History of Atoms Worksheet Answers Key
Exploring the History of Atoms: A Comprehensive Guide
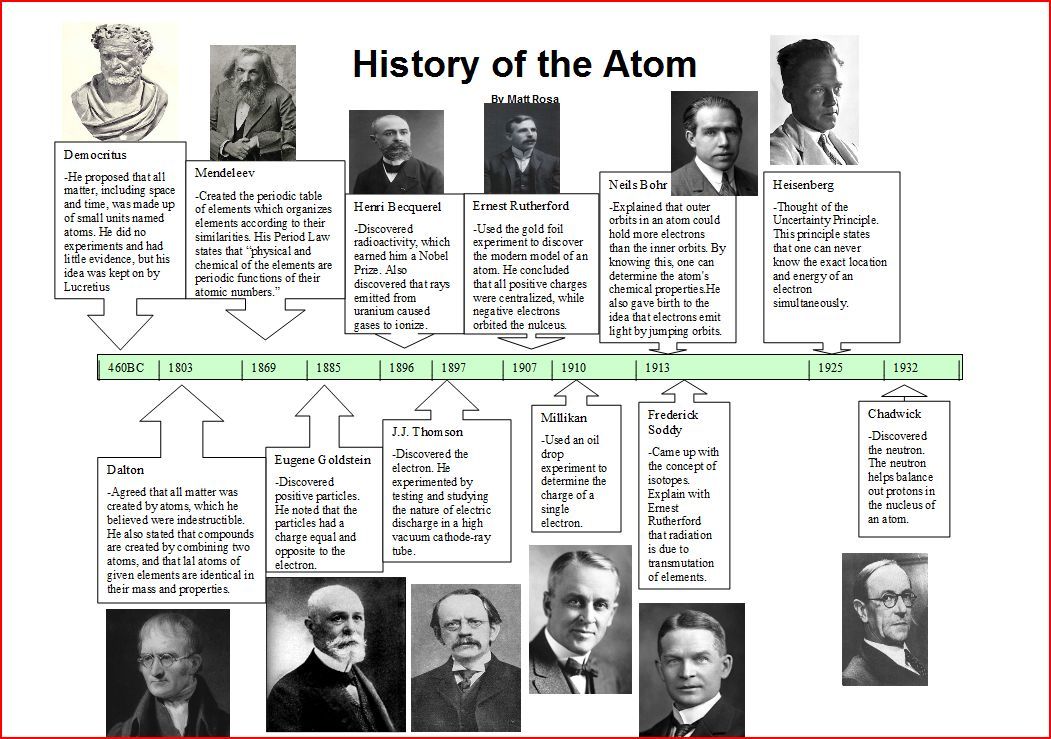
The concept of atoms has been around for thousands of years, with ancient philosophers such as Democritus and Epicurus proposing the idea that matter is composed of tiny indivisible particles. However, it wasn’t until the 19th century that the modern atomic theory began to take shape. In this article, we’ll delve into the history of atoms, from the early beginnings to the current understanding of atomic structure.
Early Theories: Democritus and Epicurus
The idea of atoms dates back to ancient Greece, where philosophers such as Democritus and Epicurus proposed the concept of indivisible particles. Democritus, in particular, is credited with developing the first atomic theory, which stated that matter is composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. Epicurus later expanded on this idea, suggesting that atoms were eternal and indestructible.
Key Points:
- Democritus proposed the first atomic theory around 450 BCE.
- Epicurus expanded on Democritus’ idea, suggesting that atoms were eternal and indestructible.
The Discovery of Elements: Antoine Lavoisier
In the 18th century, Antoine Lavoisier discovered the elements oxygen and hydrogen, which laid the foundation for the modern periodic table. Lavoisier’s work showed that elements were composed of unique combinations of atoms, and his discovery of oxygen led to a greater understanding of combustion and the role of atoms in chemical reactions.
Key Points:
- Antoine Lavoisier discovered the elements oxygen and hydrogen in the late 18th century.
- Lavoisier’s work laid the foundation for the modern periodic table.
John Dalton's Atomic Theory
In the early 19th century, John Dalton developed the modern atomic theory, which stated that elements are composed of small, indivisible particles called atoms. Dalton’s theory also proposed that atoms of the same element are identical in mass, size, and properties, while atoms of different elements have different masses, sizes, and properties.
Key Points:
- John Dalton developed the modern atomic theory in the early 19th century.
- Dalton’s theory proposed that atoms of the same element are identical in mass, size, and properties.
J.J. Thomson's Discovery of Electrons
In the late 19th century, J.J. Thomson discovered the electron, which revolutionized the understanding of atomic structure. Thomson’s experiments showed that atoms are composed of smaller particles called electrons, which are negatively charged and orbit the nucleus.
Key Points:
- J.J. Thomson discovered the electron in the late 19th century.
- Thomson’s experiments showed that atoms are composed of smaller particles called electrons.
Ernest Rutherford's Nuclear Atom
In the early 20th century, Ernest Rutherford developed the nuclear atom model, which proposed that atoms have a small, dense nucleus surrounded by electrons. Rutherford’s model was a significant departure from earlier theories, which suggested that atoms were composed of a uniform, indivisible mass.
Key Points:
- Ernest Rutherford developed the nuclear atom model in the early 20th century.
- Rutherford’s model proposed that atoms have a small, dense nucleus surrounded by electrons.
Niels Bohr's Atomic Model
In the 1920s, Niels Bohr developed the Bohr model of the atom, which proposed that electrons occupy specific energy levels, or shells, around the nucleus. Bohr’s model also introduced the concept of electron spin and the idea that electrons can jump from one energy level to another.
Key Points:
- Niels Bohr developed the Bohr model of the atom in the 1920s.
- Bohr’s model proposed that electrons occupy specific energy levels, or shells, around the nucleus.
Current Understanding of Atomic Structure
Today, our understanding of atomic structure is based on the principles of quantum mechanics and the discoveries of numerous scientists over the centuries. Atoms are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons, with protons and neutrons making up the nucleus and electrons orbiting around it.
Key Points:
- Atoms are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
- Protons and neutrons make up the nucleus, while electrons orbit around it.
Worksheets Answers Key
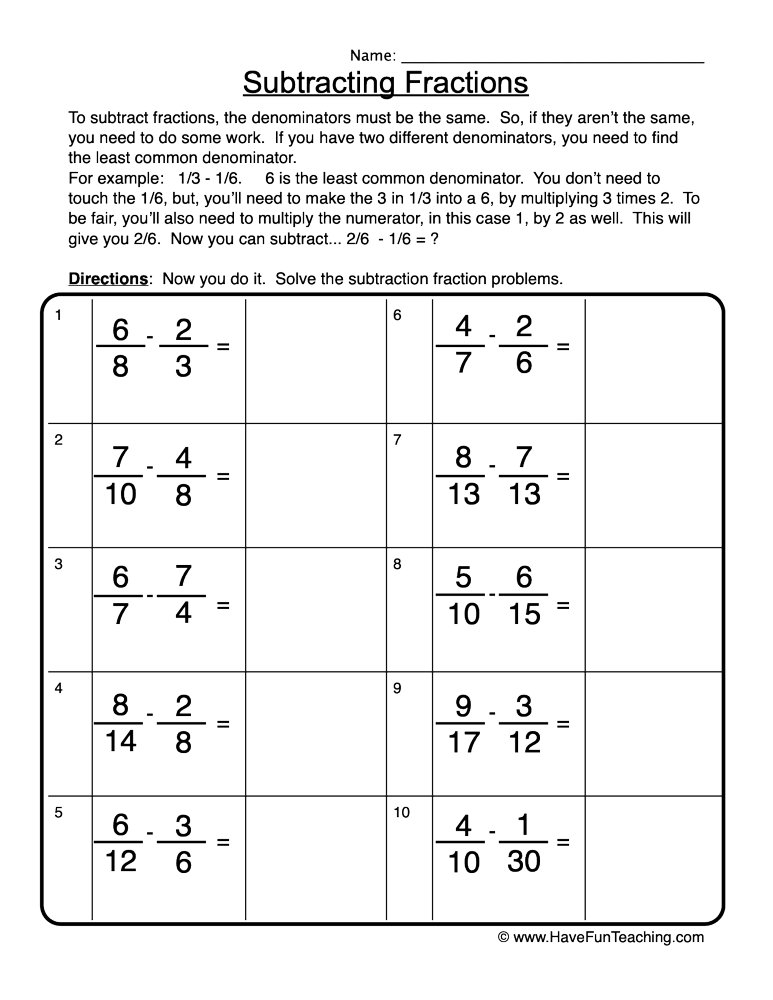
Worksheet 1: Early Theories
- Who proposed the first atomic theory?
- Answer: Democritus
- Who expanded on Democritus’ idea of atoms?
- Answer: Epicurus
Worksheet 2: Discovery of Elements
- Who discovered the elements oxygen and hydrogen?
- Answer: Antoine Lavoisier
- What was the significance of Lavoisier’s discovery?
- Answer: Lavoisier’s discovery laid the foundation for the modern periodic table.
Worksheet 3: John Dalton’s Atomic Theory
- What was the main idea of Dalton’s atomic theory?
- Answer: Dalton’s theory proposed that elements are composed of small, indivisible particles called atoms.
- What was a key feature of Dalton’s theory?
- Answer: Dalton’s theory proposed that atoms of the same element are identical in mass, size, and properties.
Worksheet 4: J.J. Thomson’s Discovery of Electrons
- Who discovered the electron?
- Answer: J.J. Thomson
- What was the significance of Thomson’s discovery?
- Answer: Thomson’s discovery revolutionized the understanding of atomic structure.
Worksheet 5: Ernest Rutherford’s Nuclear Atom
- Who developed the nuclear atom model?
- Answer: Ernest Rutherford
- What was the main idea of Rutherford’s model?
- Answer: Rutherford’s model proposed that atoms have a small, dense nucleus surrounded by electrons.
Worksheet 6: Niels Bohr’s Atomic Model
- Who developed the Bohr model of the atom?
- Answer: Niels Bohr
- What was the main idea of Bohr’s model?
- Answer: Bohr’s model proposed that electrons occupy specific energy levels, or shells, around the nucleus.
Worksheet 7: Current Understanding of Atomic Structure
- What is the current understanding of atomic structure?
- Answer: Atoms are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons, with protons and neutrons making up the nucleus and electrons orbiting around it.
- What is the significance of the current understanding of atomic structure?
- Answer: The current understanding of atomic structure is based on the principles of quantum mechanics and the discoveries of numerous scientists over the centuries.
What is the main idea of John Dalton's atomic theory?
+Dalton's theory proposed that elements are composed of small, indivisible particles called atoms.
Who discovered the electron?
+J.J. Thomson discovered the electron in the late 19th century.
What is the current understanding of atomic structure?
+Atoms are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons, with protons and neutrons making up the nucleus and electrons orbiting around it.
In conclusion, the history of atoms is a rich and fascinating topic that spans thousands of years. From the early theories of Democritus and Epicurus to the current understanding of atomic structure, our knowledge of atoms has evolved significantly over the centuries. By studying the history of atoms, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the scientists who contributed to our understanding of the atomic world.