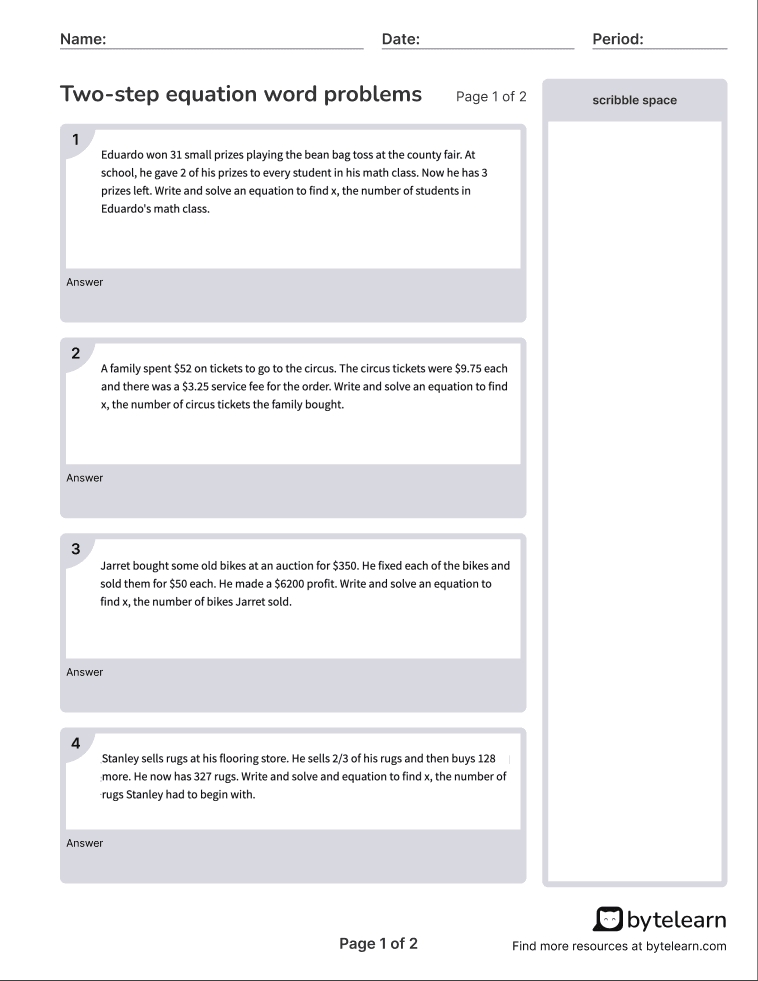
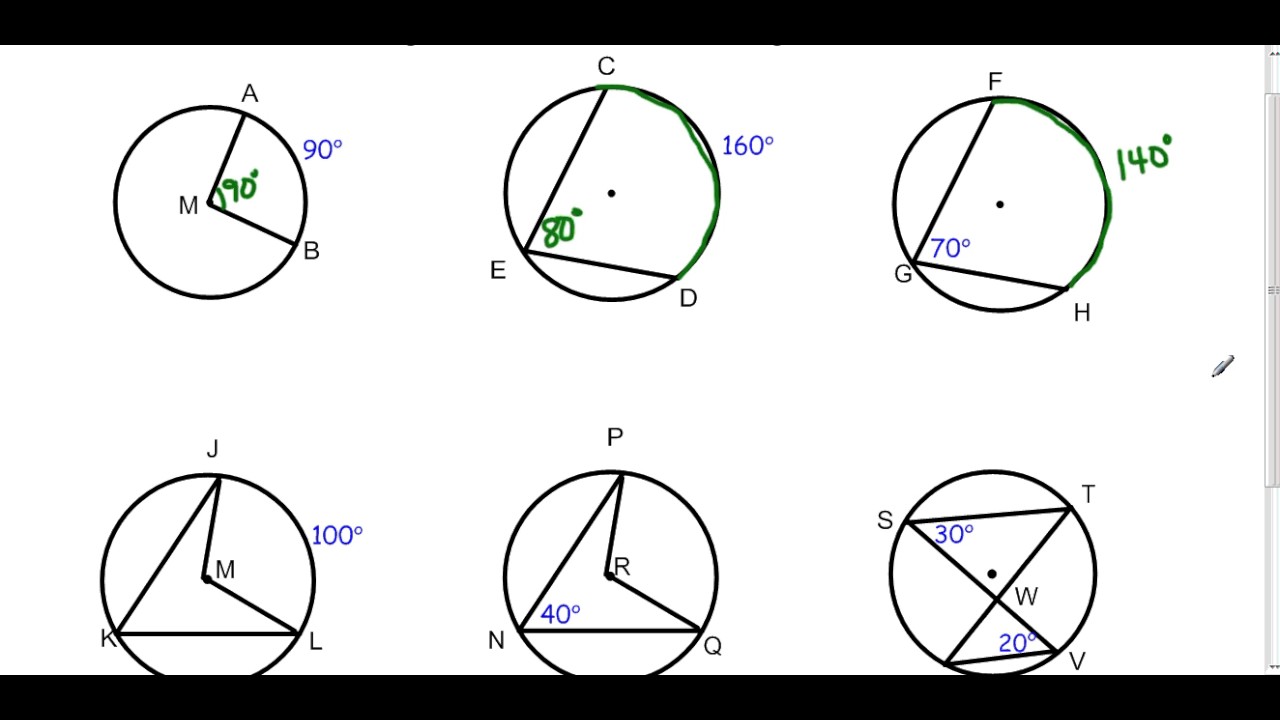
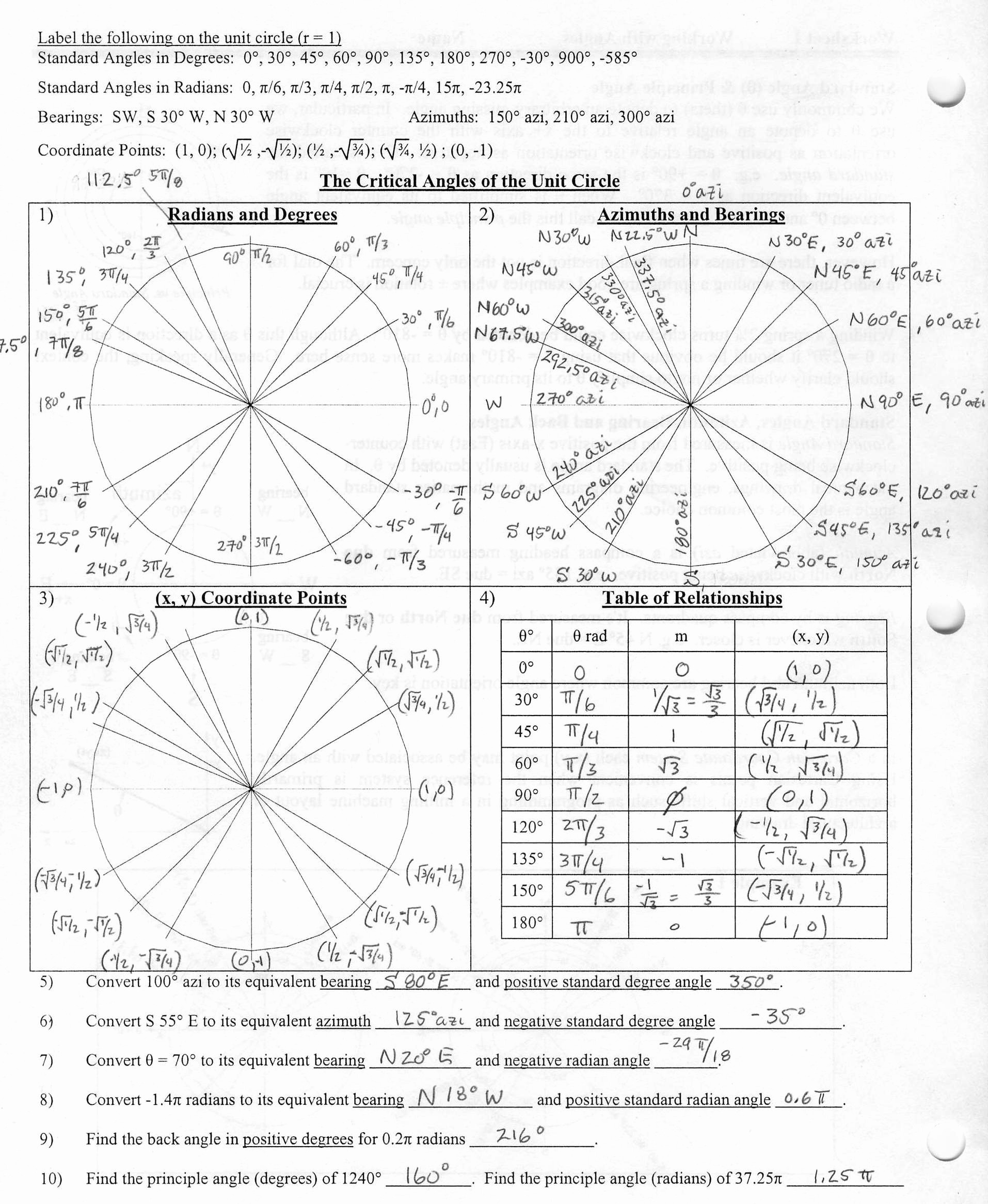
Atomic Theory Timeline: Key Discoveries and Dates

Atomic Theory Timeline: Key Discoveries and Dates
The atomic theory has undergone significant developments over the centuries, from ancient philosophers to modern scientists. This timeline highlights key discoveries and dates that have shaped our understanding of the atomic structure.
Ancient Philosophers (500 BCE - 500 CE)
- Democritus (460 BCE - 370 BCE): Proposed the concept of atoms as indivisible particles that make up all matter.
- Epicurus (341 BCE - 270 BCE): Developed the idea that atoms are eternal and indestructible.
- Lucretius (99 BCE - 55 BCE): Wrote “De Rerum Natura,” a poem that describes the atomic theory and its implications.
Modern Era (1500 - 1800)
- Pierre Gassendi (1592 - 1655): Revived the atomic theory and proposed that atoms are small, indivisible particles.
- Robert Boyle (1627 - 1691): Conducted experiments that led to the development of the modern concept of elements and compounds.
- Antoine Lavoisier (1743 - 1794): Discovered oxygen and developed a systematic method for naming elements.
Atomic Structure (1800 - 1900)
- John Dalton (1766 - 1844): Proposed the modern atomic theory, which states that elements are composed of small, indivisible particles called atoms.
- Michael Faraday (1791 - 1867): Discovered the principles of electrolysis and proposed the concept of ions.
- William Thomson (Lord Kelvin) (1824 - 1907): Developed the kinetic theory of gases, which describes the behavior of atoms and molecules.
Subatomic Particles (1900 - 1950)
- J.J. Thomson (1856 - 1940): Discovered the electron and proposed the “plum pudding” model of the atom.
- Ernest Rutherford (1871 - 1937): Conducted the famous gold foil experiment, which led to the discovery of the nucleus.
- Niels Bohr (1885 - 1962): Developed the Bohr model of the atom, which describes the arrangement of electrons in energy levels.
Nuclear Physics (1950 - present)
- James Chadwick (1891 - 1974): Discovered the neutron and developed the concept of nuclear fission.
- Enrico Fermi (1901 - 1954): Conducted the first controlled nuclear chain reaction and developed the theory of beta decay.
- Murray Gell-Mann (1929 - 2019): Developed the theory of quarks and gluons, which describes the behavior of subatomic particles.

| Scientist | Discovery | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Democritus | Proposed the concept of atoms | 460 BCE |
| John Dalton | Proposed the modern atomic theory | 1803 |
| J.J. Thomson | Discovered the electron | 1897 |
| Ernest Rutherford | Discovered the nucleus | 1911 |
| James Chadwick | Discovered the neutron | 1932 |
🔍 Note: The dates listed are approximate and represent the year of publication or discovery.
In conclusion, the atomic theory has undergone significant developments over the centuries, from ancient philosophers to modern scientists. Understanding the key discoveries and dates in this timeline provides a comprehensive overview of the atomic structure and its implications.
What is the atomic theory?
+The atomic theory is a scientific concept that describes the structure and behavior of atoms, which are the building blocks of matter.
Who is credited with the discovery of the electron?
+J.J. Thomson is credited with the discovery of the electron in 1897.
What is the Bohr model of the atom?
+The Bohr model of the atom is a scientific concept that describes the arrangement of electrons in energy levels around the nucleus.
Related Terms:
- Atomic theory Timeline Worksheet PDF
- Atomic theory Timeline Project pdf
- Atomic theory timeline Project examples
- Atomic theory Worksheet PDF