Slope Intercept Form Worksheet with Simple Equations
Understanding the Slope-Intercept Form
The slope-intercept form is a fundamental concept in algebra, used to represent linear equations in a simple and intuitive way. This form is widely used in various fields, including physics, engineering, and economics, to model real-world phenomena. In this article, we will delve into the world of slope-intercept form, explore its basics, and provide a worksheet with simple equations for practice.
What is the Slope-Intercept Form?
The slope-intercept form is a way of writing a linear equation in the form:
y = mx + b
Where:
- y is the dependent variable (the output)
- m is the slope (a measure of how steep the line is)
- x is the independent variable (the input)
- b is the y-intercept (the point where the line crosses the y-axis)
This form is useful because it allows us to easily identify the slope and y-intercept of a line, which can be used to graph the line, make predictions, and analyze the relationship between variables.
How to Graph a Line in Slope-Intercept Form
Graphing a line in slope-intercept form is straightforward. Here are the steps:
- Plot the y-intercept (b) on the y-axis.
- Use the slope (m) to determine the direction and steepness of the line. A positive slope indicates a line that slopes upward from left to right, while a negative slope indicates a line that slopes downward from left to right.
- Use the slope to plot additional points on the line. For example, if the slope is 2, you can plot a point 2 units up and 1 unit to the right of the y-intercept.
Simple Equations in Slope-Intercept Form
Here are a few simple equations in slope-intercept form:
- y = 2x + 3 (slope = 2, y-intercept = 3)
- y = -1x - 2 (slope = -1, y-intercept = -2)
- y = 0.5x + 1 (slope = 0.5, y-intercept = 1)
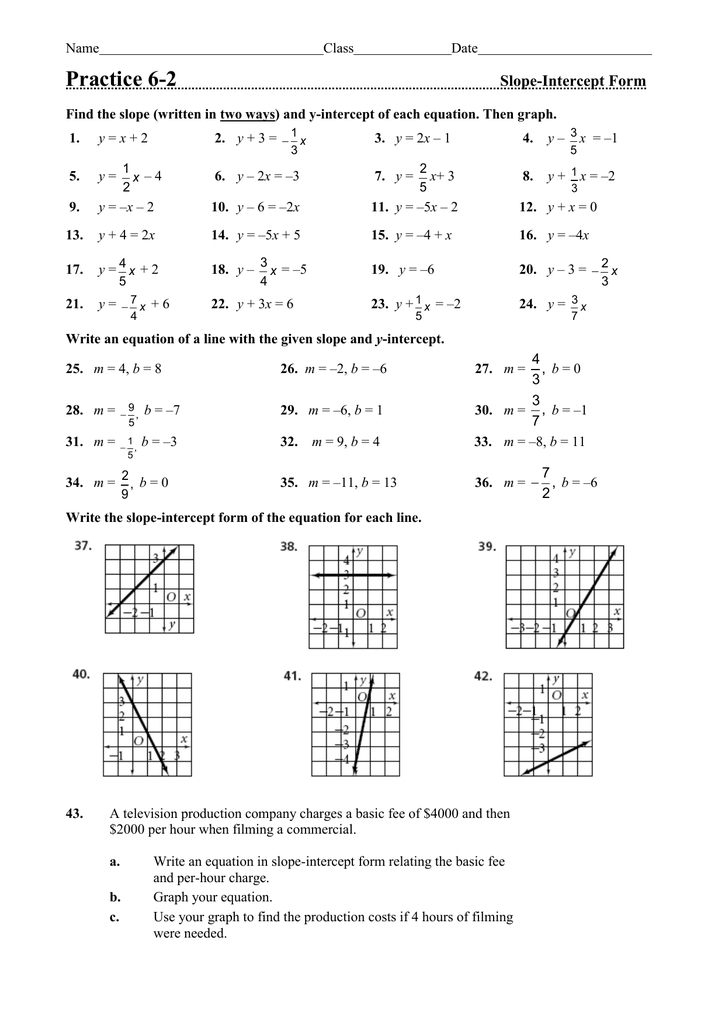
Worksheet: Simple Equations in Slope-Intercept Form
Practice your skills by working through the following worksheet:
| Equation | Slope (m) | y-Intercept (b) |
|---|---|---|
| y = 3x - 2 | ____________ | ____________ |
| y = -2x + 1 | ____________ | ____________ |
| y = 0.75x - 3 | ____________ | ____________ |
| y = x + 2 | ____________ | ____________ |
| y = -4x - 1 | ____________ | ____________ |
Solutions
- y = 3x - 2: Slope (m) = 3, y-Intercept (b) = -2
- y = -2x + 1: Slope (m) = -2, y-Intercept (b) = 1
- y = 0.75x - 3: Slope (m) = 0.75, y-Intercept (b) = -3
- y = x + 2: Slope (m) = 1, y-Intercept (b) = 2
- y = -4x - 1: Slope (m) = -4, y-Intercept (b) = -1
📝 Note: Remember to always check your work and use the slope-intercept form to graph the lines and verify your answers.
In conclusion, the slope-intercept form is a powerful tool for representing linear equations and graphing lines. With practice and patience, you can become proficient in using this form to analyze and solve problems in algebra and beyond.
What is the slope-intercept form?
+The slope-intercept form is a way of writing a linear equation in the form y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
How do I graph a line in slope-intercept form?
+To graph a line in slope-intercept form, plot the y-intercept on the y-axis, use the slope to determine the direction and steepness of the line, and plot additional points using the slope.
What is the slope of the line y = 2x + 3?
+The slope of the line y = 2x + 3 is 2.