6 Essential Tips for Solving Chemical Reaction Worksheets
Chemical reactions are a fundamental concept in chemistry, and understanding how to solve them is crucial for any student or professional in the field. However, solving chemical reaction worksheets can be a daunting task, especially for those who are new to chemistry. In this article, we will provide six essential tips for solving chemical reaction worksheets, along with examples and explanations to help you master this skill.
Tip 1: Understand the Basics of Chemical Reactions
Before you start solving chemical reaction worksheets, it’s essential to understand the basics of chemical reactions. A chemical reaction is a process in which one or more substances (reactants) are converted into new substances (products). Chemical reactions involve the breaking and forming of chemical bonds, and they can be represented using chemical equations.
Key Concepts:
- Reactants: The substances that are consumed or used up in the reaction.
- Products: The substances that are formed or produced in the reaction.
- Chemical equation: A symbolic representation of the reaction, using chemical formulas and arrows to show the direction of the reaction.
Tip 2: Balance the Chemical Equation
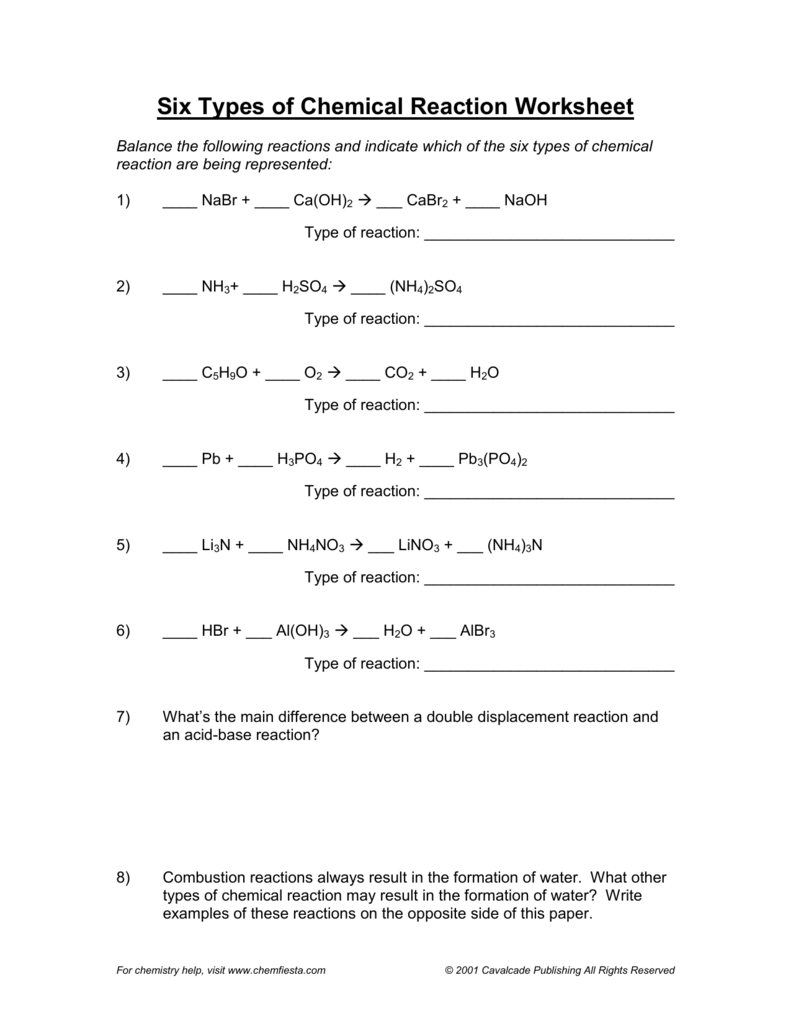
Balancing a chemical equation is a critical step in solving chemical reaction worksheets. A balanced equation ensures that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both the reactant and product sides.
Step-by-Step Process:
- Write the unbalanced equation.
- Count the number of atoms of each element on both sides.
- Add coefficients (numbers in front of the formulas) to balance the equation.
Example:
Unbalanced equation: Ca + O2 → CaO Balanced equation: 2Ca + O2 → 2CaO
👉 Note: Make sure to balance the equation by adding coefficients, not by changing the formulas of the reactants or products.
Tip 3: Identify the Type of Reaction
Chemical reactions can be classified into different types, such as synthesis, decomposition, single displacement, double displacement, and combustion reactions. Identifying the type of reaction can help you solve the problem more efficiently.
Types of Reactions:
- Synthesis reaction: Two or more reactants combine to form a single product.
- Decomposition reaction: A single reactant breaks down into two or more products.
- Single displacement reaction: One element displaces another element from a compound.
- Double displacement reaction: Two compounds exchange partners.
- Combustion reaction: A substance reacts with oxygen to produce heat and light.
Tip 4: Use Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry is the study of the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions. It involves using mole ratios to calculate the amount of reactants and products.
Key Concepts:
- Mole ratio: The ratio of the number of moles of one substance to the number of moles of another substance.
- Limiting reactant: The reactant that is completely consumed in the reaction.
Example:
Calculate the amount of oxygen required to burn 1 mole of methane (CH4).
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
Mole ratio: 1 mole CH4 : 2 moles O2
👉 Note: Make sure to use the correct mole ratios and limiting reactant to solve stoichiometry problems.
Tip 5: Use Dimensional Analysis
Dimensional analysis is a technique used to solve problems involving multiple units. It involves using conversion factors to cancel out units and solve for the desired quantity.
Key Concepts:
- Conversion factor: A ratio of two quantities with different units.
- Dimensional analysis: A technique used to cancel out units and solve for the desired quantity.
Example:
Calculate the volume of oxygen required to burn 1 mole of methane (CH4), given that the density of oxygen is 1.14 g/L.
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
Mole ratio: 1 mole CH4 : 2 moles O2
Conversion factor: 1 mole O2 = 32 g O2
👉 Note: Make sure to use the correct conversion factors and dimensional analysis to solve problems involving multiple units.
Tip 6: Practice, Practice, Practice
The key to mastering chemical reaction worksheets is practice. Start with simple problems and gradually move on to more complex ones.
Practice Tips:
- Start with simple problems, such as balancing equations and identifying reaction types.
- Gradually move on to more complex problems, such as stoichiometry and dimensional analysis.
- Practice problems from different sources, such as textbooks, online resources, and worksheets.
By following these six essential tips, you can improve your skills in solving chemical reaction worksheets and become more confident in your ability to tackle complex chemistry problems.
Now, let’s summarize the key points:
- Understand the basics of chemical reactions, including reactants, products, and chemical equations.
- Balance the chemical equation by adding coefficients, not by changing the formulas of the reactants or products.
- Identify the type of reaction, such as synthesis, decomposition, single displacement, double displacement, and combustion reactions.
- Use stoichiometry to calculate the amount of reactants and products.
- Use dimensional analysis to solve problems involving multiple units.
- Practice, practice, practice, starting with simple problems and gradually moving on to more complex ones.
What is the importance of balancing chemical equations?
+Balancing chemical equations is crucial to ensure that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both the reactant and product sides. This ensures that the equation accurately represents the chemical reaction.
What is the difference between a synthesis reaction and a decomposition reaction?
+A synthesis reaction involves two or more reactants combining to form a single product, whereas a decomposition reaction involves a single reactant breaking down into two or more products.
How do I calculate the amount of reactants and products in a chemical reaction?
+Use stoichiometry to calculate the amount of reactants and products. This involves using mole ratios to determine the number of moles of each substance involved in the reaction.
Related Terms:
- Chemical reaction Worksheet pdf
- Types of chemical reaction worksheet
- Balancing chemical reactions worksheet pdf