Master 10 Essential Anatomical Terms Easily

Understanding Anatomical Terminology: A Key to Medical Success
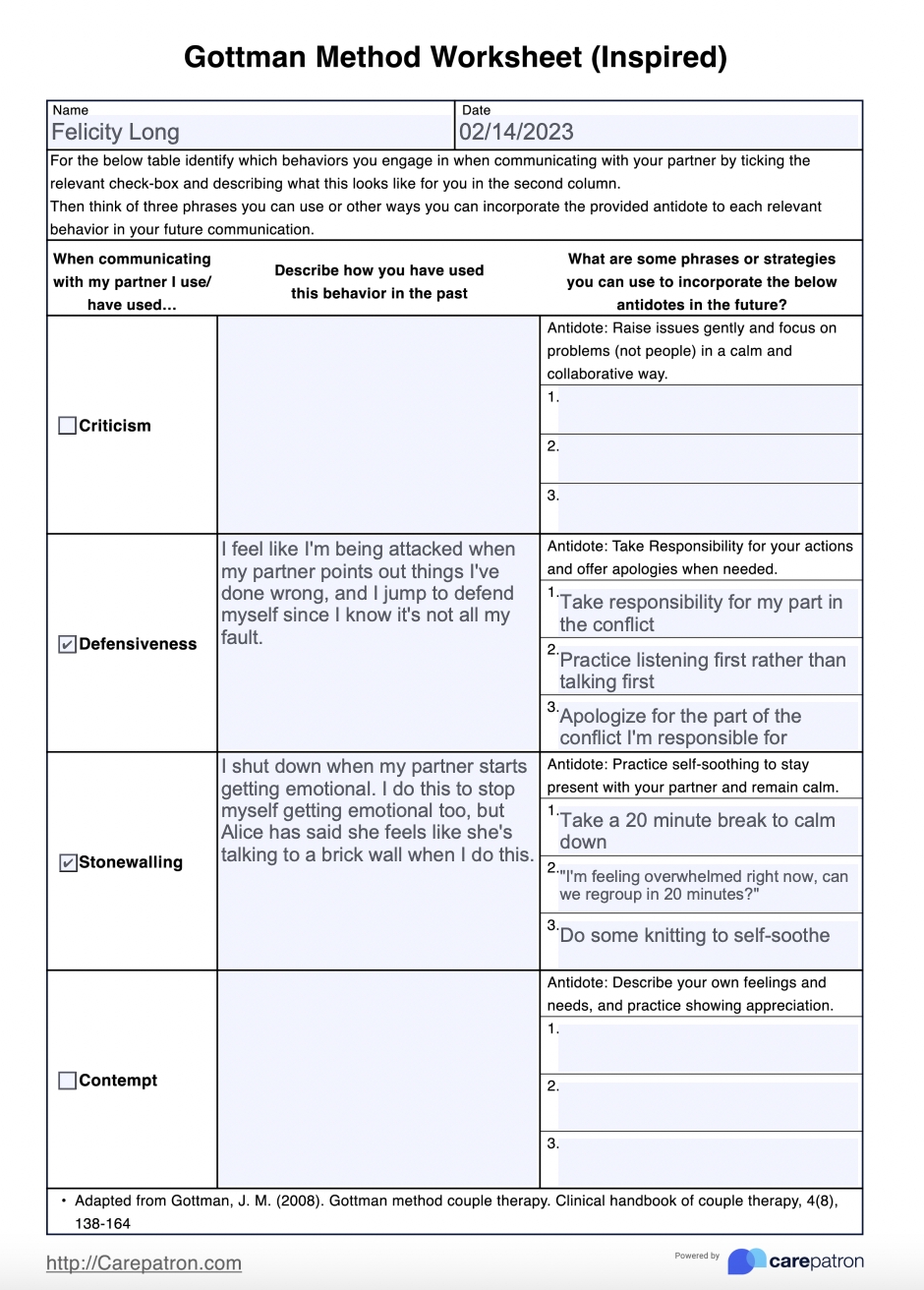
Anatomical terminology is the foundation of medical education. It is used to describe the human body and its various structures, allowing healthcare professionals to communicate effectively and accurately. Mastering anatomical terms can seem daunting, but with the right approach, it can be made easy. In this article, we will explore 10 essential anatomical terms that every medical student or professional should know.
1. Proximal and Distal: Understanding Directional Terms
Directional terms are used to describe the location of structures in relation to each other. Proximal refers to the part of a structure that is closer to the center of the body, while distal refers to the part that is farther away. For example, the proximal end of the femur (thigh bone) is the end that connects to the hip joint, while the distal end is the end that connects to the knee joint.
2. Anterior and Posterior: Understanding Front and Back
Anterior refers to the front of the body or a structure, while posterior refers to the back. For example, the anterior surface of the heart is the front surface, which faces the sternum (breastbone), while the posterior surface is the back surface, which faces the spine.
3. Superior and Inferior: Understanding Top and Bottom
Superior refers to the top or upper part of a structure, while inferior refers to the bottom or lower part. For example, the superior vena cava is a vein that carries blood from the upper body to the heart, while the inferior vena cava carries blood from the lower body to the heart.
4. Medial and Lateral: Understanding Middle and Side
Medial refers to the middle or inner part of a structure, while lateral refers to the side or outer part. For example, the medial meniscus is a cartilage structure in the knee joint that is located on the inner side of the joint, while the lateral meniscus is located on the outer side.
5. Dorsal and Ventral: Understanding Back and Front in the Context of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Dorsal refers to the back or posterior part of the brain and spinal cord, while ventral refers to the front or anterior part. For example, the dorsal horn of the spinal cord is the posterior part of the spinal cord, which receives sensory information from the body, while the ventral horn is the anterior part, which sends motor signals to the muscles.
6. Ipsilateral and Contralateral: Understanding Same-Side and Opposite-Side Relationships
Ipsilateral refers to a relationship between two structures on the same side of the body, while contralateral refers to a relationship between two structures on opposite sides of the body. For example, the left arm and left leg are ipsilateral, while the left arm and right leg are contralateral.
7. Unilateral and Bilateral: Understanding One-Side and Two-Side Relationships
Unilateral refers to a structure or condition that affects only one side of the body, while bilateral refers to a structure or condition that affects both sides of the body. For example, a unilateral injury affects only one side of the body, while a bilateral injury affects both sides.
8. Sagittal, Coronal, and Transverse: Understanding Planes of the Body
The body can be divided into three planes: sagittal, coronal, and transverse.
- Sagittal refers to the plane that divides the body into left and right halves.
- Coronal refers to the plane that divides the body into front and back halves.
- Transverse refers to the plane that divides the body into top and bottom halves.
9. Palmar and Plantar: Understanding Hand and Foot Surfaces
Palmar refers to the surface of the hand, while plantar refers to the surface of the foot. For example, the palmar surface of the hand is the surface that faces downwards, while the plantar surface of the foot is the surface that faces downwards.
10. Prone and Supine: Understanding Body Positions
Prone refers to the position of lying on one’s stomach, while supine refers to the position of lying on one’s back. For example, a patient may be placed in a prone position for a surgical procedure, while a supine position may be used for an examination or diagnostic test.
💡 Note: Mastering anatomical terminology requires practice and repetition. Try to use these terms in context to reinforce your understanding.
In conclusion, mastering anatomical terminology is a crucial step in medical education. By understanding these 10 essential terms, you can improve your communication skills and accurately describe the human body and its various structures. Remember to practice and reinforce your knowledge to become proficient in anatomical terminology.
What is the difference between proximal and distal?
+Proximal refers to the part of a structure that is closer to the center of the body, while distal refers to the part that is farther away.
What is the meaning of sagittal, coronal, and transverse planes?
+The sagittal plane divides the body into left and right halves, the coronal plane divides the body into front and back halves, and the transverse plane divides the body into top and bottom halves.
What is the difference between ipsilateral and contralateral?
+Ipsilateral refers to a relationship between two structures on the same side of the body, while contralateral refers to a relationship between two structures on opposite sides of the body.
Related Terms:
- Anatomical Terminology Worksheet pdf
- Anatomy terminology
- Anatomy terminology quiz
- Anatomy movement pdf