Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers for Easy Learning
Understanding Atomic Structure: A Comprehensive Guide
The atomic structure is a fundamental concept in chemistry that helps us understand the building blocks of matter. It’s essential to grasp the basics of atomic structure to excel in chemistry and related fields. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of atomic structure, exploring its components, types, and significance.
What is Atomic Structure?
Atomic structure refers to the arrangement of electrons, protons, and neutrons within an atom. It’s the blueprint of an atom, showcasing how these subatomic particles interact and combine to form the atom’s overall structure.
Components of Atomic Structure
An atom consists of three primary components:
- Protons: Positively charged particles that reside in the nucleus (center) of the atom.
- Neutrons: Particles with no charge that accompany protons in the nucleus.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit around the nucleus.
Types of Atomic Structure
There are two main types of atomic structure:
- Atomic Number: The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, which determines the element’s identity.
- Mass Number: The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus, which determines the atom’s mass.
Electron Configuration
Electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons in an atom. It’s typically represented by the Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle. The Aufbau principle states that electrons occupy the lowest available energy levels, while the Pauli exclusion principle states that each orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons with opposite spins.
Importance of Atomic Structure
Understanding atomic structure is crucial in various fields, including:
- Chemistry: Atomic structure helps us understand chemical reactions, bonding, and the properties of elements.
- Physics: Atomic structure is essential in understanding the behavior of matter and energy at the atomic and subatomic level.
- Biology: Atomic structure helps us understand the structure and function of biomolecules, such as DNA and proteins.
Common Atomic Structure Mistakes
When working with atomic structure, it’s essential to avoid common mistakes, such as:
- Incorrect electron configuration: Failing to follow the Aufbau principle and Pauli exclusion principle can lead to incorrect electron configuration.
- Confusing atomic number and mass number: Failing to distinguish between atomic number and mass number can lead to errors in identifying elements and their properties.
🚨 Note: When working with atomic structure, always double-check your calculations and ensure you're using the correct units and notation.
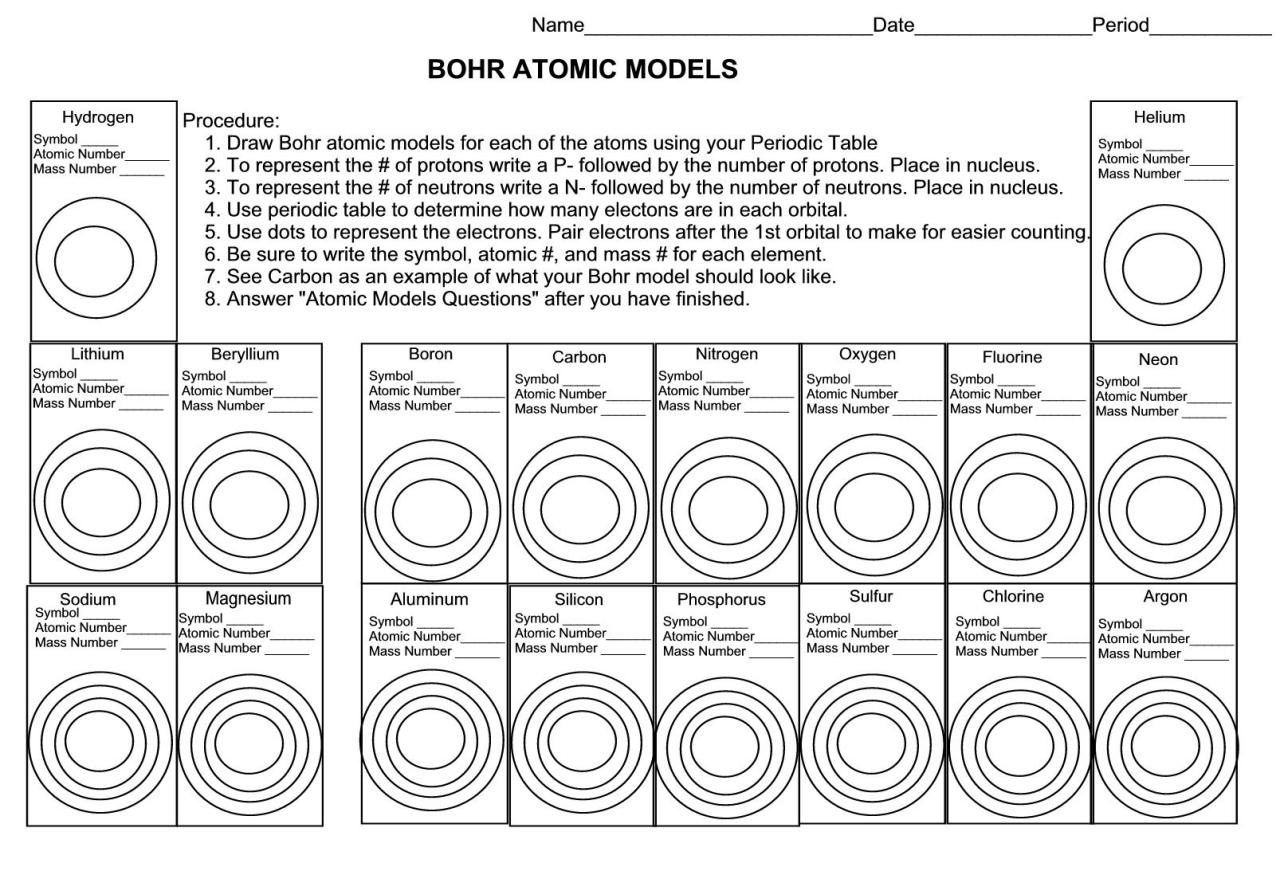
Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
To help you reinforce your understanding of atomic structure, we’ve included answers to common worksheet questions:

| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the atomic number of carbon? | 6 |
| What is the mass number of oxygen? | 16 |
| What is the electron configuration of neon? | 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ |
| What is the number of protons in a hydrogen atom? | 1 |
Conclusion
Atomic structure is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics that helps us understand the building blocks of matter. By grasping the components, types, and significance of atomic structure, you’ll be better equipped to excel in these fields. Remember to avoid common mistakes and practice, practice, practice to reinforce your understanding.
What is the difference between atomic number and mass number?
+Atomic number refers to the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, while mass number refers to the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus.
What is the Aufbau principle?
+The Aufbau principle states that electrons occupy the lowest available energy levels in an atom.
What is the significance of atomic structure in chemistry?
+Understanding atomic structure helps us understand chemical reactions, bonding, and the properties of elements.