Mastering Electric Circuits with Easy Worksheet Exercises

Understanding the Basics of Electric Circuits
Electric circuits are a fundamental part of modern technology, powering everything from smartphones to homes and businesses. Understanding how electric circuits work is essential for anyone interested in pursuing a career in electrical engineering, electronics, or related fields. In this article, we’ll explore the basics of electric circuits, including the key components, types of circuits, and how to calculate circuit parameters using easy worksheet exercises.
Key Components of Electric Circuits
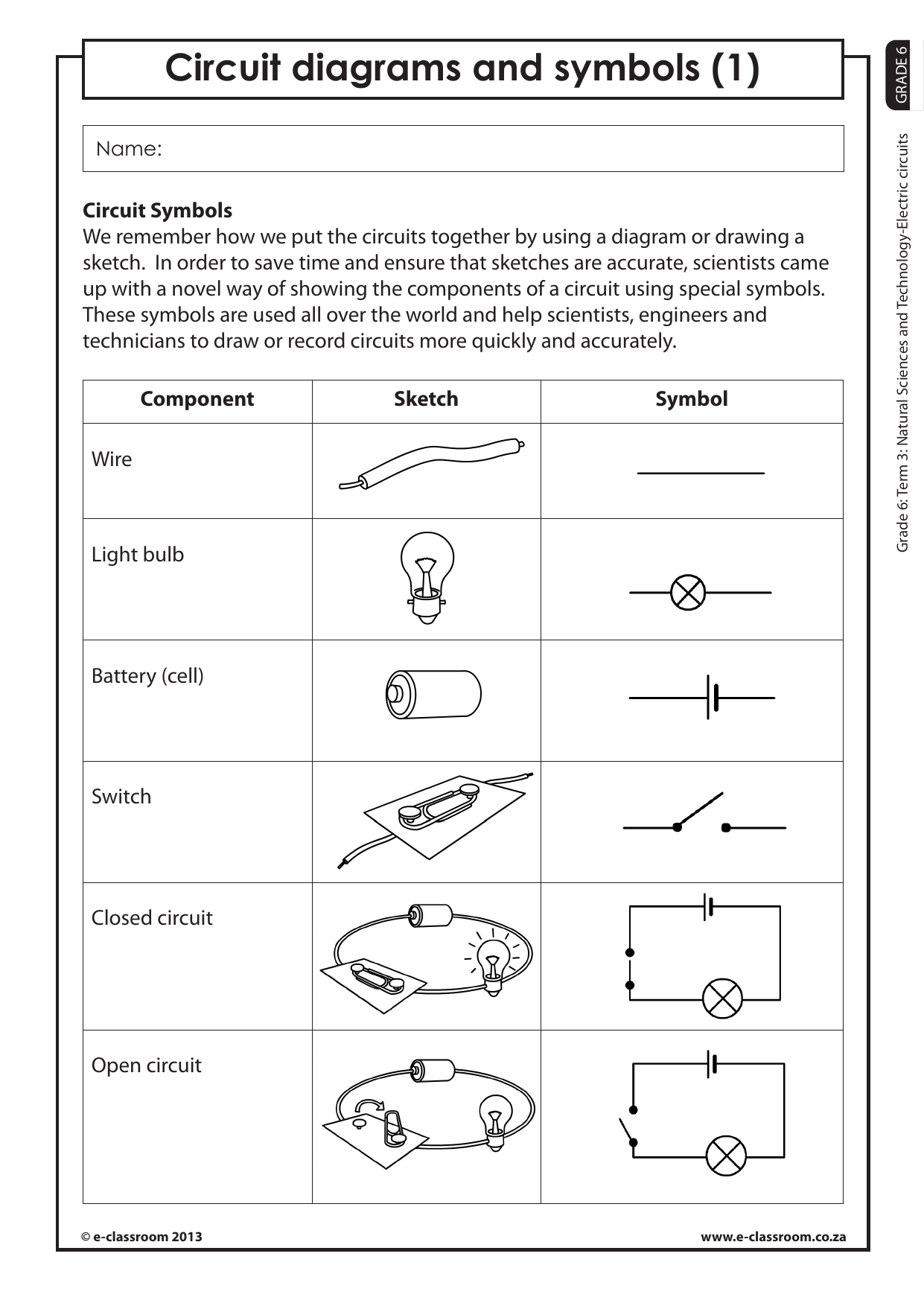
An electric circuit consists of several key components, including:
- Conductors: Materials that allow electricity to flow through them, such as copper wire.
- Insulators: Materials that prevent electricity from flowing through them, such as rubber or plastic.
- Resistors: Components that reduce the flow of electricity, measured in ohms (Ω).
- Capacitors: Components that store electric charge, measured in farads (F).
- Inductors: Components that store magnetic energy, measured in henries (H).
- Switches: Components that control the flow of electricity by opening or closing the circuit.
- Batteries: Components that provide a source of voltage, measured in volts (V).
Types of Electric Circuits
There are two main types of electric circuits:
- Series Circuits: Components are connected one after the other, and the current flows through each component in sequence.
- Parallel Circuits: Components are connected between the same two points, and the current flows through each component independently.
Calculating Circuit Parameters
To calculate circuit parameters, such as voltage, current, and resistance, we can use the following formulas:
- Ohm’s Law: V = IR (Voltage = Current x Resistance)
- Power Formula: P = VI (Power = Voltage x Current)
Using these formulas, we can calculate the voltage, current, and resistance of a circuit using simple worksheet exercises.
📝 Note: These formulas assume a simple DC circuit. For AC circuits, more complex formulas are required.
Worksheet Exercise 1: Calculating Voltage and Current
Suppose we have a series circuit with a 9V battery, a 2Ω resistor, and a 4Ω resistor. Calculate the voltage and current of the circuit.
| Component | Voltage (V) | Current (I) |
|---|---|---|
| Battery | 9V | - |
| Resistor 1 | - | - |
| Resistor 2 | - | - |
Using Ohm’s Law, we can calculate the current of the circuit:
I = V/R = 9V / (2Ω + 4Ω) = 1.5A
Then, we can calculate the voltage of each component:
V1 = I x R1 = 1.5A x 2Ω = 3V V2 = I x R2 = 1.5A x 4Ω = 6V
| Component | Voltage (V) | Current (I) |
|---|---|---|
| Battery | 9V | - |
| Resistor 1 | 3V | 1.5A |
| Resistor 2 | 6V | 1.5A |
Worksheet Exercise 2: Calculating Power
Suppose we have a parallel circuit with a 12V battery, a 3Ω resistor, and a 6Ω resistor. Calculate the power of the circuit.
| Component | Voltage (V) | Current (I) |
|---|---|---|
| Battery | 12V | - |
| Resistor 1 | - | - |
| Resistor 2 | - | - |
Using the Power Formula, we can calculate the power of the circuit:
P = VI = 12V x (12V / (3Ω + 6Ω)) = 12V x 2A = 24W
Then, we can calculate the power of each component:
P1 = V x I = 12V x (12V / 3Ω) = 48W P2 = V x I = 12V x (12V / 6Ω) = 24W
| Component | Voltage (V) | Current (I) | Power (W) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery | 12V | - | 24W |
| Resistor 1 | 12V | 4A | 48W |
| Resistor 2 | 12V | 2A | 24W |
By mastering these simple worksheet exercises, you’ll be well on your way to understanding the basics of electric circuits and preparing yourself for more advanced topics in electrical engineering.
In conclusion, electric circuits are a fundamental part of modern technology, and understanding how they work is essential for anyone interested in pursuing a career in electrical engineering or related fields. By mastering the key components, types of circuits, and calculating circuit parameters using simple worksheet exercises, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle more advanced topics in electrical engineering.
What is the difference between a series and parallel circuit?
+A series circuit is a circuit where components are connected one after the other, and the current flows through each component in sequence. A parallel circuit is a circuit where components are connected between the same two points, and the current flows through each component independently.
What is Ohm’s Law?
+Ohm’s Law is a formula that states V = IR, where V is the voltage, I is the current, and R is the resistance.
What is the Power Formula?
+The Power Formula is a formula that states P = VI, where P is the power, V is the voltage, and I is the current.
Related Terms:
- Electrical circuits KS2 Worksheet
- Electrical circuits worksheet PDF
- Electrical circuit Activity worksheets
- Drawing circuits worksheet
- Series circuit worksheet
- Electric circuit ppt