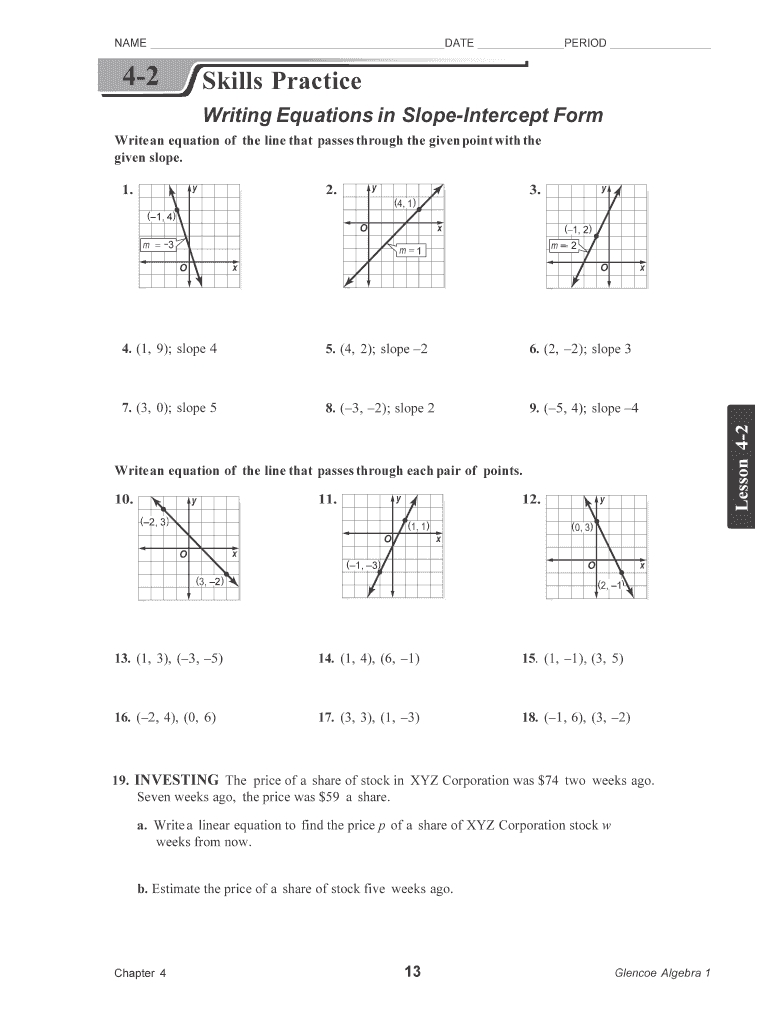
7 Ways Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Connect
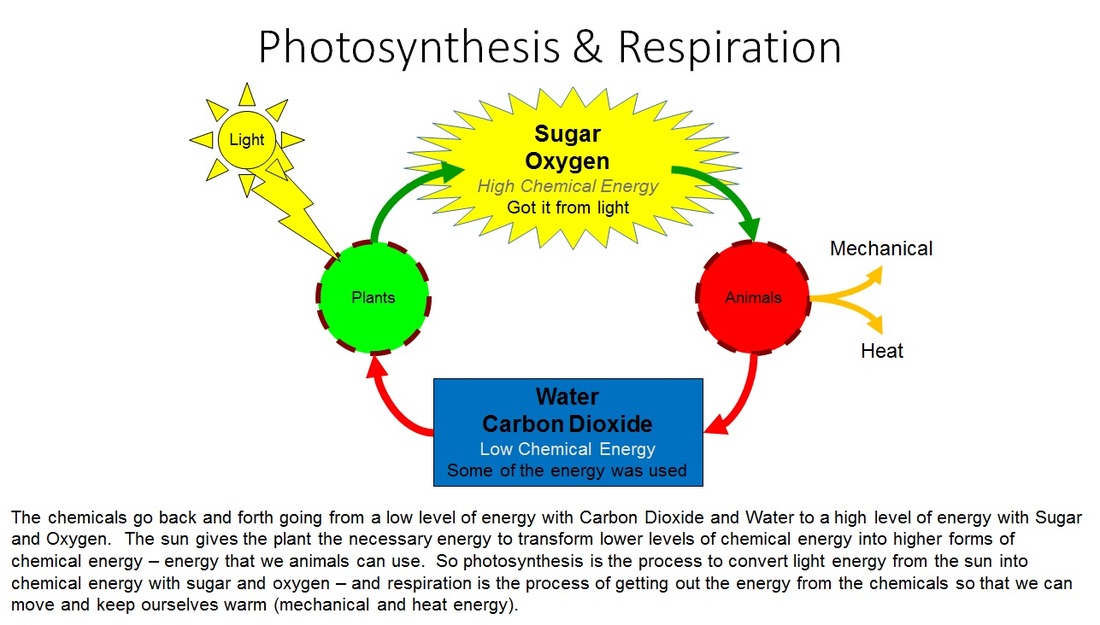
Understanding the Connection Between Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are two fundamental processes in biology that are interconnected in a way that sustains life on Earth. While they may seem like two separate entities, they are actually part of a delicate balance that maintains the flow of energy and organic compounds within ecosystems. In this article, we will explore seven ways in which photosynthesis and cellular respiration connect, highlighting their intricate relationship and the importance of this connection for life on our planet.
The Energy Connection: ATP and NADPH
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are both energy-transducing processes that rely on the production and consumption of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate). During photosynthesis, light energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. These energy-rich molecules are then used to power the conversion of CO2 into glucose, a process known as carbon fixation. In contrast, cellular respiration uses glucose and oxygen to produce ATP, releasing CO2 and water as byproducts. This energy connection highlights the cyclical nature of these two processes, where the energy produced by photosynthesis is consumed by cellular respiration.
Glucose: The Shared Currency
Glucose is the common currency that flows between photosynthesis and cellular respiration. During photosynthesis, glucose is produced through the fixation of CO2, while in cellular respiration, glucose is broken down to release energy. This glucose connection underscores the importance of photosynthesis in providing the energy-rich molecules that power cellular respiration.
Electron Transport Chains: A Common Mechanism
Both photosynthesis and cellular respiration rely on electron transport chains to generate ATP. In photosynthesis, light energy is used to drive the transfer of electrons, resulting in the production of ATP and NADPH. Similarly, in cellular respiration, electrons from glucose are passed through a series of electron transport chains, resulting in the production of ATP. This common mechanism highlights the shared biochemical pathways that underlie these two processes.
Oxygen: A Byproduct and a Reactant
Oxygen is both a byproduct of photosynthesis and a reactant in cellular respiration. During photosynthesis, oxygen is released as a byproduct of the light-dependent reactions, while in cellular respiration, oxygen is consumed to facilitate the breakdown of glucose. This oxygen connection emphasizes the interconnectedness of these two processes.
Carbon Dioxide: The Cycle of Life
Carbon dioxide is another critical component that flows between photosynthesis and cellular respiration. During photosynthesis, CO2 is fixed into glucose, while in cellular respiration, glucose is broken down to release CO2. This cycle of CO2 is essential for life on Earth, as it provides the carbon skeletons necessary for growth and development.
Thermodynamics: Energy Conservation
The connection between photosynthesis and cellular respiration is also rooted in thermodynamics. Both processes are governed by the laws of thermodynamics, which dictate the flow of energy and matter within systems. The energy produced by photosynthesis is conserved and transferred to cellular respiration, highlighting the efficiency of this energy conversion process.
Ecological Balance: A Delicate Relationship
The connection between photosynthesis and cellular respiration is not limited to the molecular level; it also has significant implications for ecological balance. The rate of photosynthesis and cellular respiration can impact the availability of oxygen and CO2, influencing the growth and development of organisms within ecosystems. This delicate balance underscores the importance of understanding the relationship between these two processes.
The Interplay of Enzymes and Coenzymes
Enzymes and coenzymes play a crucial role in facilitating the connection between photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Enzymes such as RuBisCO (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase) and cytochrome c oxidase catalyze key reactions in photosynthesis and cellular respiration, respectively. Coenzymes such as NADPH and FADH2 (flavin adenine dinucleotide) are also essential for the transfer of electrons and energy within these processes.
🌟 Note: The enzymes and coenzymes involved in photosynthesis and cellular respiration are highly specific and have evolved to optimize the efficiency of these processes.
Summary of Connections
The connections between photosynthesis and cellular respiration can be summarized as follows:
- Energy connection: ATP and NADPH
- Glucose connection: Shared currency between photosynthesis and cellular respiration
- Electron transport chains: Common mechanism for generating ATP
- Oxygen connection: Byproduct and reactant
- Carbon dioxide connection: Cycle of life
- Thermodynamics: Energy conservation
- Ecological balance: Delicate relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration
In conclusion, the connections between photosynthesis and cellular respiration are multifaceted and far-reaching. These two processes are intricately linked, with each providing the necessary energy and organic compounds for the other to function. Understanding this connection is essential for appreciating the complex relationships within ecosystems and the fundamental principles that govern life on Earth.
What is the primary connection between photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
+The primary connection between photosynthesis and cellular respiration is the energy connection, where ATP and NADPH produced by photosynthesis are consumed by cellular respiration to produce energy.
What is the role of glucose in the connection between photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
+Glucose is the shared currency that flows between photosynthesis and cellular respiration. During photosynthesis, glucose is produced through the fixation of CO2, while in cellular respiration, glucose is broken down to release energy.
How do electron transport chains connect photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
+Electron transport chains are a common mechanism used by both photosynthesis and cellular respiration to generate ATP. In photosynthesis, light energy is used to drive the transfer of electrons, resulting in the production of ATP and NADPH, while in cellular respiration, electrons from glucose are passed through a series of electron transport chains to produce ATP.