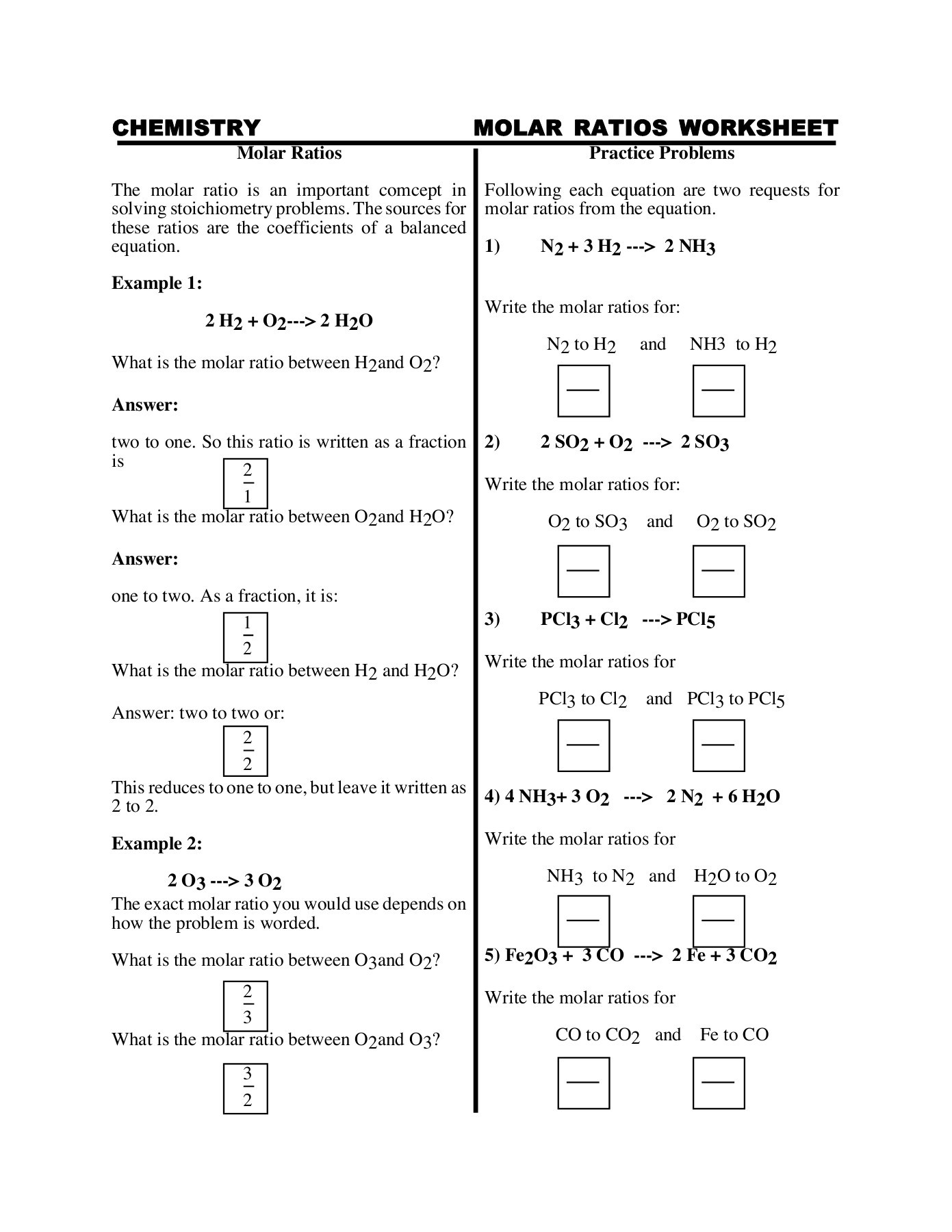
Master the Ideal Gas Law with this Essential Worksheet

The Ideal Gas Law is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics that describes the behavior of gases. It’s a crucial formula to understand, and with this worksheet, you’ll be able to master it in no time. So, let’s dive in!
Understanding the Ideal Gas Law
The Ideal Gas Law is a mathematical relationship that describes the behavior of ideal gases. It’s a combination of three gas laws: Boyle’s Law, Charles’ Law, and Avogadro’s Law. The law states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles of gas, and inversely proportional to the pressure and temperature.
The Ideal Gas Law is represented by the equation:
PV = nRT
Where:
- P is the pressure of the gas
- V is the volume of the gas
- n is the number of moles of gas
- R is the gas constant
- T is the temperature of the gas in Kelvin
Key Concepts to Remember
Before we move on to the worksheet, let’s review some key concepts to keep in mind:
- Pressure: The force exerted on a surface by a gas.
- Volume: The amount of space occupied by a gas.
- Moles: A unit of measurement for the amount of a substance.
- Temperature: The measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a gas.
- Gas Constant: A constant value that relates the pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas.
Worksheet
Now that we’ve reviewed the key concepts, let’s move on to the worksheet. This worksheet is designed to help you practice applying the Ideal Gas Law to different problems. There are five problems in total, and each problem requires you to use the Ideal Gas Law to solve for a different variable.
Problem 1:
A sample of gas has a pressure of 2.5 atm, a volume of 1.2 L, and a temperature of 300 K. How many moles of gas are present?
Solution: Use the Ideal Gas Law to solve for n.
PV = nRT (2.5 atm)(1.2 L) = n(0.0821 L atm/mol K)(300 K) n = 0.12 mol
Problem 2:
A gas has a volume of 2.5 L, a temperature of 250 K, and 0.05 mol of gas present. What is the pressure of the gas?
Solution: Use the Ideal Gas Law to solve for P.
PV = nRT P(2.5 L) = (0.05 mol)(0.0821 L atm/mol K)(250 K) P = 1.02 atm
Problem 3:
A sample of gas has a pressure of 1.5 atm, a temperature of 200 K, and 0.1 mol of gas present. What is the volume of the gas?
Solution: Use the Ideal Gas Law to solve for V.
PV = nRT (1.5 atm)V = (0.1 mol)(0.0821 L atm/mol K)(200 K) V = 2.05 L
Problem 4:
A gas has a volume of 1.8 L, a pressure of 2.2 atm, and a temperature of 300 K. How many moles of gas are present?
Solution: Use the Ideal Gas Law to solve for n.
PV = nRT (2.2 atm)(1.8 L) = n(0.0821 L atm/mol K)(300 K) n = 0.16 mol
Problem 5:
A sample of gas has a temperature of 250 K, a volume of 2.2 L, and 0.12 mol of gas present. What is the pressure of the gas?
Solution: Use the Ideal Gas Law to solve for P.
PV = nRT P(2.2 L) = (0.12 mol)(0.0821 L atm/mol K)(250 K) P = 1.33 atm
Notes
- Make sure to use the correct units for each variable.
- Pay attention to the signs of the variables, as they can affect the direction of the calculation.
- Use the gas constant ® in the correct units (L atm/mol K).
Table of Gas Constants
| Gas Constant | Units |
|---|---|
| R | 0.0821 L atm/mol K |
| R | 8.3145 J/mol K |
Conclusion
Mastering the Ideal Gas Law takes practice, but with this worksheet, you’ve taken the first step towards becoming a pro! Remember to always use the correct units and pay attention to the signs of the variables. With time and practice, you’ll be able to apply the Ideal Gas Law to any problem that comes your way.
What is the Ideal Gas Law?
+The Ideal Gas Law is a mathematical relationship that describes the behavior of ideal gases. It’s a combination of three gas laws: Boyle’s Law, Charles’ Law, and Avogadro’s Law.
What is the gas constant?
+The gas constant is a constant value that relates the pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas. It’s represented by the symbol R and has a value of 0.0821 L atm/mol K.
How do I use the Ideal Gas Law to solve problems?
+To use the Ideal Gas Law to solve problems, simply plug in the values for the variables and solve for the unknown variable. Make sure to use the correct units and pay attention to the signs of the variables.
Related Terms:
- Ideal gas Law Practice worksheet
- Combined gas Law pdf
- Ideal gas law test
- Ideal gas law conceptual questions