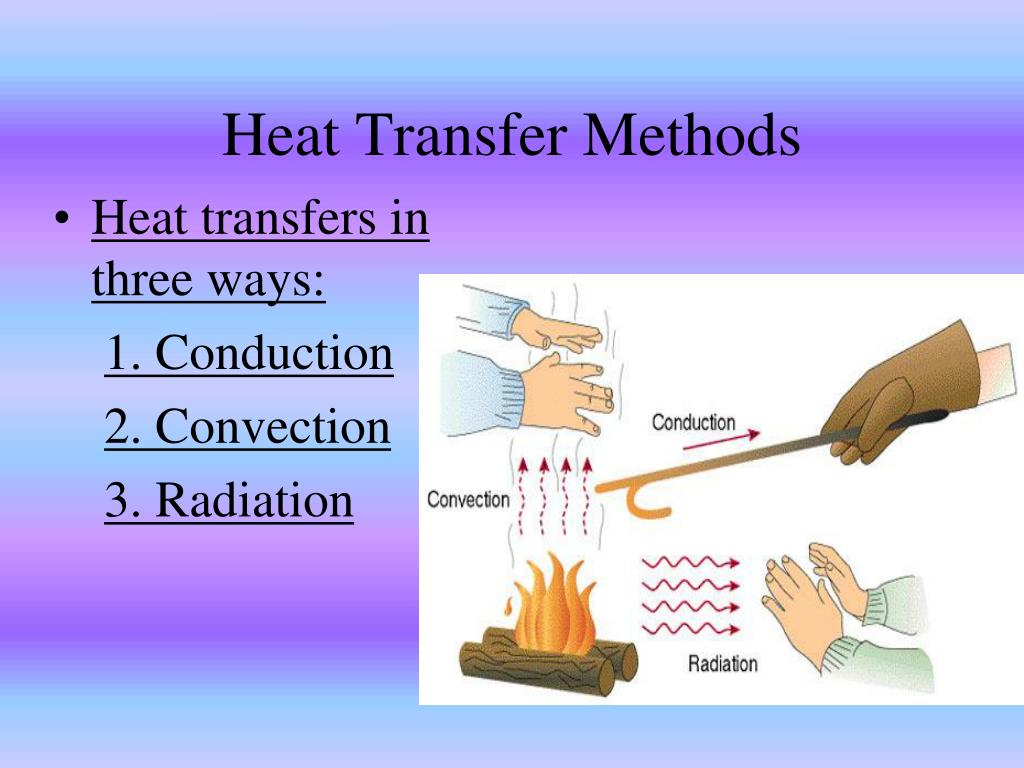
3 Ways Heat Transfer Occurs
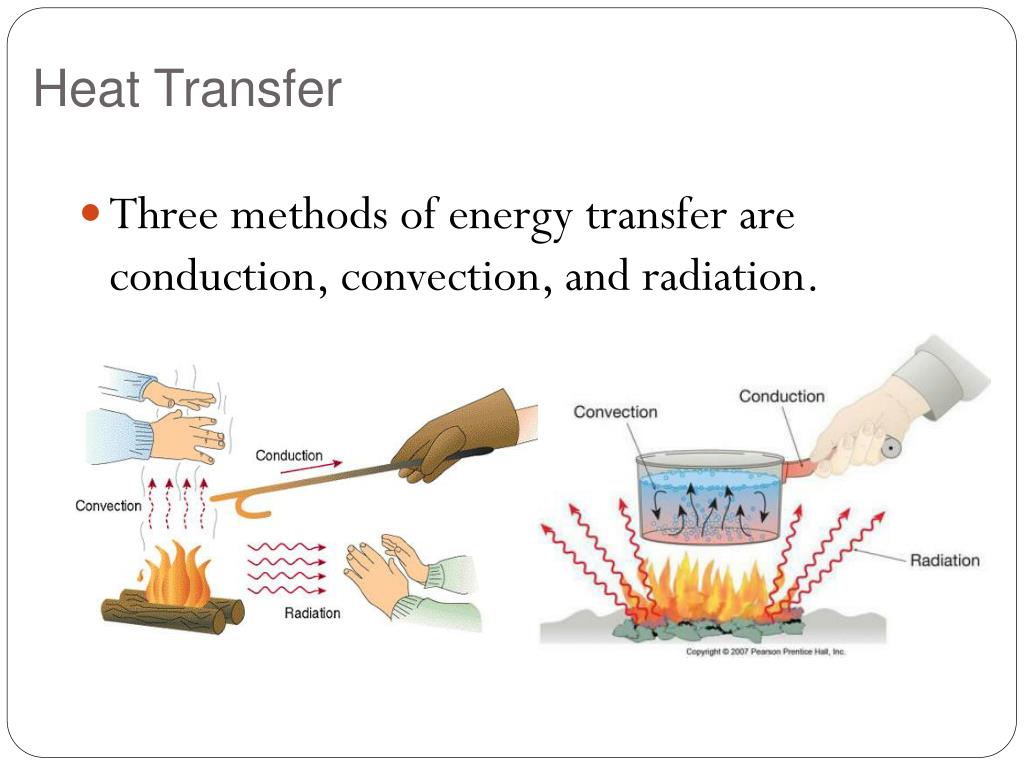
Understanding Heat Transfer: A Comprehensive Guide
Heat transfer is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering that plays a crucial role in various aspects of our daily lives. From the simplest household appliances to complex industrial systems, heat transfer is an essential process that helps us maintain a comfortable temperature, cook food, and power machinery. In this article, we will delve into the three primary methods of heat transfer, exploring their underlying principles, applications, and examples.
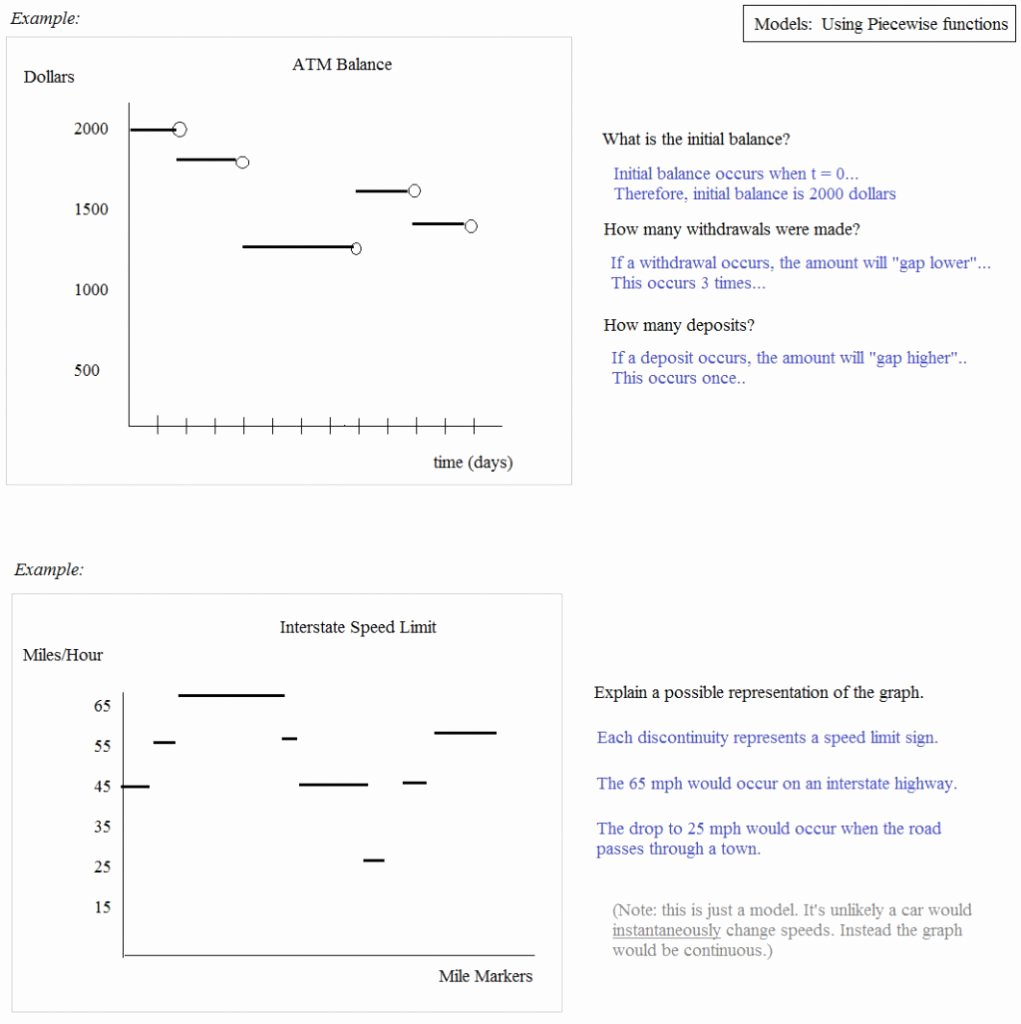
Conduction: The Transfer of Heat through Direct Contact
Conduction is the process of heat transfer that occurs when two objects are in direct physical contact. This method relies on the direct transfer of energy between particles, where the molecules of one object collide with the molecules of another object, causing the energy to flow from the hotter object to the cooler object. The rate of heat transfer via conduction depends on the thermal conductivity of the materials involved, the surface area in contact, and the temperature difference between the objects.
Examples of Conduction:
- Holding a hot cup of coffee and feeling the heat transfer to your hands
- Cooking food on a metal pan, where the heat from the stove is transferred to the food through the pan
- Using a metal spoon to stir a hot beverage, where the heat is transferred from the liquid to the spoon
Convection: The Transfer of Heat through Fluids
Convection is the process of heat transfer that occurs when a fluid (liquid or gas) is heated, causing it to expand and rise. As the heated fluid rises, it is replaced by cooler fluid, which is then heated, creating a cycle of heat transfer. This process can occur naturally, such as in the atmosphere, or artificially, such as in a heating system.
Examples of Convection:
- Boiling water on a stove, where the heated water rises and is replaced by cooler water
- Using a radiator to heat a room, where the heated water flows through the radiator and is cooled by the surrounding air
- Weather patterns, such as wind and ocean currents, which are driven by the convection of heat in the atmosphere
Radiation: The Transfer of Heat through Electromagnetic Waves
Radiation is the process of heat transfer that occurs when energy is transmitted through electromagnetic waves, such as light and radio waves. This method does not require a medium to transfer heat, as the energy is transmitted through space. The rate of heat transfer via radiation depends on the temperature of the objects involved, as well as their surface properties.
Examples of Radiation:
- Feeling the warmth of the sun on your skin, where the energy is transferred through electromagnetic waves
- Using a microwave oven to heat food, where the energy is transferred through electromagnetic waves
- The glow of a light bulb, where the energy is transferred through electromagnetic waves
🔍 Note: In reality, most heat transfer processes involve a combination of these three methods, rather than a single method in isolation.
| Method | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Conduction | Direct transfer of energy between particles | Holding a hot cup of coffee, cooking food on a metal pan |
| Convection | Transfer of heat through fluids | Boiling water, using a radiator to heat a room |
| Radiation | Transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves | Feeling the warmth of the sun, using a microwave oven |
Understanding Heat Transfer in Real-World Applications
Heat transfer plays a critical role in various industries, including:
- Aerospace Engineering: Heat transfer is crucial in the design of aircraft and spacecraft, where temperature fluctuations can affect performance and safety.
- Chemical Processing: Heat transfer is used to control chemical reactions, separate mixtures, and purify substances.
- Electronics: Heat transfer is used to cool electronic components, such as computer chips and smartphones.
In conclusion, heat transfer is an essential process that occurs in various forms, including conduction, convection, and radiation. Understanding these methods and their applications is crucial in designing and optimizing systems that involve heat transfer. By recognizing the importance of heat transfer, we can improve the efficiency and safety of various industries and technologies.
What is the difference between conduction and convection?
+Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct contact between objects, while convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids.
Can heat transfer occur through more than one method simultaneously?
+Yes, most heat transfer processes involve a combination of conduction, convection, and radiation.
How is heat transfer used in everyday life?
+Heat transfer is used in various applications, including cooking, heating and cooling systems, and electronic devices.