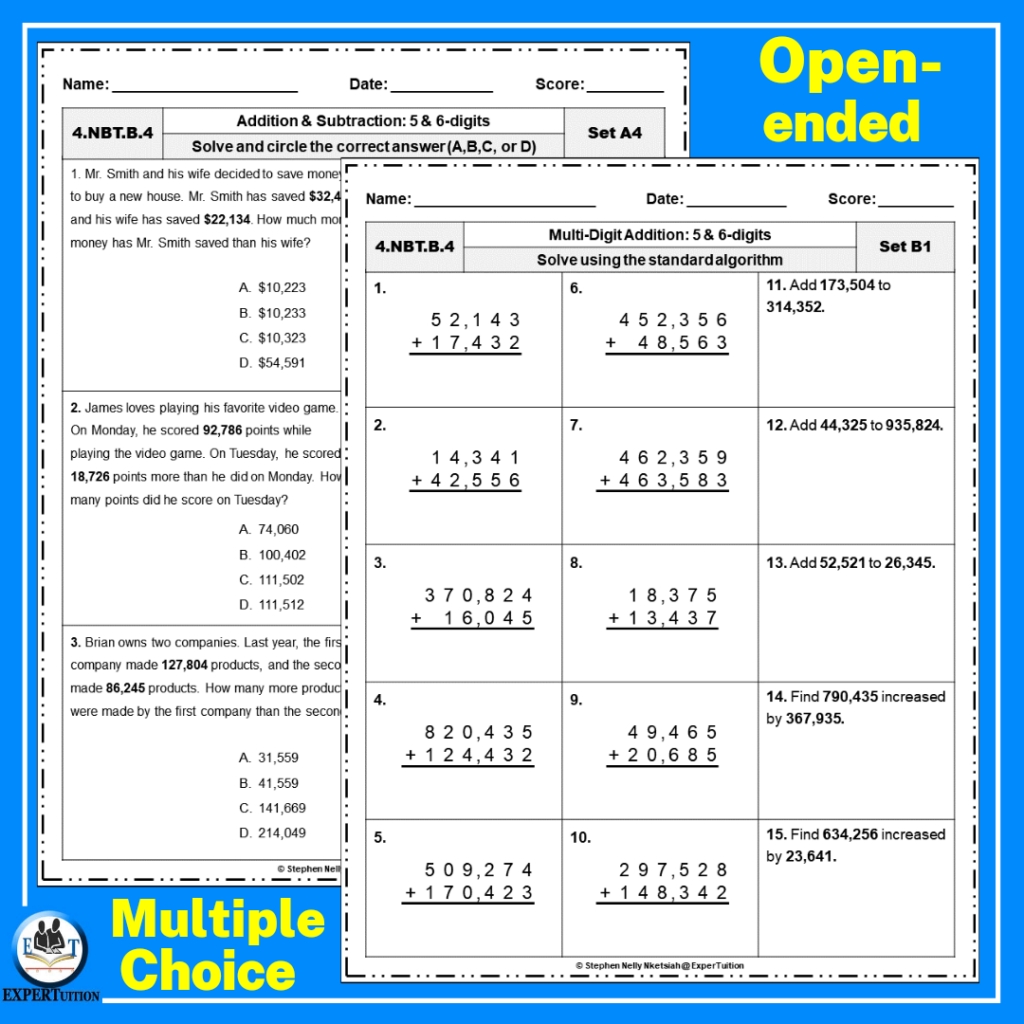
5 Ways to Master the Size of Things in Chemistry

Understanding the Concept of Size in Chemistry
In chemistry, the size of atoms, molecules, and ions is a fundamental concept that plays a crucial role in determining their physical and chemical properties. Mastering the size of things in chemistry is essential for understanding various chemical phenomena, such as chemical bonding, reactivity, and thermodynamics. In this article, we will explore five ways to master the size of things in chemistry.
1. Understanding Atomic Radii
Atomic radii refer to the distance from the nucleus of an atom to the outermost electron in its ground state. Atomic radii are typically measured in picometers (pm) or angstroms (Å). Understanding atomic radii is crucial in chemistry because it helps predict the size of atoms and ions, which in turn affects their chemical behavior.
To master atomic radii, you need to understand the following key points:
- Atomic radii increase down a group in the periodic table due to the addition of new energy levels.
- Atomic radii decrease across a period in the periodic table due to the increase in effective nuclear charge.
- Atomic radii are affected by the number of electrons in an atom, with more electrons resulting in a larger atomic radius.
💡 Note: Atomic radii are not fixed values and can vary depending on the specific atom and its environment.
2. Learning About Ionic Radii
Ionic radii refer to the distance from the nucleus of an ion to the outermost electron in its ground state. Ionic radii are typically measured in picometers (pm) or angstroms (Å). Understanding ionic radii is essential in chemistry because it helps predict the size of ions, which affects their chemical behavior and interactions with other ions.
To master ionic radii, you need to understand the following key points:
- Ionic radii increase with the increase in charge on an ion, with higher charges resulting in smaller ionic radii.
- Ionic radii decrease with the increase in atomic number, with heavier atoms having smaller ionic radii.
- Ionic radii are affected by the electron configuration of an ion, with ions having a full outer energy level having smaller ionic radii.
3. Understanding Molecular Size and Shape
Molecular size and shape refer to the overall dimensions and geometry of a molecule. Understanding molecular size and shape is crucial in chemistry because it affects the physical and chemical properties of a molecule, such as its boiling point, melting point, and reactivity.
To master molecular size and shape, you need to understand the following key points:
- Molecular size and shape are determined by the type and arrangement of atoms in a molecule.
- Molecular size and shape are affected by the presence of lone pairs and multiple bonds.
- Molecular size and shape can be predicted using molecular models and computational methods.

| Molecular Shape | Description |
|---|---|
| Linear | A molecule with a straight chain of atoms. |
| Bent | A molecule with a bent or V-shaped chain of atoms. |
| Trigonal Planar | A molecule with a triangular arrangement of atoms. |
4. Mastering the Concept of Size in Chemical Bonding
Size plays a crucial role in chemical bonding, as it affects the strength and type of bonds formed between atoms. Understanding the concept of size in chemical bonding is essential in chemistry because it helps predict the chemical behavior of atoms and molecules.
To master the concept of size in chemical bonding, you need to understand the following key points:
- Size affects the overlap of atomic orbitals, with larger atoms having more extensive overlap.
- Size affects the electronegativity of atoms, with larger atoms having lower electronegativity.
- Size affects the strength of bonds, with larger atoms forming weaker bonds.
🔗 Note: Size is just one of the many factors that affect chemical bonding. Other factors, such as electronegativity and orbital overlap, also play a crucial role.
5. Applying Size Concepts to Real-World Problems
Mastering the size of things in chemistry requires applying size concepts to real-world problems. This involves using size concepts to predict the chemical behavior of atoms and molecules, as well as to design new materials and products.
To apply size concepts to real-world problems, you need to understand the following key points:
- Size affects the physical and chemical properties of materials, such as their melting point, boiling point, and reactivity.
- Size affects the performance of materials in various applications, such as catalysis, energy storage, and biomedical devices.
- Size can be used to design new materials and products with specific properties and applications.
In conclusion, mastering the size of things in chemistry requires a deep understanding of atomic radii, ionic radii, molecular size and shape, and the concept of size in chemical bonding. By applying size concepts to real-world problems, you can predict the chemical behavior of atoms and molecules, design new materials and products, and solve complex problems in chemistry.
What is the importance of size in chemistry?
+Size plays a crucial role in chemistry because it affects the physical and chemical properties of atoms and molecules, such as their boiling point, melting point, and reactivity.
How does size affect chemical bonding?
+Size affects the overlap of atomic orbitals, electronegativity, and the strength of bonds. Larger atoms have more extensive overlap, lower electronegativity, and form weaker bonds.
What is the difference between atomic radii and ionic radii?
+Atomic radii refer to the distance from the nucleus of an atom to the outermost electron in its ground state, while ionic radii refer to the distance from the nucleus of an ion to the outermost electron in its ground state.