5 Ways to Master Boyle's and Charles' Laws
Understanding the Foundations of Gas Laws
In the realm of chemistry and physics, understanding the behavior of gases is crucial. Two fundamental principles that govern the behavior of gases are Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law. These laws, discovered by Robert Boyle and Jacques Charles, respectively, provide the foundation for understanding the relationships between pressure, volume, and temperature of gases. Mastering these laws is essential for students, researchers, and professionals in various scientific fields. In this article, we will delve into the world of Boyle’s and Charles’ Laws, exploring their definitions, applications, and providing practical tips for mastering them.
Boyle's Law: The Pressure-Volume Relationship
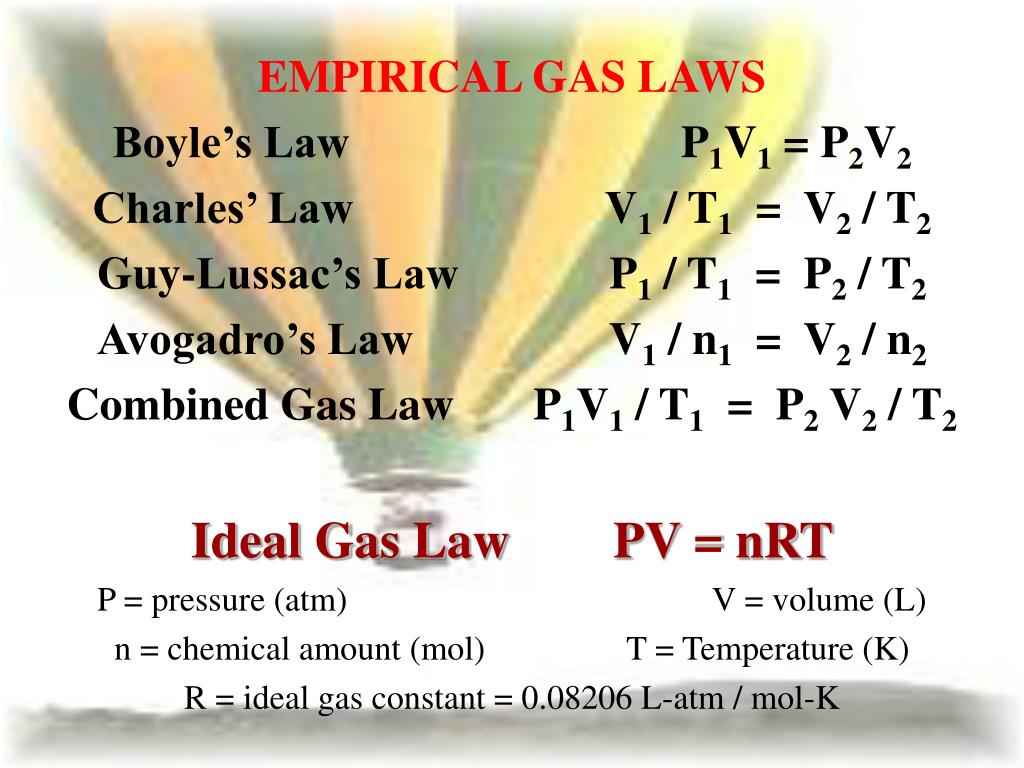
Boyle’s Law states that, at constant temperature, the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to the pressure applied to it. Mathematically, this can be expressed as:
P1V1 = P2V2
where P1 and V1 are the initial pressure and volume, and P2 and V2 are the final pressure and volume.
To illustrate this concept, imagine a gas contained in a cylinder with a movable piston. If the pressure applied to the piston is increased, the volume of the gas will decrease, and vice versa.
📝 Note: Boyle's Law only applies to ideal gases, which do not exist in reality. However, real gases can be approximated as ideal gases under certain conditions.
Charles' Law: The Temperature-Volume Relationship
Charles’ Law states that, at constant pressure, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to the temperature. Mathematically, this can be expressed as:
V1 / T1 = V2 / T2
where V1 and T1 are the initial volume and temperature, and V2 and T2 are the final volume and temperature.
To visualize this concept, imagine a gas contained in a cylinder with a fixed pressure. If the temperature of the gas is increased, the volume will also increase, and vice versa.
📝 Note: Charles' Law assumes that the temperature is measured in Kelvin (K), not Celsius (°C) or Fahrenheit (°F).
5 Ways to Master Boyle's and Charles' Laws
Now that we have explored the definitions and principles of Boyle’s and Charles’ Laws, let’s dive into some practical tips for mastering them:
1. Understand the Ideal Gas Equation
The ideal gas equation is a fundamental concept that combines Boyle’s and Charles’ Laws:
PV = nRT
where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the number of moles, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature.
Understanding this equation will help you to better grasp the relationships between pressure, volume, and temperature.
2. Practice with Sample Problems
Practice makes perfect! Solve sample problems that involve Boyle’s and Charles’ Laws to reinforce your understanding of these concepts. You can find sample problems online or in textbooks.
3. Use Visual Aids and Diagrams
Visual aids and diagrams can help to illustrate the concepts of Boyle’s and Charles’ Laws. Create diagrams to show the relationships between pressure, volume, and temperature.
4. Conduct Experiments
Conducting experiments can help to reinforce your understanding of Boyle’s and Charles’ Laws. You can conduct simple experiments using a gas cylinder, piston, and thermometer.
5. Apply to Real-World Scenarios
Apply Boyle’s and Charles’ Laws to real-world scenarios, such as:
- Scuba diving: Understanding Boyle’s Law can help scuba divers to avoid decompression sickness.
- Weather forecasting: Charles’ Law can help meteorologists to predict weather patterns.
By applying these laws to real-world scenarios, you can see their practical relevance and importance.
In conclusion, mastering Boyle’s and Charles’ Laws requires a deep understanding of the relationships between pressure, volume, and temperature. By following the tips outlined above, you can develop a strong foundation in these fundamental principles of chemistry and physics.
What is the main difference between Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law?
+Boyle’s Law describes the relationship between pressure and volume, while Charles’ Law describes the relationship between temperature and volume.
Can Boyle’s Law be applied to real gases?
+While Boyle’s Law only applies to ideal gases, real gases can be approximated as ideal gases under certain conditions.
How can I practice solving problems involving Boyle’s and Charles’ Laws?
+You can find sample problems online or in textbooks, and practice solving them to reinforce your understanding of these laws.
Related Terms:
- Boyle's Law Worksheet answer key
- Boyle's Law worksheets