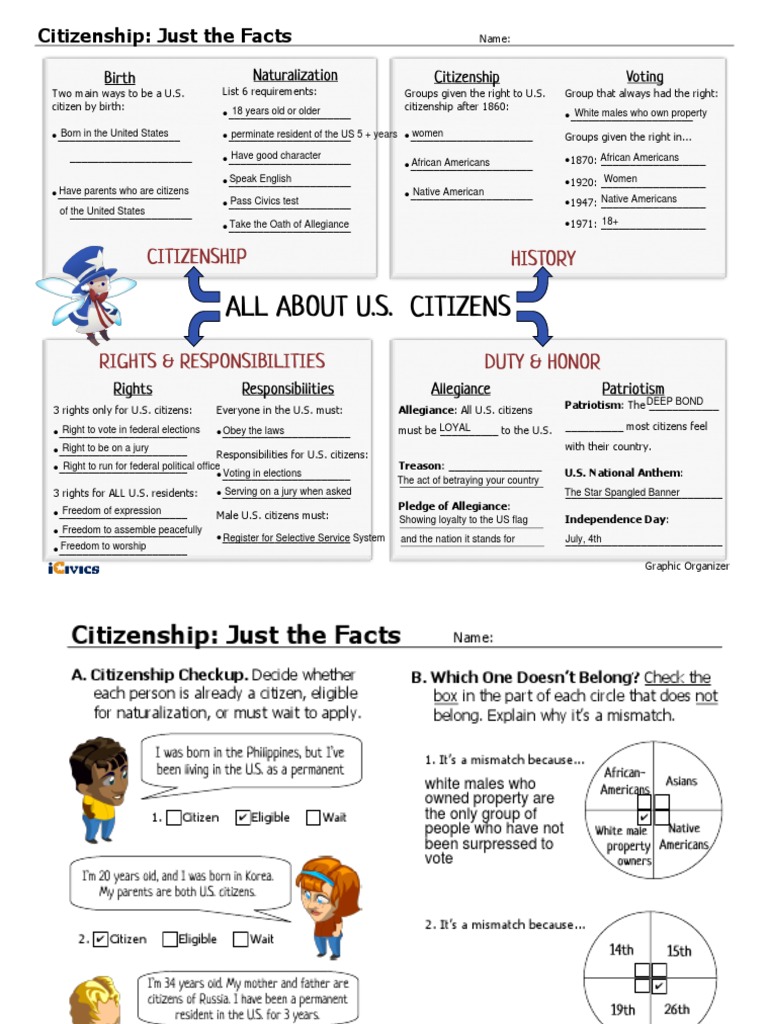
Citizenship Facts Worksheet Answer Key
Understanding Citizenship: A Comprehensive Guide
As a fundamental aspect of a country's identity and a crucial element of a person's life, citizenship plays a vital role in shaping the relationship between individuals and the state. The concept of citizenship is multifaceted, encompassing various rights, responsibilities, and obligations. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of citizenship, covering its definition, types, benefits, and responsibilities, as well as exploring the process of acquiring citizenship.
What is Citizenship?
Citizenship is a legal status granted by a country to individuals, conferring on them the rights and responsibilities of being a member of that society. It is a fundamental aspect of a country's identity, shaping the relationship between the state and its citizens. Citizenship can be acquired through various means, including birth, naturalization, or descent.
Types of Citizenship
There are several types of citizenship, each with its unique characteristics and implications:
- Jus Soli (Right of the Soil): This type of citizenship is acquired by being born in a particular country. The United States, for example, grants citizenship to anyone born within its territory.
- Jus Sanguinis (Right of Blood): This type of citizenship is acquired through descent, where an individual becomes a citizen of a country through their parents or ancestors. Many European countries follow this principle.
- Naturalization: This type of citizenship is acquired through the process of naturalization, where an individual meets specific requirements, such as residency, language proficiency, and passing a citizenship test.
- Some countries allow individuals to hold dual citizenship, where an individual can be a citizen of two or more countries simultaneously.
Benefits of Citizenship
Citizenship offers numerous benefits, including:
- Voting Rights: Citizens have the right to participate in the democratic process, casting their votes in local and national elections.
- Right to Live and Work: Citizens have the right to live and work in their country of citizenship, enjoying the same rights and protections as native-born citizens.
- Travel Freedom: Citizens enjoy greater travel freedom, with the ability to travel to other countries without the need for visas or permits.
- Access to Public Benefits: Citizens are eligible for public benefits, such as healthcare, education, and social welfare programs.
Responsibilities of Citizenship
While citizenship offers numerous benefits, it also comes with several responsibilities, including:
- Obeying the Law: Citizens are expected to obey the laws of their country, respecting the rights and freedoms of others.
- Paying Taxes: Citizens are required to pay taxes, contributing to the public purse and supporting the functioning of the state.
- Participating in the Democratic Process: Citizens are encouraged to participate in the democratic process, exercising their right to vote and engaging in public debate.
- Defending the Country: In some countries, citizens may be required to serve in the military or participate in national defense efforts.
Acquiring Citizenship
The process of acquiring citizenship varies depending on the country and the individual's circumstances. Here are the general steps involved in acquiring citizenship:
- Meet the Eligibility Criteria: Individuals must meet the eligibility criteria set by the country, which may include requirements such as residency, language proficiency, and passing a citizenship test.
- Submit an Application: Individuals must submit an application for citizenship, providing required documents and information.
- Pass a Citizenship Test: In some countries, individuals may be required to pass a citizenship test, demonstrating their knowledge of the country's history, culture, and values.
- Attend an Interview: In some cases, individuals may be required to attend an interview with immigration officials or citizenship examiners.
- Take the Oath of Allegiance: Once the application is approved, individuals must take the oath of allegiance, swearing loyalty to their new country.
📝 Note: The process of acquiring citizenship may vary depending on the country and individual circumstances. It's essential to consult the relevant authorities and seek professional advice to ensure a smooth and successful application process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, citizenship is a complex and multifaceted concept that plays a vital role in shaping the relationship between individuals and the state. Understanding the different types of citizenship, benefits, and responsibilities is essential for individuals seeking to acquire citizenship. By following the steps outlined in this article and seeking professional advice, individuals can navigate the citizenship application process with confidence.
What is the difference between jus soli and jus sanguinis?
+Jus soli refers to citizenship acquired through birth in a particular country, while jus sanguinis refers to citizenship acquired through descent, where an individual becomes a citizen of a country through their parents or ancestors.
Can I hold dual citizenship?
+Yes, some countries allow individuals to hold dual citizenship, where an individual can be a citizen of two or more countries simultaneously. However, it’s essential to check the laws and regulations of the countries involved to ensure that dual citizenship is allowed.
What is the oath of allegiance?
+The oath of allegiance is a promise to swear loyalty to a country, its constitution, and its laws. It is a solemn vow taken by individuals when they acquire citizenship, demonstrating their commitment to their new country.
Related Terms:
- American citizenship lesson plan



