7 Ways DNA Structure and Replication Works

Understanding the Fundamentals of DNA Structure and Replication
Deoxyribonucleic acid, commonly known as DNA, is a complex molecule that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and function of all living organisms. The structure and replication of DNA are fundamental concepts in molecular biology, and understanding these processes is crucial for appreciating the intricacies of life.
The Structure of DNA
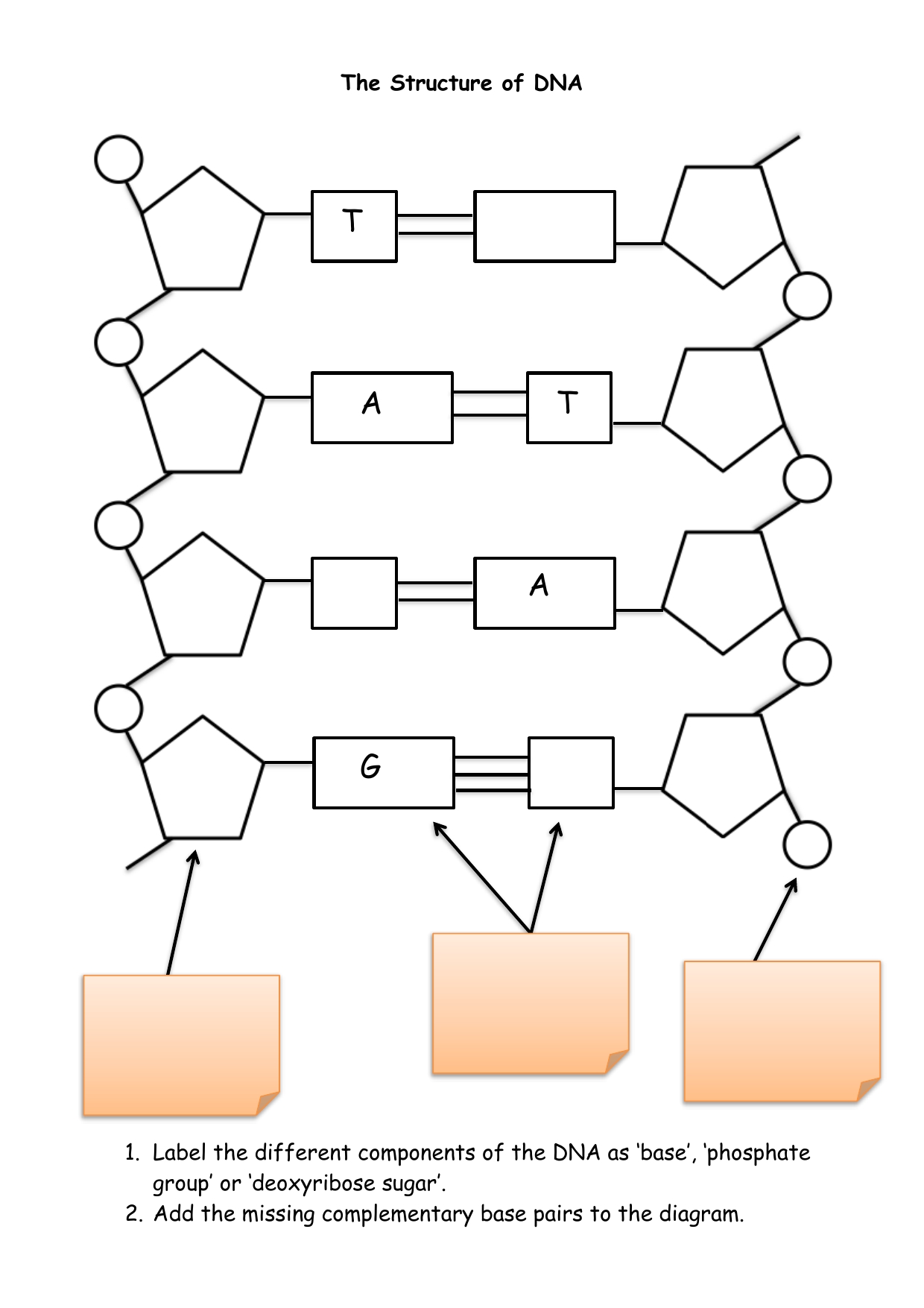
The structure of DNA is often compared to a twisted ladder, with two complementary strands of nucleotides coiled together in a double helix formation. Each nucleotide is composed of three components: a sugar molecule called deoxyribose, a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases - adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine ©, and thymine (T). The sequence of these nitrogenous bases determines the genetic information encoded in the DNA molecule.
🔬 Note: The discovery of the DNA structure by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953 revolutionized the field of molecular biology.
Base Pairing and Hydrogen Bonding
The nitrogenous bases on opposite strands of DNA are paired in a specific manner, with adenine (A) pairing with thymine (T) and guanine (G) pairing with cytosine ©. These base pairs are held together by hydrogen bonds, which are relatively weak chemical bonds that play a crucial role in maintaining the stability of the DNA molecule.
| Base Pair | Hydrogen Bonds |
|---|---|
| Adenine (A) - Thymine (T) | 2 hydrogen bonds |
| Guanine (G) - Cytosine (C) | 3 hydrogen bonds |
The Replication Process
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an exact copy of its DNA before cell division. This process involves the unwinding of the double helix, the synthesis of new strands, and the repair of any errors that may occur.
Step 1: Unwinding of the Double Helix
The replication process begins with the unwinding of the double helix at a specific region called the origin of replication. This unwinding creates a replication fork, where the DNA molecule is separated into two strands.
Step 2: Synthesis of New Strands
An enzyme called DNA polymerase reads the template strands and matches the incoming nucleotides to the base pairing rules (A-T and G-C). The nucleotides are then linked together to form a new strand of DNA.
Step 3: Proofreading and Editing
As the new strands are synthesized, DNA polymerase also proofreads and edits the DNA molecule to correct any errors that may have occurred during replication.
🔍 Note: DNA replication is a semi-conservative process, meaning that the new DNA molecule contains one old strand and one new strand.
Leading Strand Synthesis
The leading strand is synthesized continuously, with DNA polymerase reading the template strand and adding nucleotides to the new strand.
Lagging Strand Synthesis
The lagging strand is synthesized in short, discontinuous segments called Okazaki fragments. Each Okazaki fragment is about 1000-2000 nucleotides long and is synthesized in the 5’ to 3’ direction.
Replication in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
While the basic process of DNA replication is similar in prokaryotes and eukaryotes, there are some key differences. Prokaryotes, such as bacteria, have a single circular chromosome, whereas eukaryotes, such as plants and animals, have multiple linear chromosomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the structure and replication of DNA are fundamental processes that are essential for life. Understanding these processes is crucial for appreciating the intricacies of molecular biology and the mechanisms that govern the behavior of living organisms.
What is the structure of DNA?
+DNA is a double-stranded molecule with two complementary strands of nucleotides coiled together in a double helix formation.
What is the purpose of DNA replication?
+DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an exact copy of its DNA before cell division.
What are Okazaki fragments?
+Okazaki fragments are short, discontinuous segments of DNA that are synthesized on the lagging strand during DNA replication.



