Cell Transport Practice Worksheet Exercises and Answers
Cell Transport Practice Worksheet Exercises and Answers
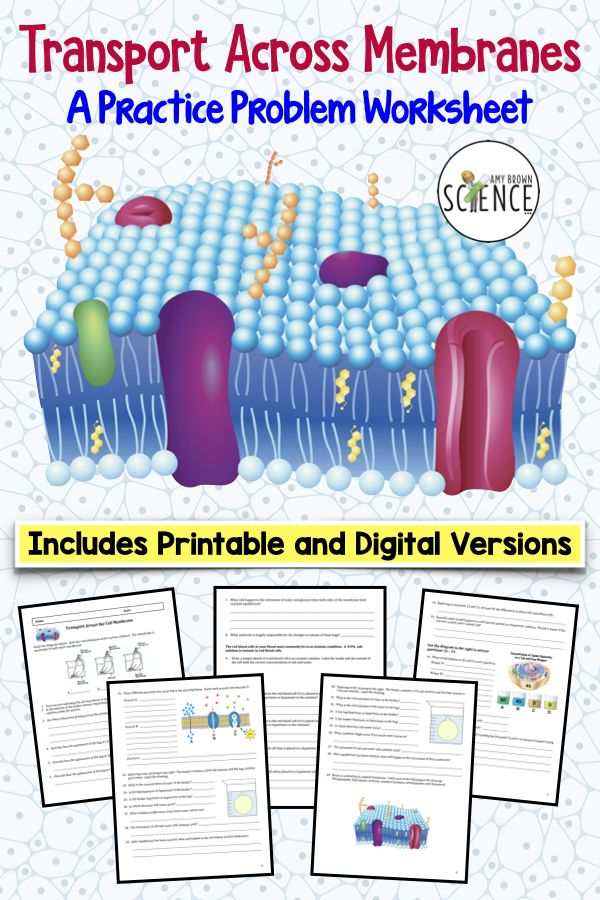
Cells are the basic units of life, and they require various substances to function properly. Cell transport is the process by which cells move molecules across their cell membranes. This process is essential for maintaining proper cellular function, and it involves several different types of transport mechanisms. In this practice worksheet, we will explore some of the key concepts related to cell transport, and provide exercises and answers to help you better understand this topic.
Types of Cell Transport
There are several different types of cell transport, including:
- Passive transport: This type of transport involves the movement of molecules across the cell membrane without the use of energy. Examples of passive transport include diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion.
- Active transport: This type of transport involves the movement of molecules across the cell membrane using energy. Examples of active transport include endocytosis, exocytosis, and active transport pumps.
Passive Transport Exercises
- What is the main difference between diffusion and osmosis?
- Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, while osmosis is the movement of water molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration through a selectively permeable membrane.
- What is facilitated diffusion?
- Facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport that involves the use of transport proteins to help molecules cross the cell membrane.
- What is the purpose of the sodium-potassium pump?
- The sodium-potassium pump is an example of active transport that helps maintain the proper balance of sodium and potassium ions across the cell membrane.
Active Transport Exercises
- What is endocytosis?
- Endocytosis is a type of active transport that involves the uptake of molecules or particles into the cell through the formation of vesicles.
- What is exocytosis?
- Exocytosis is a type of active transport that involves the release of molecules or particles from the cell through the fusion of vesicles with the cell membrane.
- What is the purpose of active transport pumps?
- Active transport pumps use energy to transport molecules across the cell membrane against their concentration gradient.
Cell Transport Mechanisms Exercises
- What is the role of the cell membrane in cell transport?
- The cell membrane acts as a selectively permeable barrier that regulates the movement of molecules into and out of the cell.
- What is the function of transport proteins in cell transport?
- Transport proteins help facilitate the movement of molecules across the cell membrane by providing a channel or binding site for the molecule to attach to.
- What is the difference between a channel protein and a carrier protein?
- A channel protein forms a pore in the cell membrane that allows molecules to pass through, while a carrier protein binds to a molecule and carries it across the cell membrane.
Answers to Exercises
Passive Transport Exercises:
The main difference between diffusion and osmosis is that diffusion involves the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, while osmosis involves the movement of water molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration through a selectively permeable membrane.
Facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport that involves the use of transport proteins to help molecules cross the cell membrane.
The sodium-potassium pump is an example of active transport that helps maintain the proper balance of sodium and potassium ions across the cell membrane.
Active Transport Exercises:
Endocytosis is a type of active transport that involves the uptake of molecules or particles into the cell through the formation of vesicles.
Exocytosis is a type of active transport that involves the release of molecules or particles from the cell through the fusion of vesicles with the cell membrane.
Active transport pumps use energy to transport molecules across the cell membrane against their concentration gradient.
Cell Transport Mechanisms Exercises:
The cell membrane acts as a selectively permeable barrier that regulates the movement of molecules into and out of the cell.
Transport proteins help facilitate the movement of molecules across the cell membrane by providing a channel or binding site for the molecule to attach to.
A channel protein forms a pore in the cell membrane that allows molecules to pass through, while a carrier protein binds to a molecule and carries it across the cell membrane.
📝 Note: This practice worksheet is designed to help you better understand the concepts related to cell transport. Make sure to review the answers carefully and ask your instructor if you have any questions or need further clarification.
What is the main difference between passive and active transport?
+
Passive transport involves the movement of molecules across the cell membrane without the use of energy, while active transport involves the movement of molecules across the cell membrane using energy.
What is the purpose of the cell membrane in cell transport?
+
The cell membrane acts as a selectively permeable barrier that regulates the movement of molecules into and out of the cell.
What is the difference between a channel protein and a carrier protein?
+
A channel protein forms a pore in the cell membrane that allows molecules to pass through, while a carrier protein binds to a molecule and carries it across the cell membrane.
Related Terms:
- Cell transport Worksheet PDF
- Cell transport answer Key
- Cell Transport Review Worksheet PDF