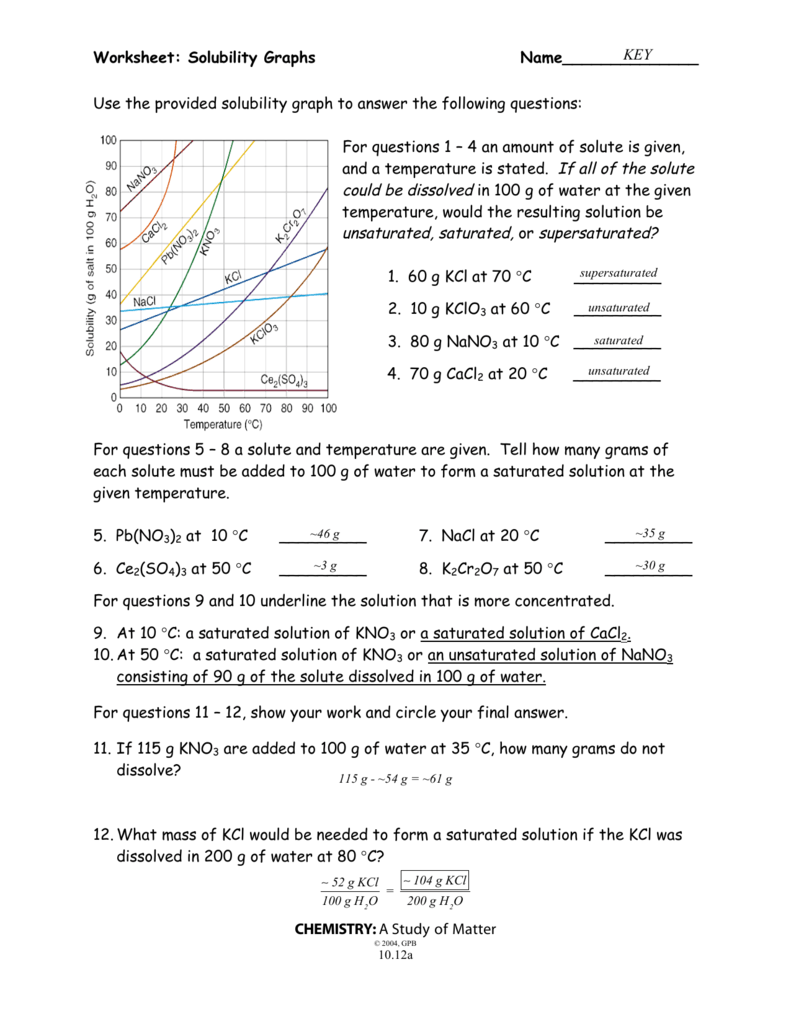
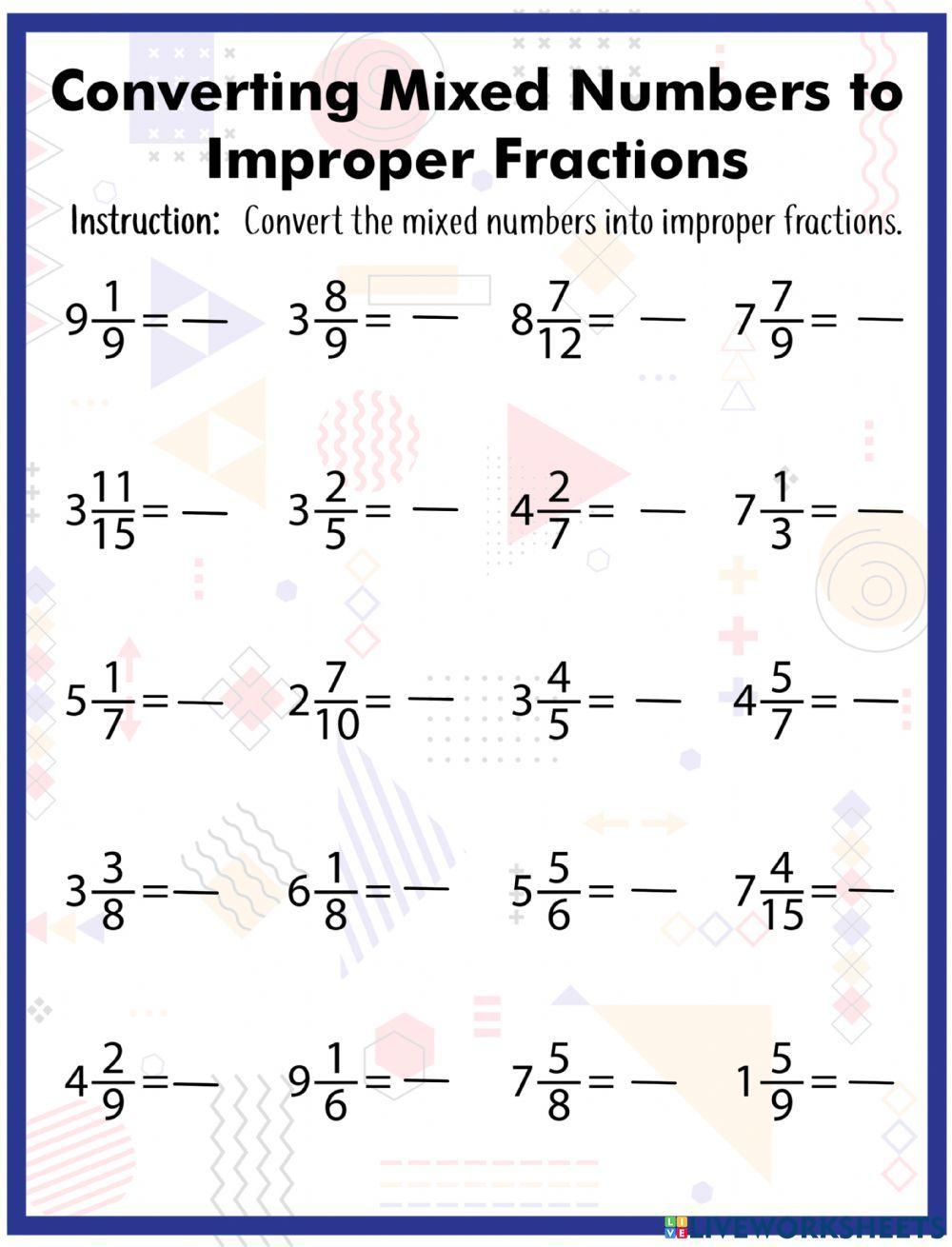
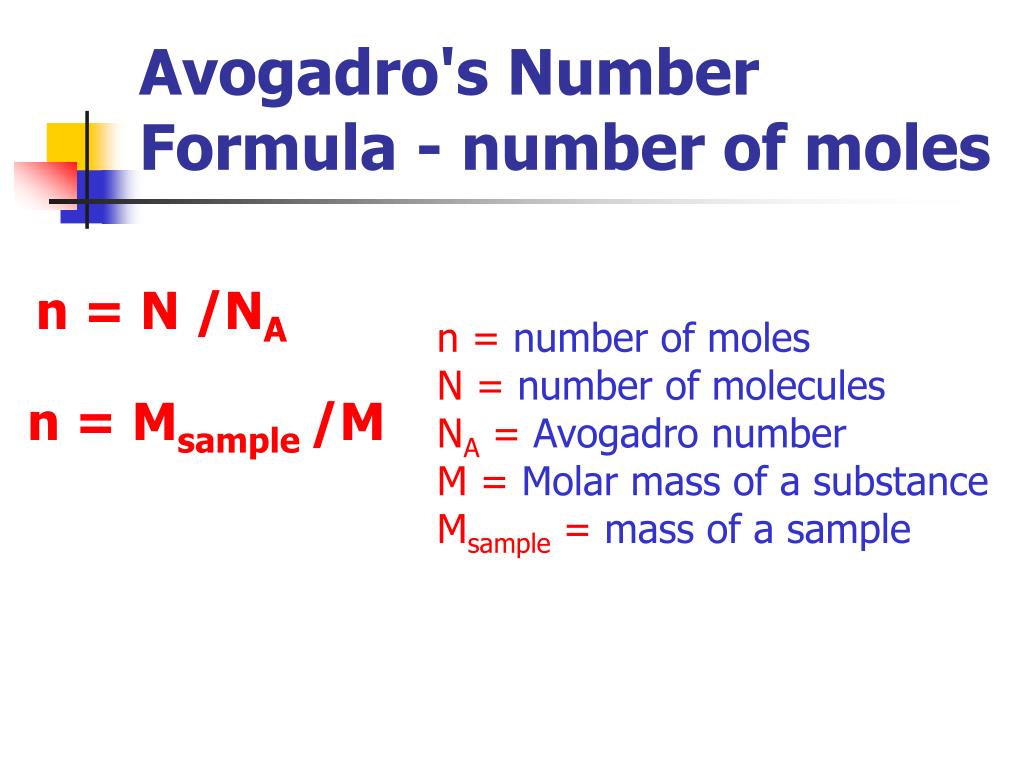
Food Webs and Food Chains Worksheet Answer Key Guide

Understanding Food Webs and Food Chains
Food webs and food chains are essential concepts in ecology, representing the feeding relationships between different species within an ecosystem. While often used interchangeably, these terms have distinct meanings, which are crucial for understanding the structure and dynamics of ecosystems. This guide will delve into the definitions, differences, and importance of food webs and food chains, accompanied by a comprehensive worksheet answer key.
What is a Food Chain?
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms that eat other organisms as a source of food and energy. It starts with a producer (usually a plant) and ends with a top predator. Each level in the chain is known as a trophic level. The energy flows from one level to the next, with each organism consuming the one below it. A typical food chain might look like this:
Producers (plants) → Primary consumers (herbivores) → Secondary consumers (carnivores) → Tertiary consumers (top predators)
What is a Food Web?
A food web, on the other hand, is a complex network of interconnected food chains. It shows how various species are related to each other through feeding relationships, representing a more realistic and dynamic picture of ecosystems. In a food web, each species can occupy multiple trophic levels, and energy flows through multiple pathways.
Differences Between Food Webs and Food Chains
The key differences between food webs and food chains are:
- Linearity vs. Complexity: Food chains are linear, whereas food webs are complex networks.
- Single Pathway vs. Multiple Pathways: Food chains show a single pathway of energy flow, while food webs depict multiple pathways.
- Simple Representation vs. Realistic Representation: Food chains provide a simplified view of ecosystems, whereas food webs offer a more realistic representation.
Importance of Food Webs and Food Chains
Understanding food webs and food chains is crucial for:
- Ecosystem Management: Recognizing the feeding relationships between species helps in managing ecosystems, predicting the impact of invasive species, and understanding the effects of climate change.
- Conservation: Identifying key species and their roles in food webs informs conservation efforts, ensuring the protection of critical species and their habitats.
- Ecological Research: Studying food webs and food chains advances our understanding of ecosystem dynamics, energy flow, and nutrient cycling.
Worksheet Answer Key
Section 1: Multiple Choice
- What is the primary difference between a food chain and a food web? a) Length b) Complexity c) Energy flow d) Species diversity
Answer: b) Complexity
- Which of the following is an example of a food chain? a) Plant → Mouse → Hawk → Snake b) Plant → Mouse → Hawk → Lion → Elephant c) Plant → Mouse → Hawk → Lion → Elephant → Snake d) Plant → Mouse → Hawk
Answer: a) Plant → Mouse → Hawk → Snake
Section 2: Short Answers
- Describe the difference between a producer and a primary consumer.
Answer: A producer (usually a plant) makes its own food through photosynthesis, while a primary consumer (herbivore) eats the producer to obtain energy.
- What is the role of a top predator in a food chain?
Answer: A top predator has no natural predators within the ecosystem and plays a crucial role in regulating the population sizes of other species.
Section 3: Essay Questions
- Explain the importance of understanding food webs and food chains in ecosystem management.
Answer: Understanding food webs and food chains is crucial for ecosystem management as it helps predict the impact of invasive species, climate change, and other disturbances on ecosystem dynamics. It also informs conservation efforts, ensuring the protection of critical species and their habitats.
- Describe the differences between food chains and food webs, and explain why food webs are a more realistic representation of ecosystems.
Answer: Food chains are linear sequences of organisms that eat other organisms, while food webs are complex networks of interconnected food chains. Food webs are a more realistic representation of ecosystems because they depict multiple pathways of energy flow and show how various species are related to each other through feeding relationships.
🐝 Note: This guide provides a comprehensive overview of food webs and food chains, along with a worksheet answer key. It is essential to understand these concepts to appreciate the complexity and dynamics of ecosystems.
In conclusion, food webs and food chains are fundamental concepts in ecology, representing the feeding relationships between different species within an ecosystem. While food chains provide a simplified view of ecosystems, food webs offer a more realistic representation of the complex interactions between species. Understanding these concepts is crucial for ecosystem management, conservation, and ecological research.
What is the primary difference between a food chain and a food web?
+
The primary difference between a food chain and a food web is complexity. A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms, while a food web is a complex network of interconnected food chains.
Why are food webs more realistic than food chains?
+
Food webs are more realistic because they depict multiple pathways of energy flow and show how various species are related to each other through feeding relationships.
What is the role of a top predator in a food chain?
+
A top predator has no natural predators within the ecosystem and plays a crucial role in regulating the population sizes of other species.