Molar Ratios Made Easy: Balancing Chemical Equations
Understanding Molar Ratios and Their Importance in Balancing Chemical Equations
Chemical equations are a crucial part of chemistry, representing the reaction between substances. However, to accurately represent these reactions, chemists must ensure that the equations are balanced. This is where molar ratios come into play. Molar ratios are the proportions of reactants and products in a balanced chemical equation. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of molar ratios, explaining their importance and providing a step-by-step guide on how to use them to balance chemical equations.
What are Molar Ratios?
Molar ratios are the ratios of the number of moles of reactants to the number of moles of products in a balanced chemical equation. They are essential in chemistry because they help us understand the quantities of reactants required to produce a specific amount of product. Molar ratios are calculated by dividing the number of moles of a reactant or product by the number of moles of another reactant or product.
Why are Molar Ratios Important?
Molar ratios are crucial in balancing chemical equations because they ensure that the law of conservation of mass is obeyed. This law states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. By using molar ratios, chemists can ensure that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both the reactant and product sides of the equation.
How to Balance Chemical Equations Using Molar Ratios
Balancing chemical equations using molar ratios involves several steps:
- Write the unbalanced equation.
- Count the number of atoms of each element on both the reactant and product sides.
- Use molar ratios to balance the equation.
Here’s an example:
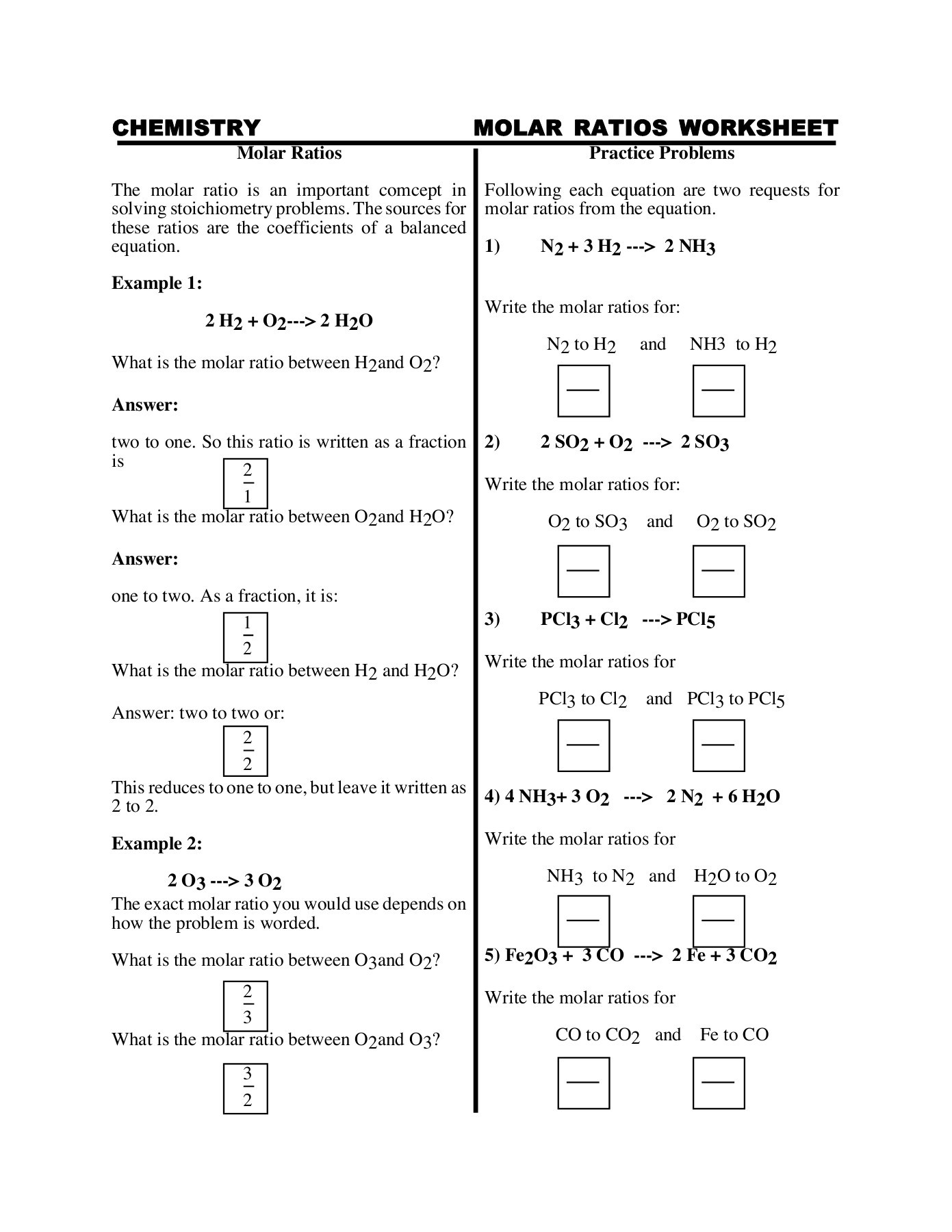
Unbalanced Equation: H2 + O2 → H2O
- Count the number of atoms of each element:
| Element | Reactants | Products |
|---|---|---|
| H | 2 | 2 |
| O | 2 | 1 |
- Use molar ratios to balance the equation:
Balanced Equation: 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
In this example, the molar ratio of H2 to O2 is 2:1. This means that for every 2 moles of H2, 1 mole of O2 is required to produce 2 moles of H2O.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Molar Ratios
When using molar ratios to balance chemical equations, there are several common mistakes to avoid:
- Not counting the number of atoms correctly: Make sure to count the number of atoms of each element on both the reactant and product sides.
- Not using the correct molar ratios: Ensure that you use the correct molar ratios to balance the equation.
- Adding or removing atoms incorrectly: Avoid adding or removing atoms from the equation. Instead, use coefficients to balance the equation.
⚠️ Note: Molar ratios can be used to balance complex chemical equations, but they require a good understanding of chemistry and algebra.
Conclusion
Molar ratios are a powerful tool in chemistry, allowing us to balance chemical equations and ensure that the law of conservation of mass is obeyed. By understanding how to use molar ratios, chemists can accurately represent chemical reactions and predict the quantities of reactants required to produce a specific amount of product.
Molar ratios are not just important in balancing chemical equations; they also have real-world applications in fields such as engineering, medicine, and environmental science. By mastering the use of molar ratios, chemists can unlock new discoveries and innovations that can benefit society.
What is the difference between a molar ratio and a mole ratio?
+A molar ratio and a mole ratio are often used interchangeably, but they have slightly different meanings. A molar ratio refers to the ratio of the number of moles of reactants to the number of moles of products in a balanced chemical equation. A mole ratio, on the other hand, refers to the ratio of the number of moles of one substance to the number of moles of another substance.
Can molar ratios be used to balance complex chemical equations?
+Yes, molar ratios can be used to balance complex chemical equations. However, they require a good understanding of chemistry and algebra. Molar ratios can be used to balance equations with multiple reactants and products, as well as equations with coefficients.
What are some common applications of molar ratios?
+Molar ratios have several common applications, including balancing chemical equations, predicting the quantities of reactants required to produce a specific amount of product, and calculating the yields of chemical reactions. They are also used in fields such as engineering, medicine, and environmental science.
Related Terms:
- Mole ratio Worksheet with Answers
- Stoichiometry Worksheet
- Mole Ratio Worksheet pdf answers
- Molar ratio practice problems
- Stoichiometry Practice Worksheet with answers
- Stoichiometry test with answers pdf