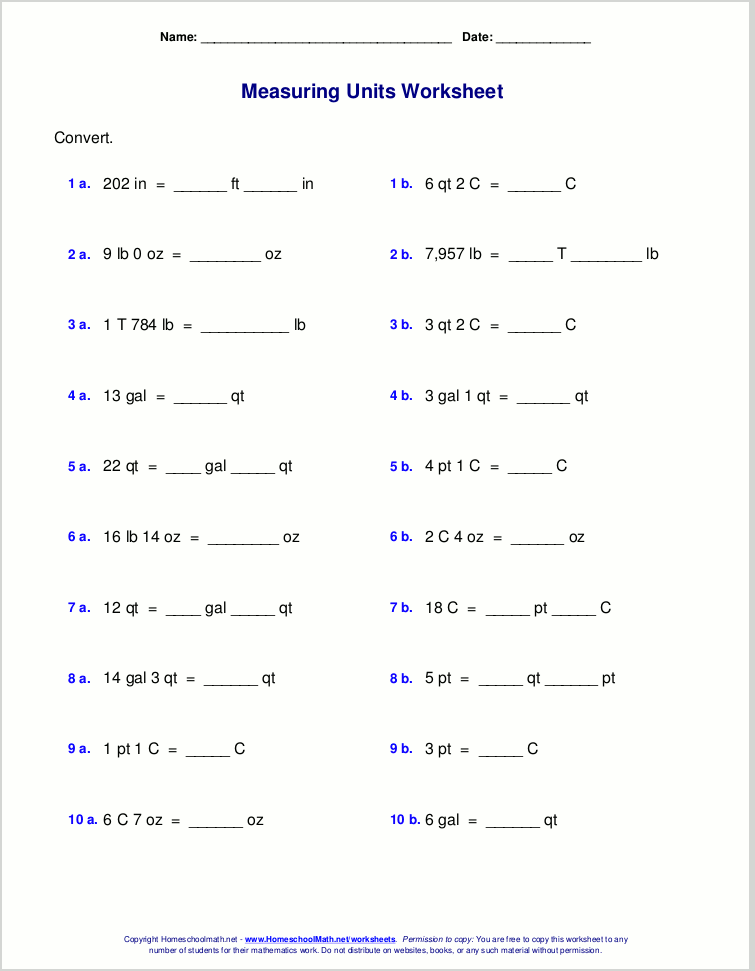
Bohr Model Worksheet Answer Key: Simplified Atom Solutions
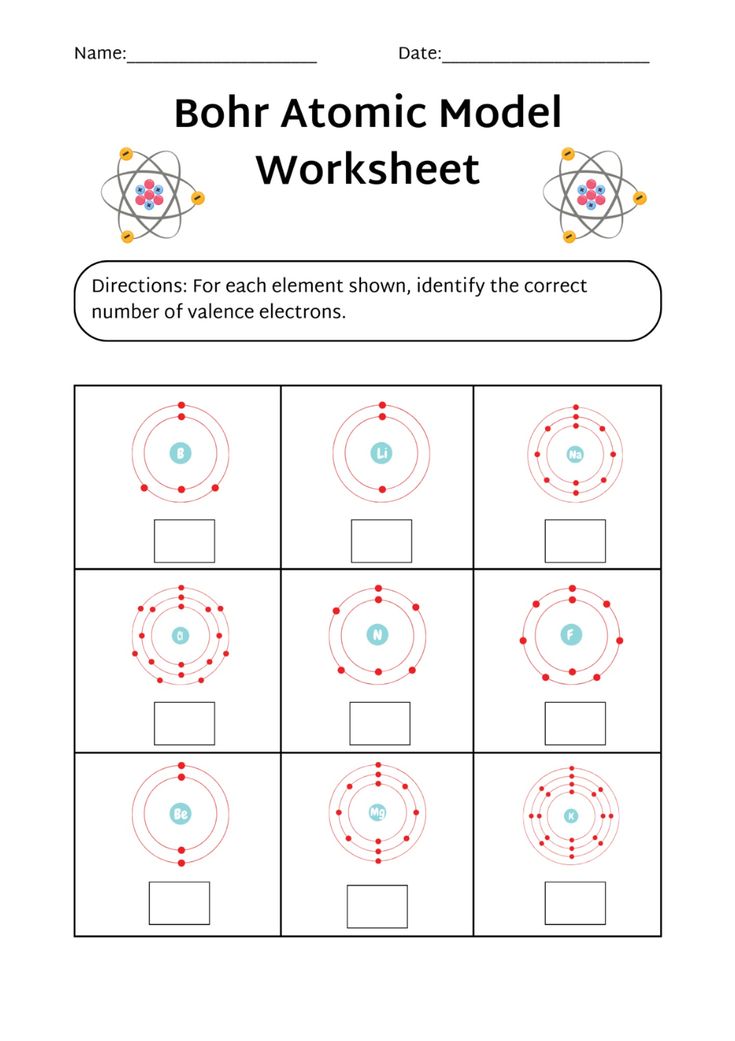
Understanding the Bohr Model of the Atom
The Bohr model, proposed by Niels Bohr in 1913, is a simplified representation of the atom that describes the arrangement of electrons around the nucleus. This model is a crucial concept in chemistry and physics, helping students understand the structure and properties of atoms. In this article, we will delve into the Bohr model, its key components, and provide a comprehensive answer key to a Bohr model worksheet.
Key Components of the Bohr Model
The Bohr model consists of the following key components:
- Nucleus: The central part of the atom, containing protons and neutrons.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in energy levels or shells.
- Energy Levels: The regions around the nucleus where electrons are found, also known as electron shells.
- Electron Shells: The specific energy levels that electrons occupy, denoted by integers (1, 2, 3, etc.).
Bohr Model Worksheet Answer Key
Below is a simplified Bohr model worksheet answer key to help students understand the concepts.
Section 1: Multiple Choice Questions
- What is the Bohr model of the atom? a) A detailed representation of the atom b) A simplified representation of the atom c) A model of the molecule d) A model of the nucleus
Answer: b) A simplified representation of the atom
- Which of the following is NOT a key component of the Bohr model? a) Nucleus b) Electrons c) Protons d) Neutrons
Answer: c) Protons (While protons are part of the nucleus, they are not a separate key component of the Bohr model.)
- What are the regions around the nucleus where electrons are found called? a) Energy Levels b) Electron Shells c) Orbitals d) Atoms
Answer: a) Energy Levels
Section 2: Short Answer Questions
- Describe the nucleus of an atom.
Answer: The nucleus is the central part of the atom, containing protons and neutrons.
- What are electron shells, and how are they denoted?
Answer: Electron shells are specific energy levels that electrons occupy, denoted by integers (1, 2, 3, etc.).
Section 3: Fill-in-the-Blank Questions
- The Bohr model describes the arrangement of _______________________ around the nucleus.
Answer: electrons
- The nucleus of an atom contains _______________________ and _______________________.
Answer: protons, neutrons
Section 4: Matching Questions
Match the following terms with their correct definitions:
- Energy Level
- Electron Shell
- Nucleus
- Electron
Definitions: a) A specific energy level that electrons occupy b) A negatively charged particle that orbits the nucleus c) The central part of the atom, containing protons and neutrons d) The regions around the nucleus where electrons are found
Answers: 1. d) The regions around the nucleus where electrons are found 2. a) A specific energy level that electrons occupy 3. c) The central part of the atom, containing protons and neutrons 4. b) A negatively charged particle that orbits the nucleus
Important Notes
- The Bohr model is a simplified representation of the atom, not a detailed representation.
- Electrons occupy specific energy levels or shells around the nucleus.
- The nucleus contains protons and neutrons.
📝 Note: The Bohr model is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics, but it has limitations and has been largely replaced by more advanced models, such as the quantum mechanical model.
What is the Bohr model of the atom?
+The Bohr model is a simplified representation of the atom that describes the arrangement of electrons around the nucleus.
What are the key components of the Bohr model?
+The key components of the Bohr model are the nucleus, electrons, energy levels, and electron shells.
What is the limitation of the Bohr model?
+The Bohr model is a simplified representation of the atom and has been largely replaced by more advanced models, such as the quantum mechanical model.
The Bohr model is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics, providing a simplified representation of the atom. By understanding the key components of the Bohr model, students can gain a deeper understanding of the structure and properties of atoms.