marked the beginning of the decline of the Catholic Church’s authority and the emergence of new Christian denominations. Understanding the causes, key figures, and impact of the Reformation can provide valuable insights into the complexities of Christian history and the diversity of Christianity today.
Related Terms:
- Protestant Reformation worksheet PDF
- English Reformation Worksheet
- Reformation activity