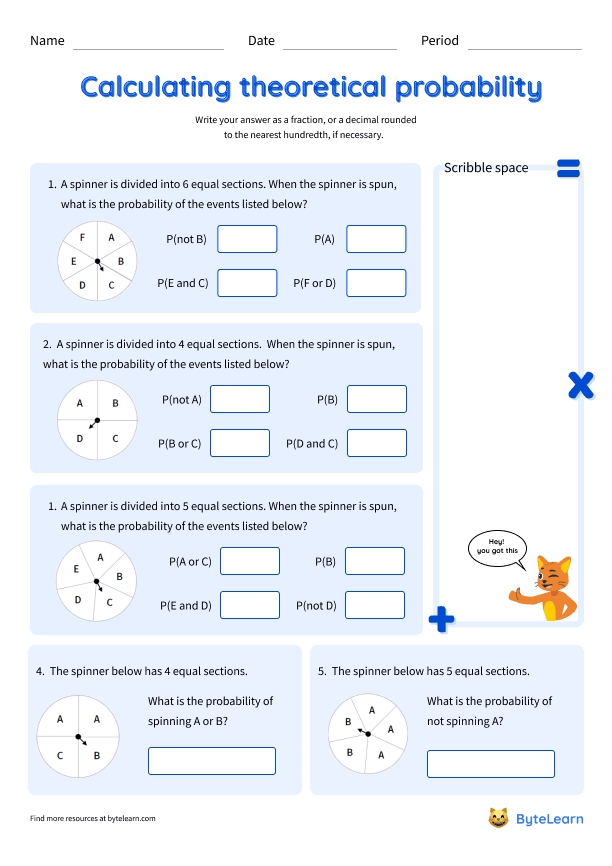
Experimental Probability Worksheet
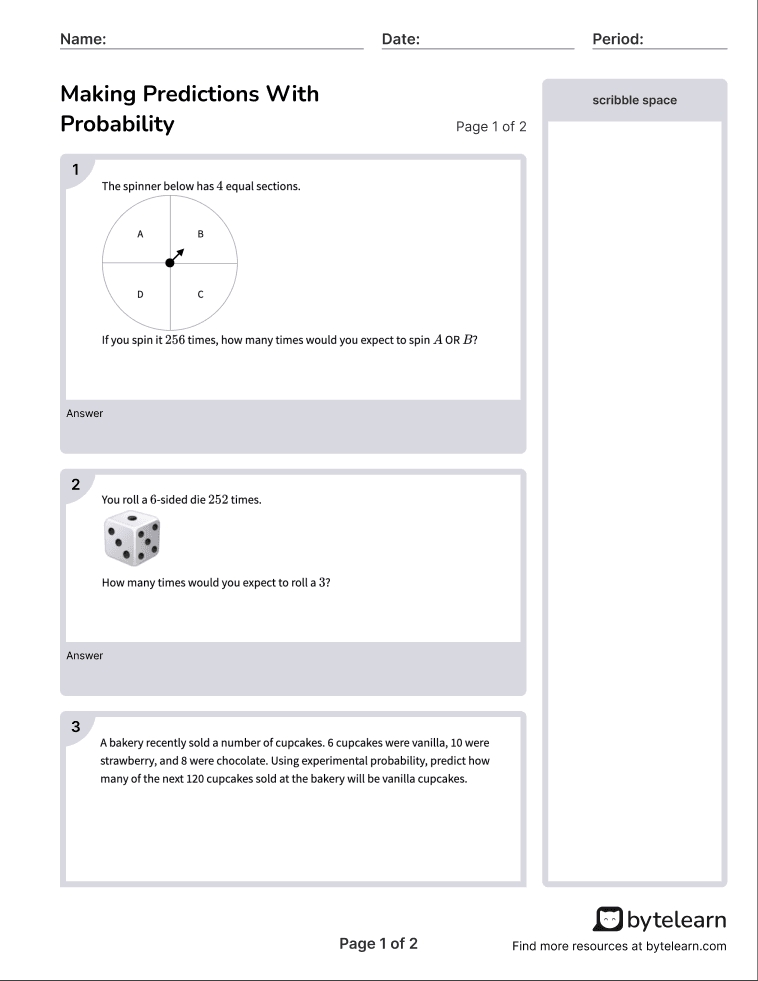
Understanding Experimental Probability
Experimental probability is a branch of probability that deals with the probability of an event occurring based on repeated trials or experiments. It is an essential concept in statistics and is used to make predictions about future events. In this worksheet, we will explore the concept of experimental probability and provide examples to help you understand it better.
What is Experimental Probability?
Experimental probability is the probability of an event occurring based on the results of repeated trials or experiments. It is calculated by dividing the number of times the event occurs by the total number of trials.
Formula: Experimental Probability = Number of times the event occurs / Total number of trials
How to Calculate Experimental Probability
To calculate experimental probability, you need to follow these steps:
- Conduct repeated trials or experiments.
- Count the number of times the event occurs.
- Count the total number of trials.
- Divide the number of times the event occurs by the total number of trials.
Example: A coin is flipped 10 times, and it lands heads up 4 times. What is the experimental probability of getting heads?
- Number of times the event occurs (heads) = 4
- Total number of trials = 10
- Experimental Probability = 4⁄10 = 0.4
Types of Events
In probability, events can be classified into different types:
- Independent events: Events that do not affect the outcome of other events.
- Dependent events: Events that affect the outcome of other events.
- Mutually exclusive events: Events that cannot occur at the same time.
- Complementary events: Events that have a probability of 1 when combined.
Experimental Probability vs. Theoretical Probability
Experimental probability and theoretical probability are two different types of probability.
- Theoretical probability is the probability of an event occurring based on the number of favorable outcomes divided by the total number of possible outcomes.
- Experimental probability is the probability of an event occurring based on repeated trials or experiments.
Example: A fair six-sided die is rolled. The theoretical probability of getting a 6 is 1⁄6, but the experimental probability may vary depending on the number of trials.
| Theoretical Probability | Experimental Probability |
|---|---|
| Based on the number of favorable outcomes divided by the total number of possible outcomes | Based on repeated trials or experiments |
| Does not change | May vary depending on the number of trials |
📝 Note: Experimental probability is often used in real-life situations where theoretical probability is difficult to calculate or unknown.
Real-Life Applications of Experimental Probability
Experimental probability has many real-life applications:
- Quality control: Manufacturers use experimental probability to test the quality of their products.
- Medical research: Researchers use experimental probability to test the effectiveness of new medicines.
- Insurance: Insurance companies use experimental probability to calculate the likelihood of accidents or natural disasters.
Common Misconceptions about Experimental Probability
Here are some common misconceptions about experimental probability:
- Misconception 1: Experimental probability is the same as theoretical probability.
- Misconception 2: Experimental probability is always accurate.
- Misconception 3: Experimental probability is only used in statistics.
📝 Note: Experimental probability is an estimate of the probability of an event occurring based on repeated trials or experiments. It may not be accurate and should be used with caution.
Conclusion
Experimental probability is an essential concept in statistics that deals with the probability of an event occurring based on repeated trials or experiments. It is calculated by dividing the number of times the event occurs by the total number of trials. Experimental probability has many real-life applications and is often used in quality control, medical research, and insurance. However, it is essential to understand the misconceptions about experimental probability and use it with caution.
What is experimental probability?
+Experimental probability is the probability of an event occurring based on the results of repeated trials or experiments.
How is experimental probability calculated?
+Experimental probability is calculated by dividing the number of times the event occurs by the total number of trials.
What is the difference between experimental probability and theoretical probability?
+Experimental probability is the probability of an event occurring based on repeated trials or experiments, while theoretical probability is the probability of an event occurring based on the number of favorable outcomes divided by the total number of possible outcomes.