Animal Cell Labeling Worksheet
Understanding the Structure of Animal Cells
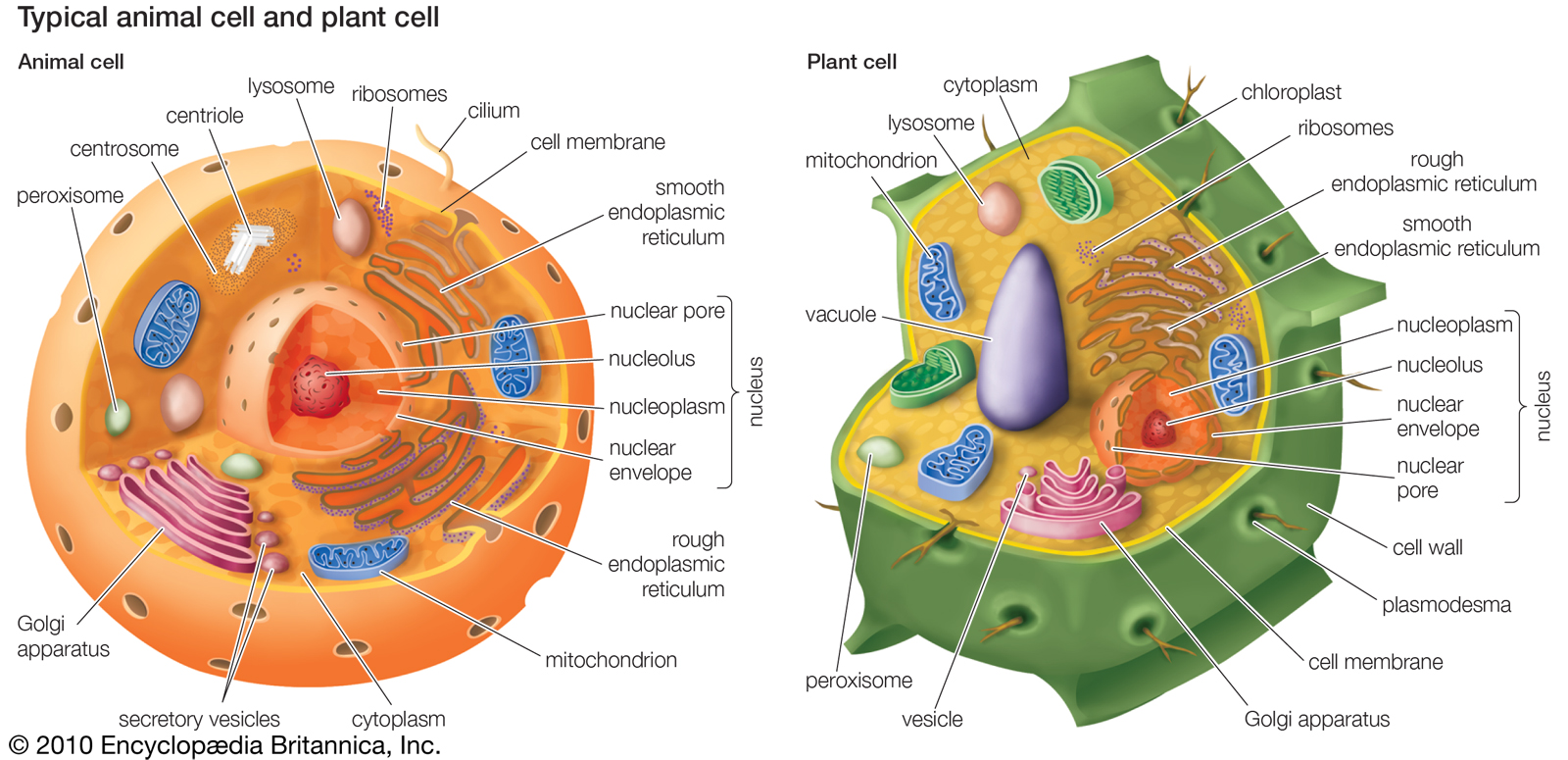
Animal cells are the building blocks of life for all living organisms, from simple sponges to complex humans. They are the smallest units of life that can function independently, and they are incredibly diverse in terms of their shape, size, and function. In this article, we will explore the structure of animal cells, including the different organelles and their functions.
The Components of an Animal Cell
An animal cell consists of several organelles, each with its own unique function. Here are the main components of an animal cell:
- Plasma Membrane: The plasma membrane, also known as the cell membrane, is the outermost layer of the cell. It is a semi-permeable membrane that separates the cell from its environment and regulates the movement of materials in and out of the cell.
- Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance inside the cell membrane. It is where many of the cell’s metabolic reactions take place and is home to many organelles.
- Nucleus: The nucleus is the control center of the cell. It contains most of the cell’s genetic material, or DNA, and is responsible for regulating the cell’s growth, reproduction, and function.
- Mitochondria: Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell. They generate energy for the cell through a process called cellular respiration.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): The ER is a network of membranous tubules and cisternae that is involved in protein synthesis, transport, and storage.
- Ribosomes: Ribosomes are small organelles that are responsible for protein synthesis. They read the sequence of nucleotides in messenger RNA (mRNA) and assemble amino acids into proteins.
- Lysosomes: Lysosomes are membrane-bound sacs that contain digestive enzymes. They break down and recycle cellular waste and foreign substances.
- Golgi Apparatus: The Golgi apparatus is a complex of flattened sacs and tubules that is involved in protein modification, sorting, and packaging.
- Cytoskeleton: The cytoskeleton is a network of protein filaments that provides structural support and shape to the cell. It is also involved in cell movement and division.
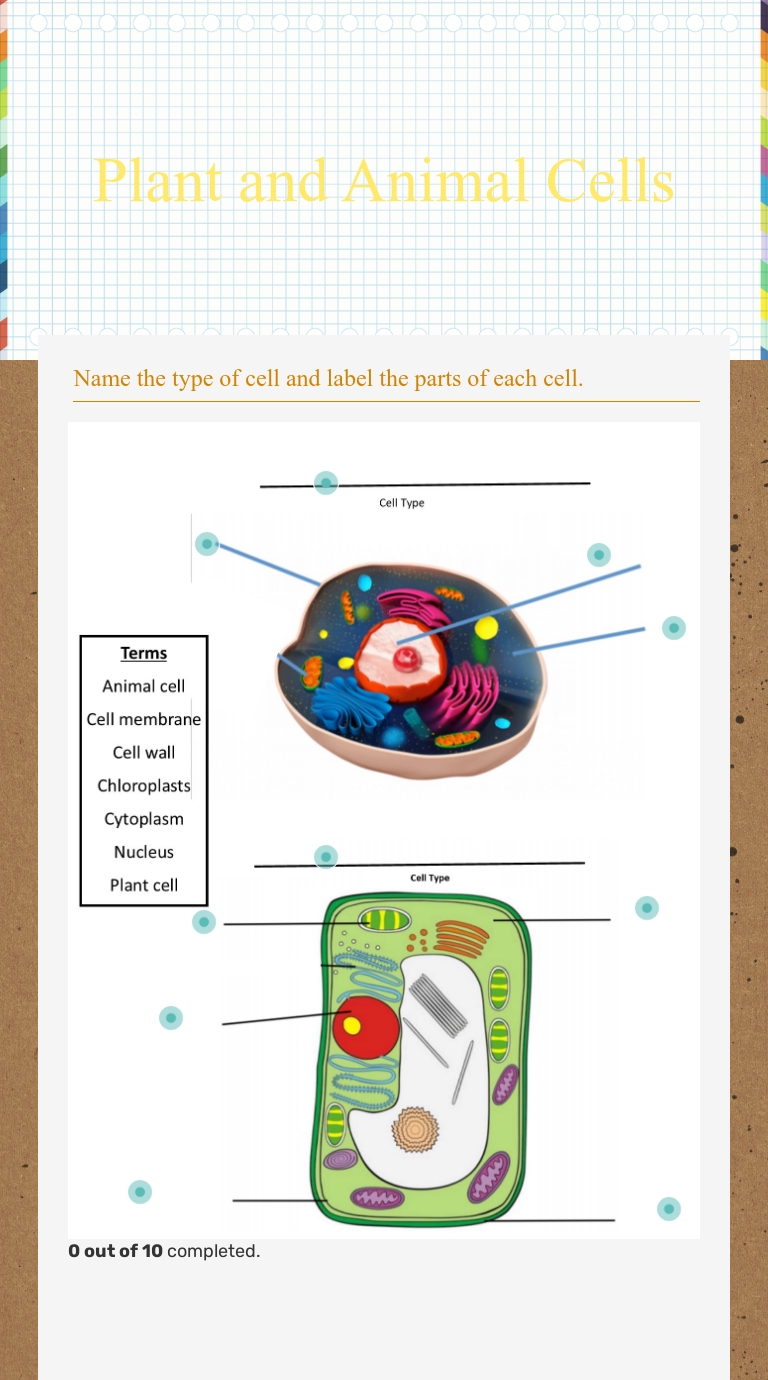
Labeling an Animal Cell Diagram
Now that we have explored the different components of an animal cell, let’s practice labeling an animal cell diagram. Here is a simple diagram of an animal cell:

|
|
Label the following structures:
|
📝 Note: You can use the above diagram as a reference to label the structures. You can also use online resources or textbooks to help you label the diagram.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When labeling an animal cell diagram, here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Confusing the nucleus with the nucleolus: The nucleus is the control center of the cell, while the nucleolus is a region within the nucleus where ribosome synthesis occurs.
- Misidentifying the mitochondria: Mitochondria are often mistaken for other organelles, such as lysosomes or peroxisomes.
- Forgetting to label the cytoskeleton: The cytoskeleton is an important component of the cell that provides structural support and shape.
Conclusion
In conclusion, labeling an animal cell diagram requires a good understanding of the different components of the cell and their functions. By practicing labeling diagrams, you can improve your knowledge of cell biology and develop your critical thinking skills. Remember to avoid common mistakes and use online resources or textbooks to help you label the diagram accurately.
What is the function of the plasma membrane?
+The plasma membrane is a semi-permeable membrane that separates the cell from its environment and regulates the movement of materials in and out of the cell.
What is the role of the mitochondria in the cell?
+Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell. They generate energy for the cell through a process called cellular respiration.
What is the difference between the nucleus and the nucleolus?
+The nucleus is the control center of the cell, while the nucleolus is a region within the nucleus where ribosome synthesis occurs.
Related Terms:
- Animal cell labeling worksheet PDF
- Animal cell worksheet PDF
- Animal cell Worksheet answers
- Animal cell Labeled
- Cell labeling worksheet answers