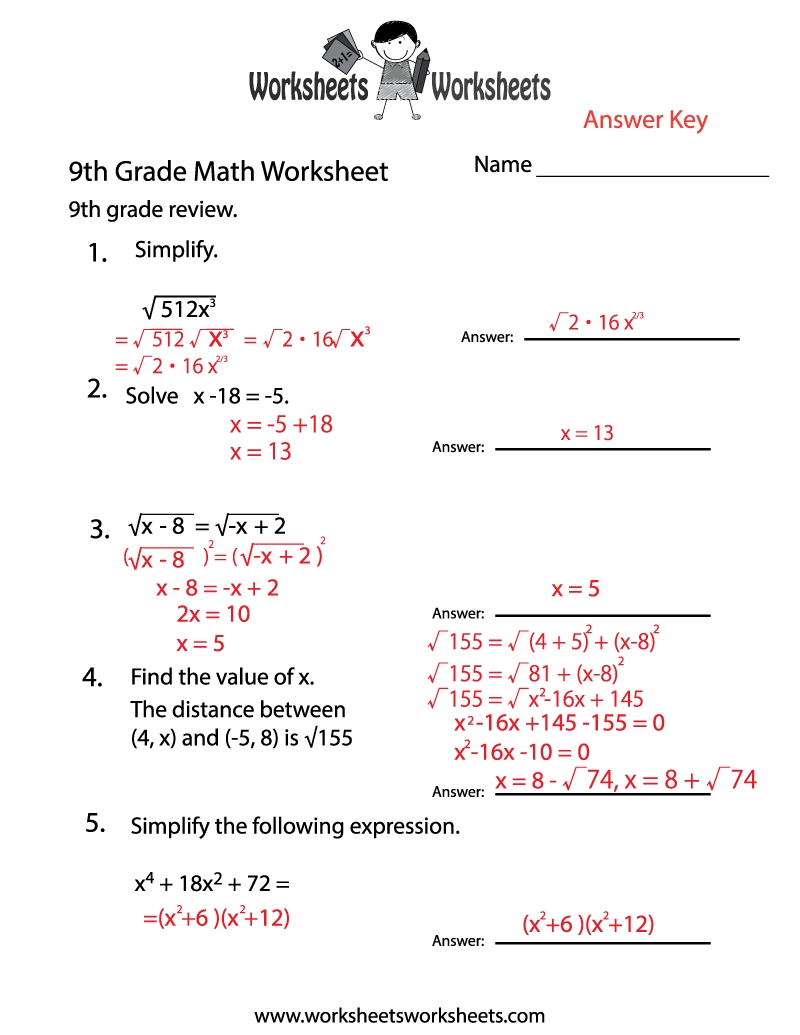
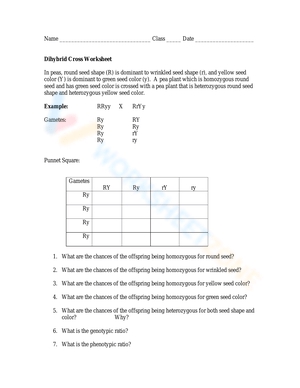
Dihybrid Cross Worksheet Answer Key Simplified

Understanding Dihybrid Cross
A dihybrid cross is a breeding experiment that involves two different traits or genes. It’s a fundamental concept in genetics, which helps us understand how different genes interact and influence the characteristics of an organism. In this explanation, we’ll explore the dihybrid cross concept, its significance, and provide a simplified worksheet answer key.
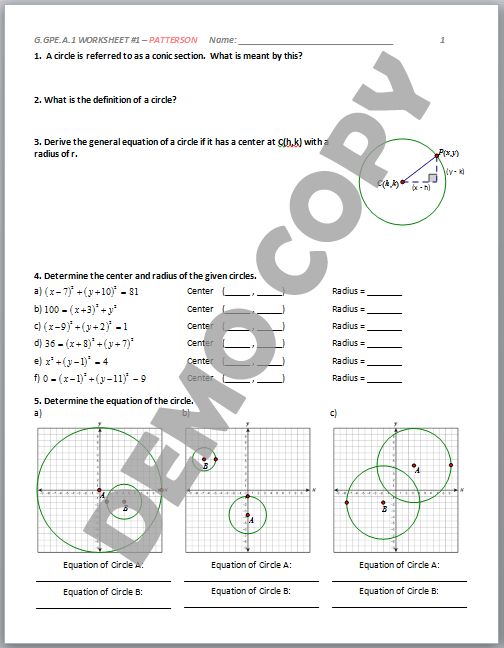
What is a Dihybrid Cross?
A dihybrid cross is a type of breeding experiment that involves two different genes or traits. It’s used to study the interaction between two genes and how they affect the phenotype of an organism. The experiment involves crossing two parents with different genotypes for two specific traits. The offspring are then analyzed to determine the genotypes and phenotypes of the two traits.
Key Terms
Before we dive into the worksheet answer key, let’s review some essential terms:
- Genotype: The genetic makeup of an organism, represented by letters (e.g., BB, Bb, or bb).
- Phenotype: The physical characteristic of an organism, resulting from the interaction of its genotype and environment.
- Dominant allele: A variant of a gene that will be expressed if an individual has one or two copies of the allele.
- Recessive allele: A variant of a gene that will only be expressed if an individual has two copies of the allele.
Dihybrid Cross Worksheet Answer Key
Here’s a simplified answer key for a dihybrid cross worksheet:
Problem 1:
Suppose we’re studying the genes that control flower color (R or r) and plant height (T or t). We cross two parents:
Parent 1: RrTt (red flowers, tall plant) Parent 2: rrTt (white flowers, tall plant)
What is the probability of the offspring having red flowers and a tall plant?
Answer:
| R | r | |
|---|---|---|
| T | RT (50%) | rT (25%) |
| t | Rt (25%) | rt (0%) |
The probability of the offspring having red flowers and a tall plant is 50% (RT genotype).
Problem 2:
We cross two parents with the following genotypes:
Parent 1: AABB (black coat, long ears) Parent 2: aabb (white coat, short ears)
What is the probability of the offspring having a black coat and long ears?
Answer:
| A | a | |
|---|---|---|
| B | AB (50%) | aB (25%) |
| b | Ab (25%) | ab (0%) |
The probability of the offspring having a black coat and long ears is 50% (AB genotype).
Problem 3:
Suppose we’re studying the genes that control eye color (B or b) and hair texture (S or s). We cross two parents:
Parent 1: BBss (brown eyes, straight hair) Parent 2: bbSs (blue eyes, curly hair)
What is the probability of the offspring having brown eyes and straight hair?
Answer:
| B | b | |
|---|---|---|
| S | BS (25%) | bS (25%) |
| s | Bs (25%) | bs (25%) |
The probability of the offspring having brown eyes and straight hair is 25% (BS genotype).
Important Notes:
- When calculating probabilities, remember to consider the genotype and phenotype of both parents.
- Use Punnett squares to visualize the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring.
- Make sure to label the genotypes and phenotypes correctly.
We hope this simplified worksheet answer key helps you understand dihybrid cross better. Remember to practice and apply these concepts to different problems to become more confident in your understanding of genetics.
What is a dihybrid cross?
+
A dihybrid cross is a breeding experiment that involves two different genes or traits. It’s used to study the interaction between two genes and how they affect the phenotype of an organism.
What is the purpose of a dihybrid cross?
+
The purpose of a dihybrid cross is to study the interaction between two genes and how they affect the phenotype of an organism.
How do I calculate the probability of a dihybrid cross?
+
To calculate the probability of a dihybrid cross, use Punnett squares to visualize the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring. Label the genotypes and phenotypes correctly, and consider the genotype and phenotype of both parents.
Related Terms:
- Dihybrid cross Worksheet PDF
- Dihybrid cross Worksheet doc