7 Key Functions of the Cell Membrane Revealed
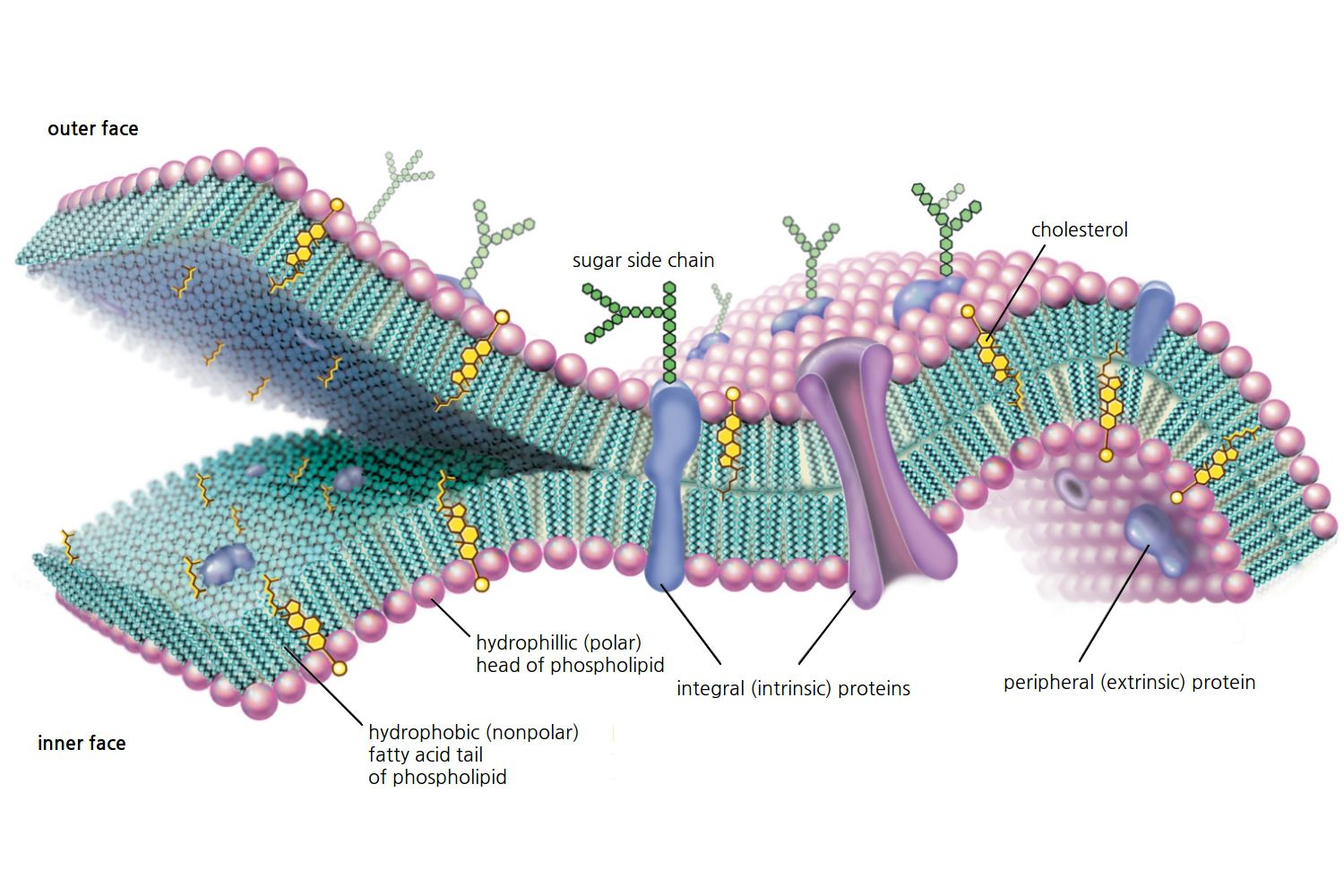
The Cell Membrane: A Critical Component of Cellular Function
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a thin layer of lipid and protein molecules that surrounds the cell and regulates the movement of materials in and out. It is a critical component of cellular function, and its importance cannot be overstated. In this article, we will explore the 7 key functions of the cell membrane, highlighting its role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and facilitating communication between the cell and its environment.
1. Selective Permeability: Regulating the Movement of Materials
One of the primary functions of the cell membrane is to regulate the movement of materials in and out of the cell. The cell membrane is semi-permeable, allowing certain molecules to pass through while restricting others. This selective permeability is crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis, as it enables the cell to control the concentration of ions, nutrients, and waste products.
🚨 Note: The cell membrane is not a static structure; it is dynamic and constantly changing to adapt to the cell's needs.
2. Cell Signaling: Facilitating Communication between Cells
The cell membrane plays a critical role in cell signaling, which is the process by which cells communicate with each other. The cell membrane contains receptors that bind to signaling molecules, such as hormones and neurotransmitters, triggering a response within the cell. This process enables cells to coordinate their behavior, respond to changes in their environment, and maintain tissue homeostasis.
3. Cell Adhesion: Maintaining Tissue Structure
Cell adhesion is the process by which cells attach to each other and to the extracellular matrix. The cell membrane contains adhesion molecules that interact with neighboring cells and the extracellular matrix, maintaining tissue structure and organization. This function is critical for maintaining tissue integrity and preventing cancer metastasis.
4. Transport of Materials: Facilitating the Movement of Molecules
The cell membrane facilitates the transport of materials across the cell boundary, enabling the cell to obtain essential nutrients and eliminate waste products. There are several types of transport mechanisms, including passive transport (diffusion and osmosis) and active transport (requiring energy).
5. Maintenance of Cellular Homeostasis
The cell membrane helps maintain cellular homeostasis by regulating the concentration of ions and molecules within the cell. It does this by controlling the movement of materials in and out of the cell, maintaining the proper pH and ionic balance, and regulating the activity of enzymes and other proteins.
6. Recognition and Binding of Substances
The cell membrane contains receptors that recognize and bind specific substances, such as hormones, neurotransmitters, and pathogens. This recognition and binding process triggers a response within the cell, enabling it to respond to changes in its environment and maintain homeostasis.
7. Regulation of Cell Growth and Division
The cell membrane plays a critical role in regulating cell growth and division. It does this by controlling the movement of molecules in and out of the cell, regulating the activity of enzymes and other proteins, and maintaining cellular homeostasis.
The cell membrane is a complex and dynamic structure that plays a critical role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and facilitating communication between the cell and its environment. Its 7 key functions highlight its importance in regulating the movement of materials, facilitating cell signaling, maintaining tissue structure, and regulating cell growth and division.
In summary, the cell membrane is a vital component of cellular function, and its importance cannot be overstated. Its 7 key functions highlight its role in maintaining cellular homeostasis, facilitating communication between cells, and regulating cell growth and division.
What is the primary function of the cell membrane?
+The primary function of the cell membrane is to regulate the movement of materials in and out of the cell, maintaining cellular homeostasis.
What is the role of the cell membrane in cell signaling?
+The cell membrane plays a critical role in cell signaling, facilitating communication between cells by recognizing and binding specific substances.
What is the relationship between the cell membrane and cellular homeostasis?
+The cell membrane helps maintain cellular homeostasis by regulating the concentration of ions and molecules within the cell, maintaining the proper pH and ionic balance, and regulating the activity of enzymes and other proteins.