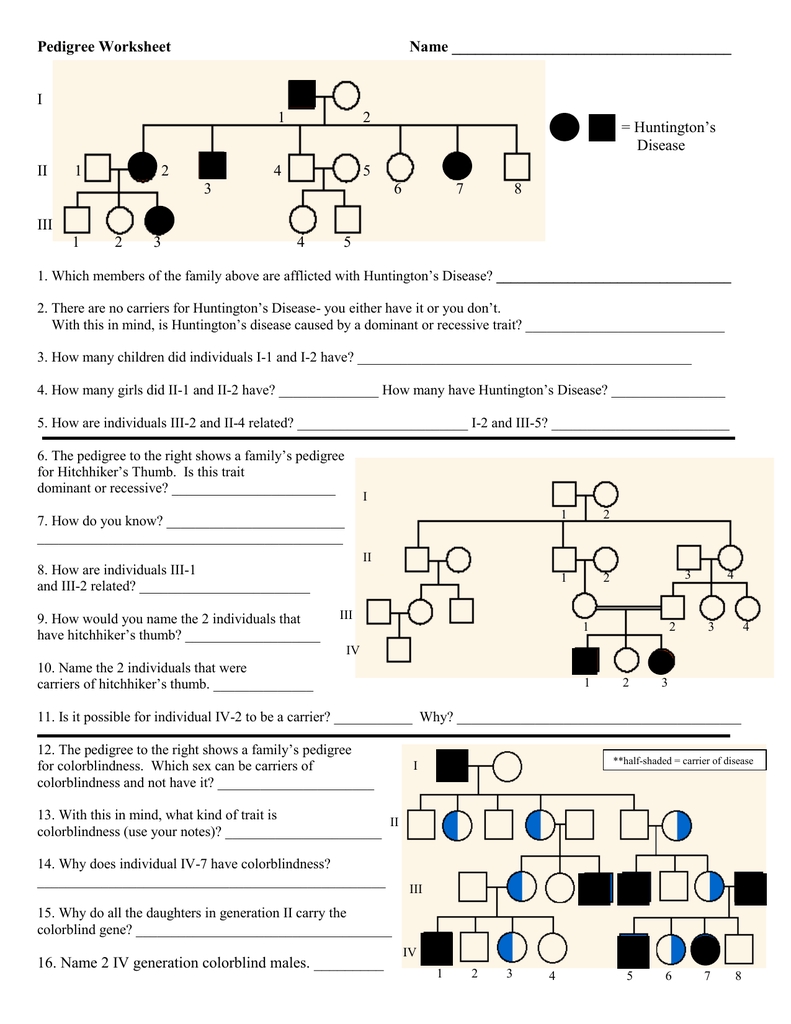
Animal Cell Labeled Worksheet
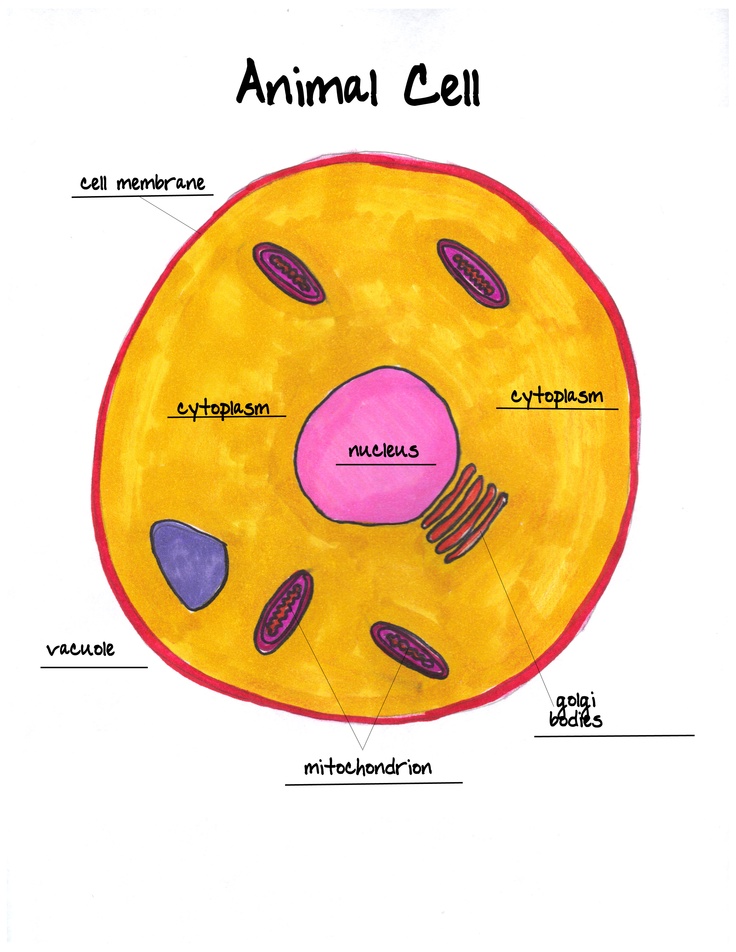
Understanding the Components of an Animal Cell
The animal cell is a fundamental unit of life, and its structure and function are crucial for the survival and operation of living organisms. The cell is a complex entity composed of various organelles, each with specific roles. This article will delve into the components of an animal cell, exploring their functions and importance.
The Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane, also known as the cell membrane, is the outermost layer of the cell that separates the cell from its environment. It is a semi-permeable membrane composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. The plasma membrane regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell, maintains cell shape, and provides a site for cell signaling.
Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance within the cell, comprising about 70% of the cell’s volume. It is a medium for chemical reactions, providing a platform for metabolic processes, such as glycolysis and protein synthesis. Cytoplasm is also responsible for maintaining the cell’s shape, supporting organelles, and facilitating the movement of materials within the cell.
Nucleus
The nucleus is the control center of the cell, containing most of the cell’s genetic material in the form of DNA. It is surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope, which regulates the movement of materials in and out of the nucleus. The nucleus plays a crucial role in cell growth, reproduction, and metabolism, as it contains the instructions for protein synthesis.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell, responsible for generating energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). These organelles are found in the cytoplasm and are involved in cellular respiration, the process of converting glucose into energy.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranous tubules and sacs within the cytoplasm. There are two types of ER: rough ER, which is involved in protein synthesis, and smooth ER, which is involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification.
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles responsible for cellular digestion and recycling. They contain digestive enzymes that break down and recycle cellular waste, such as proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids.
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus is a complex organelle involved in protein modification, sorting, and packaging. It receives proteins synthesized by the ER and modifies them by adding carbohydrates and lipids. The Golgi apparatus also packages proteins into vesicles for transport to other parts of the cell or for secretion outside the cell.
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a network of filaments that provides structural support, shape, and movement to the cell. It is composed of three types of filaments: microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments.
Centrioles
Centrioles are small, cylindrical organelles involved in the formation of cilia, flagella, and the spindle fibers that separate chromosomes during cell division.
Peroxisomes
Peroxisomes are small organelles involved in the breakdown of fatty acids and amino acids. They also play a role in the detoxification of certain substances.
Vacuoles
Vacuoles are membrane-bound organelles that store water, salts, and other substances. They help maintain cell shape and support cellular functions.
| Organelle | Function |
|---|---|
| Plasma Membrane | Regulates movement of substances, maintains cell shape, and provides a site for cell signaling |
| Cytoplasm | Provides a medium for chemical reactions, maintains cell shape, and supports organelles |
| Nucleus | Contains genetic material, regulates cell growth, reproduction, and metabolism |
| Mitochondria | Generates energy in the form of ATP |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) | Involved in protein synthesis, lipid synthesis, and detoxification |
| Lysosomes | Involved in cellular digestion and recycling |
| Golgi Apparatus | Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for transport or secretion |
| Cytoskeleton | Provides structural support, shape, and movement to the cell |
| Centrioles | Involved in the formation of cilia, flagella, and spindle fibers |
| Peroxisomes | Involved in the breakdown of fatty acids and amino acids, and detoxification |
| Vacuoles | Stores water, salts, and other substances, helps maintain cell shape |
🔍 Note: The table above provides a summary of the main organelles and their functions in an animal cell.
In conclusion, the animal cell is a complex entity composed of various organelles, each with specific roles that work together to maintain cellular functions. Understanding the structure and function of these organelles is essential for appreciating the intricate mechanisms of life.
What is the main function of the plasma membrane?
+The main function of the plasma membrane is to regulate the movement of substances in and out of the cell, maintain cell shape, and provide a site for cell signaling.
What is the role of the nucleus in an animal cell?
+The nucleus contains most of the cell’s genetic material in the form of DNA and regulates cell growth, reproduction, and metabolism.
What is the function of mitochondria in an animal cell?
+Mitochondria generate energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) for the cell.
Related Terms:
- Animal cell worksheet
- Animal cell labeling worksheet PDF
- Animal cell Worksheet answers
- Animal cell diagram simple
- Label cell parts quiz
- Animal cell diagram Class 6