Solve Linear Equations with 2 Step Equations Worksheet
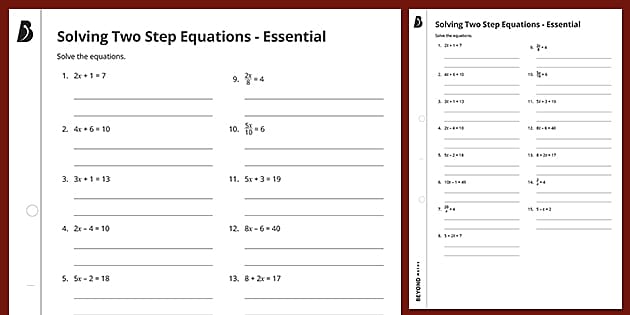
Solving linear equations is a fundamental skill in algebra and is used to solve equations in which the highest power of the variable(s) is 1. In this article, we will focus on 2-step equations, which require two operations to solve.
What are 2-Step Equations?
A 2-step equation is a type of linear equation that requires two operations to solve. These operations can be addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division. The equation has only one variable, and the goal is to isolate the variable on one side of the equation.
Example of a 2-Step Equation
Here is an example of a 2-step equation:
2x + 5 = 11
To solve this equation, we need to perform two operations: subtraction and division.
Step 1: Subtract 5 from both sides
Subtracting 5 from both sides of the equation gives us:
2x = 11 - 5 2x = 6
📝 Note: When subtracting 5 from both sides, we are essentially isolating the term with the variable (2x) on one side of the equation.
Step 2: Divide both sides by 2
Dividing both sides of the equation by 2 gives us:
x = 6 ÷ 2 x = 3
📝 Note: When dividing both sides by 2, we are essentially solving for the variable (x) and finding its value.
How to Solve 2-Step Equations
To solve 2-step equations, follow these steps:
- Identify the operations needed to solve the equation.
- Perform the first operation to isolate the term with the variable.
- Perform the second operation to solve for the variable.
Common Operations in 2-Step Equations
Here are some common operations you may encounter in 2-step equations:
- Addition and subtraction
- Multiplication and division
- Addition and multiplication
- Subtraction and division
Examples of 2-Step Equations
Here are some more examples of 2-step equations:
- x + 2 = 7 (solution: x = 5)
- 3x - 4 = 11 (solution: x = 5)
- 2x + 3 = 9 (solution: x = 3)
- x - 2 = 4 (solution: x = 6)
2-Step Equations with Negative Numbers
When working with 2-step equations with negative numbers, be careful with the signs. Remember to distribute the negative sign when subtracting or multiplying both sides of the equation.
Example:
-x + 2 = 5
To solve this equation, we need to perform two operations: subtraction and multiplication.
- Subtract 2 from both sides:
-x = 5 - 2 -x = 3
- Multiply both sides by -1:
x = -3
📝 Note: When working with negative numbers, make sure to distribute the negative sign correctly.
Conclusion
Solving 2-step equations requires a solid understanding of basic algebraic operations and the ability to follow a logical sequence of steps. By following the steps outlined in this article and practicing with examples, you can become proficient in solving 2-step equations.
What is a 2-step equation?
+A 2-step equation is a type of linear equation that requires two operations to solve. These operations can be addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division.
How do I solve a 2-step equation?
+To solve a 2-step equation, follow these steps: 1) identify the operations needed to solve the equation, 2) perform the first operation to isolate the term with the variable, and 3) perform the second operation to solve for the variable.
What are some common operations in 2-step equations?
+Some common operations in 2-step equations include addition and subtraction, multiplication and division, addition and multiplication, and subtraction and division.
Related Terms:
- 3 step Equations Worksheet
- Multi Step Equations Worksheet
- One step Equations Worksheet