Cladogram Worksheet Answer Key Guide
Understanding Cladograms: A Step-by-Step Guide
Cladograms are diagrams used in biology to show the evolutionary relationships between different species. These diagrams are essential in understanding the concept of phylogeny, which is the study of the evolutionary history of organisms. In this guide, we will walk you through a step-by-step process of reading and interpreting cladograms, and provide you with a comprehensive answer key to help you navigate through the complexities of cladogram analysis.
What is a Cladogram?
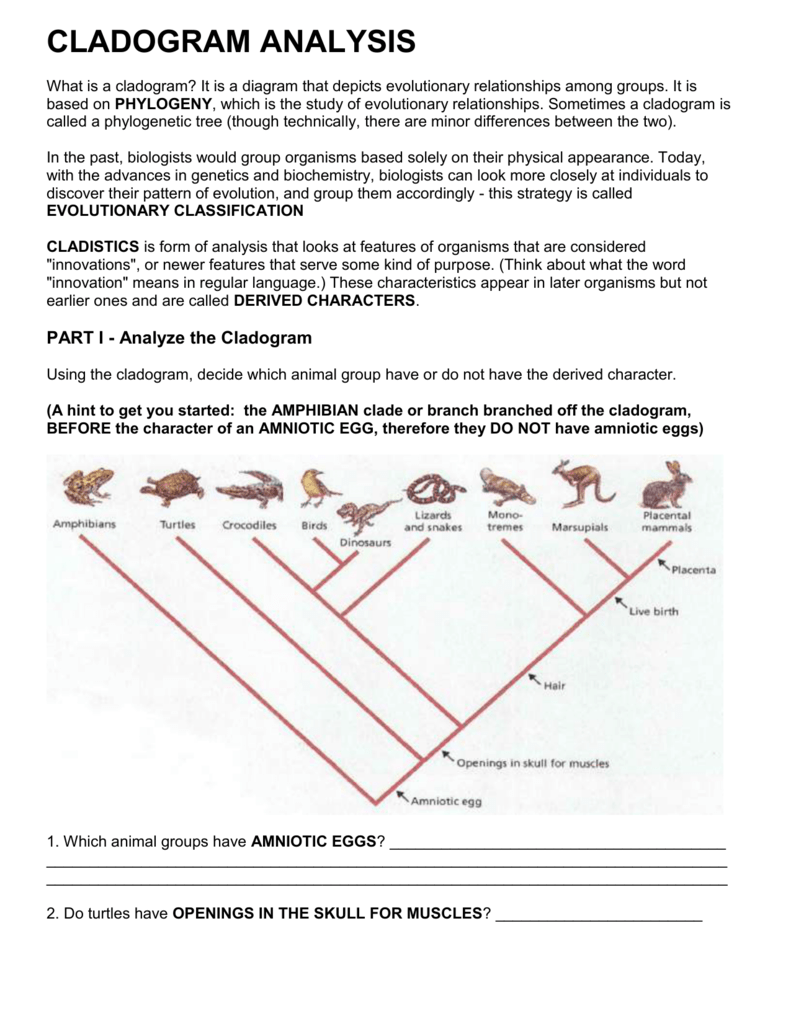
A cladogram is a tree-like diagram that shows the evolutionary relationships between different species. It is a graphical representation of the cladistic analysis, which is a method of classifying organisms based on their shared characteristics. Cladograms are used to visualize the relationships between different species and to identify the common ancestors that they share.
Components of a Cladogram
A cladogram consists of several components, including:
- Nodes: These are the points on the diagram where two or more lines meet. Nodes represent the common ancestors of the species that are connected to them.
- Lines: These are the branches that connect the nodes. Lines represent the evolutionary relationships between the species.
- Taxa: These are the species or groups of species that are represented on the diagram. Taxa are usually listed at the tips of the branches.
- Root: This is the base of the cladogram, which represents the common ancestor of all the species on the diagram.
How to Read a Cladogram
Reading a cladogram can be challenging, but with practice, you can become proficient in interpreting these diagrams. Here are the steps to follow:
- Start at the root: Begin by identifying the root of the cladogram, which represents the common ancestor of all the species on the diagram.
- Identify the nodes: Look for the nodes on the diagram, which represent the common ancestors of the species that are connected to them.
- Follow the lines: Follow the lines that connect the nodes to the taxa. Each line represents the evolutionary relationship between the species.
- Identify the taxa: Identify the taxa that are listed at the tips of the branches. These are the species or groups of species that are represented on the diagram.
Interpreting Cladograms
Interpreting cladograms requires a deep understanding of the evolutionary relationships between the species represented on the diagram. Here are some key concepts to keep in mind:
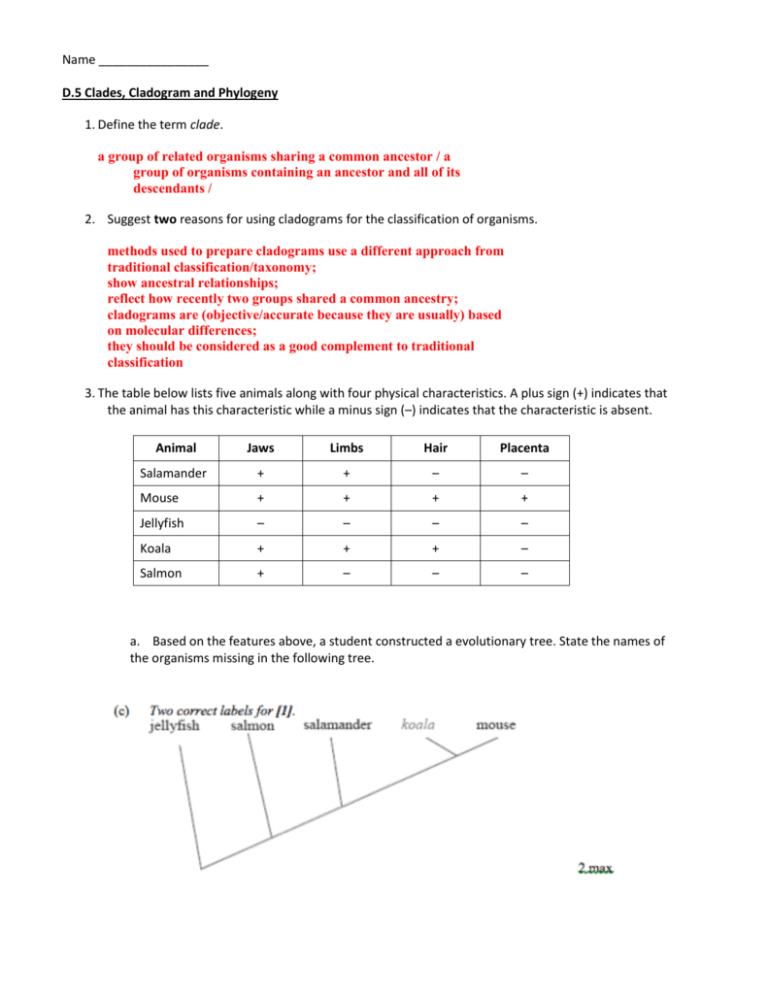
- Monophyly: A group of species is said to be monophyletic if it includes all the descendants of a common ancestor. In a cladogram, a monophyletic group is represented by a node that connects all the species in the group.
- Paraphyly: A group of species is said to be paraphyletic if it does not include all the descendants of a common ancestor. In a cladogram, a paraphyletic group is represented by a node that connects some, but not all, of the species in the group.
- Polyphyly: A group of species is said to be polyphyletic if it includes species that do not share a common ancestor. In a cladogram, a polyphyletic group is represented by multiple nodes that connect different species.
Answer Key
Here is a comprehensive answer key to help you navigate through the complexities of cladogram analysis:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the root of a cladogram? | The root of a cladogram is the common ancestor of all the species on the diagram. |
| What do the nodes on a cladogram represent? | The nodes on a cladogram represent the common ancestors of the species that are connected to them. |
| What do the lines on a cladogram represent? | The lines on a cladogram represent the evolutionary relationships between the species. |
| What are the taxa on a cladogram? | The taxa on a cladogram are the species or groups of species that are represented on the diagram. |
| What is monophyly? | Monophyly is a group of species that includes all the descendants of a common ancestor. |
| What is paraphyly? | Paraphyly is a group of species that does not include all the descendants of a common ancestor. |
| What is polyphyly? | Polyphyly is a group of species that includes species that do not share a common ancestor. |
📝 Note: This answer key is not exhaustive, and you may encounter more complex questions when working with cladograms.
Conclusion
Cladograms are powerful tools for understanding the evolutionary relationships between different species. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can become proficient in reading and interpreting cladograms. Remember to always start at the root, identify the nodes, follow the lines, and identify the taxa. With practice, you will become more comfortable working with cladograms and will be able to apply your knowledge to a wide range of biological questions.
What is the purpose of a cladogram?
+
The purpose of a cladogram is to show the evolutionary relationships between different species.
What is the difference between monophyly and paraphyly?
+
Monophyly is a group of species that includes all the descendants of a common ancestor, while paraphyly is a group of species that does not include all the descendants of a common ancestor.
How do you read a cladogram?
+
To read a cladogram, start at the root, identify the nodes, follow the lines, and identify the taxa.
Related Terms:
- Cladogram Worksheet with answers PDF
- Cladogram Worksheet pdf
- Cladogram practice problems with Answers
- Dinosaur cladogram analysis answer key
- Phylogenetic tree worksheet with answers
- Cladogram example



