10 Tips to Master Abiotic and Biotic Factors
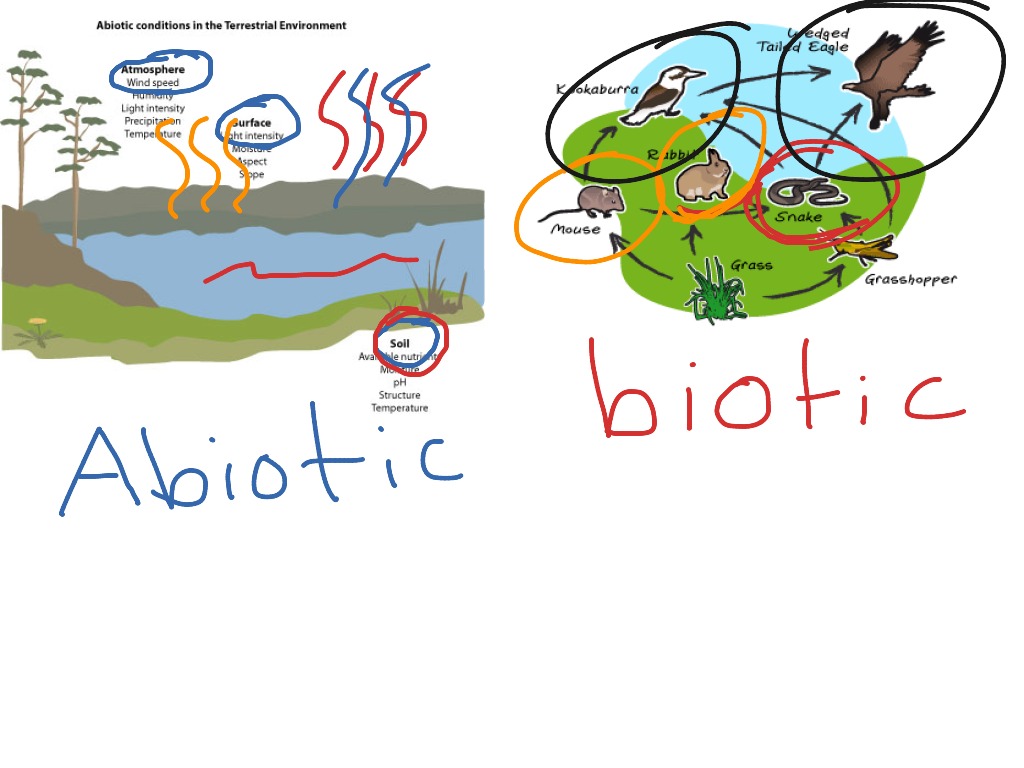
Understanding Abiotic and Biotic Factors in the Environment
The natural world is comprised of a multitude of living and non-living components that interact and influence one another in complex ways. These components can be broadly categorized into two groups: abiotic factors and biotic factors. Abiotic factors refer to non-living components such as light, temperature, water, and soil, while biotic factors encompass living organisms including plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms. Mastering the concepts of abiotic and biotic factors is essential for understanding the intricate relationships within ecosystems and for managing and conserving natural resources effectively.
Tip 1: Identify the Types of Abiotic Factors
Abiotic factors can be broadly classified into several types, including:
- Light: Essential for photosynthesis and influences the growth and distribution of plants.
- Temperature: Affects the metabolic rates of organisms and the availability of water.
- Water: Necessary for all living organisms and plays a crucial role in shaping the landscape.
- Soil: Provides support and nutrients for plants and affects the distribution of organisms.
- Topography: Influences the climate, soil formation, and the distribution of organisms.
Tip 2: Recognize the Importance of Biotic Factors
Biotic factors are living components of the ecosystem that interact with one another and with abiotic factors. These interactions can be categorized into several types, including:
- Predation: One organism feeds on another.
- Competition: Organisms compete for resources such as light, water, and nutrients.
- Symbiosis: Organisms live together in a mutually beneficial relationship.
- Decomposition: Microorganisms break down dead organic matter.
Tip 3: Analyze the Interactions Between Abiotic and Biotic Factors
The interactions between abiotic and biotic factors are complex and multifaceted. For example:
- Climate Change: Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns affect the distribution and abundance of organisms.
- Soil Erosion: Loss of topsoil affects the growth and distribution of plants.
- Pollution: Chemical pollutants can alter the physical environment and affect the health of organisms.
Tip 4: Understand the Concept of Niche
A niche refers to the specific role and position of an organism within its environment. Understanding the concept of niche is essential for recognizing how organisms interact with one another and with abiotic factors.
Tip 5: Learn About the Different Types of Ecosystems
Ecosystems can be broadly classified into several types, including:
- Terrestrial Ecosystems: Forests, grasslands, and deserts.
- Freshwater Ecosystems: Rivers, lakes, and wetlands.
- Marine Ecosystems: Coral reefs, estuaries, and open ocean.
Tip 6: Recognize the Importance of Keystone Species
Keystone species are organisms that play a unique and crucial role in maintaining the structure and function of an ecosystem. Losing a keystone species can have significant cascading effects on the entire ecosystem.
Tip 7: Understand the Concept of Trophic Levels
Trophic levels refer to the position of an organism within a food chain. Understanding trophic levels is essential for recognizing the flow of energy and nutrients within an ecosystem.
Tip 8: Learn About the Different Types of Ecological Pyramids
Ecological pyramids are graphical representations of the trophic structure of an ecosystem. There are several types of ecological pyramids, including:
- Pyramid of Numbers: Represents the number of organisms at each trophic level.
- Pyramid of Biomass: Represents the total biomass of organisms at each trophic level.
- Pyramid of Energy: Represents the flow of energy through the ecosystem.
Tip 9: Understand the Concept of Ecological Succession
Ecological succession refers to the process of change in the composition of an ecosystem over time. Understanding ecological succession is essential for recognizing how ecosystems respond to disturbances and recover from them.
Tip 10: Apply Your Knowledge to Real-World Scenarios
Applying your knowledge of abiotic and biotic factors to real-world scenarios is essential for developing a deeper understanding of the natural world and for managing and conserving natural resources effectively.
🌟 Note: Understanding abiotic and biotic factors is essential for recognizing the complex relationships within ecosystems and for managing and conserving natural resources effectively.
In summary, mastering the concepts of abiotic and biotic factors requires a deep understanding of the interactions between living and non-living components of the environment. By applying these concepts to real-world scenarios, we can develop a deeper appreciation for the natural world and work towards managing and conserving natural resources effectively.
What is the difference between abiotic and biotic factors?
+Abiotic factors refer to non-living components of the environment, such as light, temperature, and soil, while biotic factors encompass living organisms, including plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms.
Why is it important to understand the interactions between abiotic and biotic factors?
+Understanding the interactions between abiotic and biotic factors is essential for recognizing how ecosystems function and respond to disturbances, and for managing and conserving natural resources effectively.
What is a keystone species?
+A keystone species is an organism that plays a unique and crucial role in maintaining the structure and function of an ecosystem. Losing a keystone species can have significant cascading effects on the entire ecosystem.