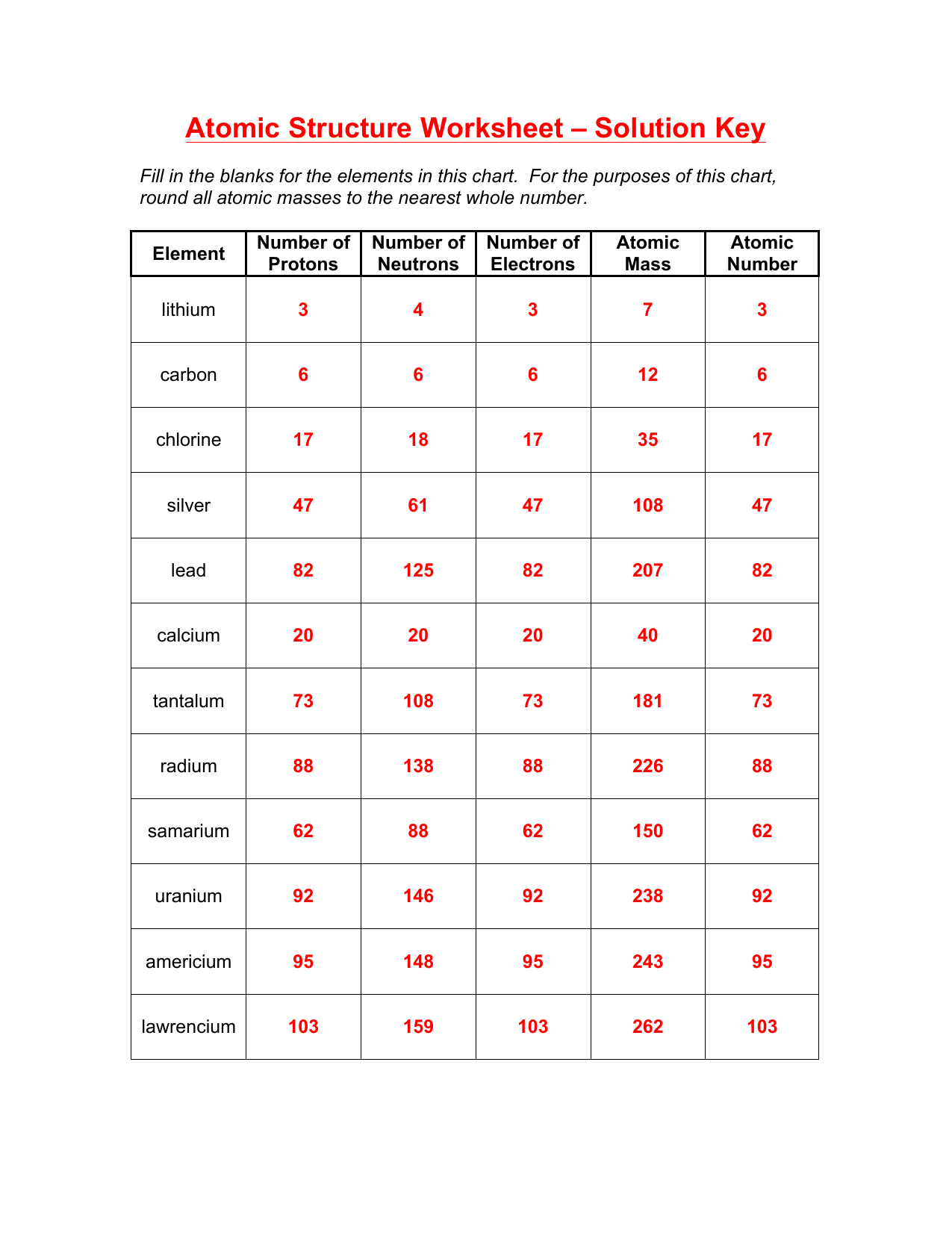
5 Ways to Improve Citing Textual Evidence Skills

Enhancing Your Ability to Cite Textual Evidence: A Key to Academic Success
The ability to cite textual evidence is a fundamental skill required in academic writing, research, and critical thinking. It involves identifying, analyzing, and incorporating evidence from texts to support arguments, claims, or conclusions. Effective citation of textual evidence demonstrates a deep understanding of the subject matter, enhances the credibility of one’s work, and promotes academic integrity. In this article, we will explore five ways to improve your citing textual evidence skills.
1. Develop a Deeper Understanding of the Text
To effectively cite textual evidence, you must first develop a thorough understanding of the text itself. This involves reading the text multiple times, taking notes, and analyzing the author’s purpose, tone, and intended audience. As you read, ask yourself questions like:
- What is the author trying to say?
- What evidence does the author use to support their claims?
- How does the author organize their ideas?
- What tone does the author use?
By asking these questions, you will gain a deeper understanding of the text and be better equipped to identify relevant evidence to support your own arguments.
2. Learn to Identify Different Types of Evidence
Textual evidence can take many forms, including:
- Direct quotes: exact words from the text
- Paraphrases: summaries of the text in your own words
- Summaries: brief overviews of the main points
- Descriptions: vivid descriptions of people, places, or events
- Statistics: numerical data or facts
To effectively cite textual evidence, you must be able to identify these different types of evidence and know when to use them. For example, direct quotes are useful for emphasizing a specific point or showing the author’s exact words, while paraphrases are better suited for summarizing complex ideas.
3. Master the Art of Quoting and Paraphrasing
Quoting and paraphrasing are essential skills for citing textual evidence. Here are some tips to keep in mind:
- Use quotes sparingly: direct quotes should be used only when the author’s exact words are necessary for understanding or emphasis.
- Paraphrase effectively: paraphrases should be in your own words, but still convey the author’s original meaning.
- Use quotation marks correctly: use quotation marks to set off direct quotes, and make sure to attribute the quote to the original author.
- Cite sources properly: always cite the source of the quote or paraphrase, using a recognized citation style (e.g., MLA, APA, Chicago).
4. Organize Your Evidence Effectively
Once you have identified and quoted or paraphrased the textual evidence, you must organize it effectively to support your argument. Here are some tips:
- Use evidence to support a claim: each piece of evidence should be used to support a specific claim or argument.
- Use transitional phrases: transitional phrases (e.g., “however,” “in addition,” “nevertheless”) help to connect evidence and ideas.
- Use clear and concise language: avoid using complex language or jargon that may confuse your reader.
5. Practice, Practice, Practice
Citing textual evidence is a skill that takes practice to develop. Here are some ways to practice:
- Read widely: read different types of texts, including fiction, nonfiction, and academic articles.
- Analyze texts: analyze texts for evidence, tone, and purpose.
- Write regularly: write regularly, using textual evidence to support your arguments.
- Seek feedback: seek feedback from peers or instructors on your citing textual evidence skills.
📝 Note: The more you practice citing textual evidence, the more comfortable you will become with the process. Start by analyzing texts and identifying evidence, and then practice incorporating that evidence into your writing.
Conclusion
Citing textual evidence is a crucial skill for academic success. By developing a deeper understanding of the text, learning to identify different types of evidence, mastering the art of quoting and paraphrasing, organizing your evidence effectively, and practicing regularly, you can improve your citing textual evidence skills. Remember to always use evidence to support your arguments, and to cite your sources properly to maintain academic integrity.
What is the purpose of citing textual evidence?
+The purpose of citing textual evidence is to support arguments, claims, or conclusions with evidence from texts, demonstrating a deep understanding of the subject matter and enhancing the credibility of one’s work.
How do I identify different types of textual evidence?
+Textual evidence can take many forms, including direct quotes, paraphrases, summaries, descriptions, and statistics. To identify these different types of evidence, read the text carefully and ask yourself questions like “What is the author trying to say?” and “What evidence does the author use to support their claims?”
How do I cite sources properly?
+To cite sources properly, use a recognized citation style (e.g., MLA, APA, Chicago) and include the author’s name, title of the work, publication date, and page numbers (if applicable).
Related Terms:
- Teacher synergy llc
- Newsela
- IXL
- BrainPOP
- Udacity
- Duolingo