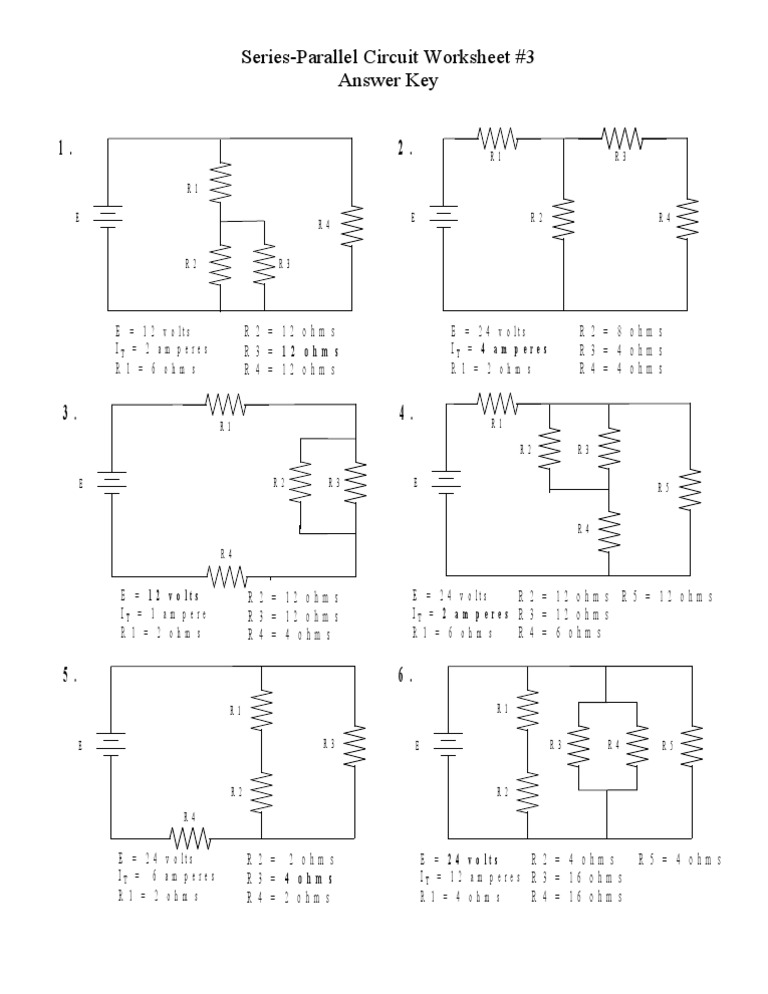
Series Circuit Problems and Solutions Worksheet

Understanding Series Circuits: Problems and Solutions
Series circuits are a fundamental concept in electronics, and understanding how to analyze and solve problems related to them is crucial for any student or professional in the field. In this article, we will delve into the world of series circuits, exploring their characteristics, and providing a comprehensive worksheet with problems and solutions to help you master this topic.
What is a Series Circuit?
A series circuit is a type of electrical circuit where components are connected one after the other, with each component having only two nodes. This means that there is only one path for current to flow through the circuit. Series circuits are commonly used in applications such as voltage dividers, voltage regulators, and alarm systems.
Characteristics of Series Circuits
Series circuits have several key characteristics that distinguish them from parallel circuits:
- Current is the same throughout the circuit: Since there is only one path for current to flow, the current is the same at all points in the circuit.
- Voltage is divided among components: The total voltage applied to the circuit is divided among the individual components, with each component having a specific voltage drop.
- Resistance is additive: The total resistance of the circuit is the sum of the individual resistances of each component.
Series Circuit Problems and Solutions Worksheet
Here are five problems to help you practice analyzing and solving series circuit problems. Take your time, and work through each problem carefully.
Problem 1: Find the total resistance and total voltage of the circuit below.
| Component | Resistance (Ω) |
|---|---|
| R1 | 10 |
| R2 | 20 |
| R3 | 30 |
Solution: Total resistance (Rt) = R1 + R2 + R3 = 10 + 20 + 30 = 60 Ω
Total voltage (Vt) = V1 + V2 + V3 = 10V + 20V + 30V = 60V
Problem 2: A series circuit consists of three resistors with values of 5 Ω, 10 Ω, and 15 Ω. If a 12V power source is applied to the circuit, find the current flowing through each resistor.
Solution: First, find the total resistance: Rt = 5 + 10 + 15 = 30 Ω
Next, find the current: I = V/Rt = 12V / 30Ω = 0.4A
Since the current is the same throughout the circuit, the current flowing through each resistor is also 0.4A.
Problem 3: A series circuit consists of two resistors with values of 2 kΩ and 3 kΩ. If a 9V power source is applied to the circuit, find the voltage drop across each resistor.
Solution: First, find the total resistance: Rt = 2k + 3k = 5kΩ
Next, find the current: I = V/Rt = 9V / 5kΩ = 0.0018A
Now, find the voltage drop across each resistor:
V1 = I x R1 = 0.0018A x 2kΩ = 3.6V
V2 = I x R2 = 0.0018A x 3kΩ = 5.4V
Problem 4: A series circuit consists of three resistors with values of 1 Ω, 2 Ω, and 3 Ω. If a 15V power source is applied to the circuit, find the power dissipated by each resistor.
Solution: First, find the total resistance: Rt = 1 + 2 + 3 = 6 Ω
Next, find the current: I = V/Rt = 15V / 6Ω = 2.5A
Now, find the power dissipated by each resistor:
P1 = I^2 x R1 = (2.5A)^2 x 1Ω = 6.25W
P2 = I^2 x R2 = (2.5A)^2 x 2Ω = 12.5W
P3 = I^2 x R3 = (2.5A)^2 x 3Ω = 18.75W
Problem 5: A series circuit consists of two resistors with values of 10 kΩ and 20 kΩ. If a 24V power source is applied to the circuit, find the voltage drop across each resistor.
Solution: First, find the total resistance: Rt = 10k + 20k = 30kΩ
Next, find the current: I = V/Rt = 24V / 30kΩ = 0.0008A
Now, find the voltage drop across each resistor:
V1 = I x R1 = 0.0008A x 10kΩ = 8V
V2 = I x R2 = 0.0008A x 20kΩ = 16V
💡 Note: Remember to always follow the order of operations (PEMDAS) when solving circuit problems, and make sure to label your units correctly.
By working through these problems, you should now have a better understanding of how to analyze and solve series circuit problems. Remember to always apply the fundamental principles of series circuits, including the fact that current is the same throughout the circuit, voltage is divided among components, and resistance is additive.
In the next section, we will summarize the key points from this article, and provide a final thoughts section to help you reinforce your understanding of series circuits.
To reinforce your understanding of series circuits, try to solve the following problems on your own:
- Find the total resistance and total voltage of a series circuit consisting of three resistors with values of 15 Ω, 25 Ω, and 35 Ω.
- A series circuit consists of two resistors with values of 1 kΩ and 2 kΩ. If a 12V power source is applied to the circuit, find the current flowing through each resistor.
Take your time, and work through each problem carefully. Good luck!
What is the main characteristic of a series circuit?
+The main characteristic of a series circuit is that current is the same throughout the circuit.
How do you find the total resistance of a series circuit?
+The total resistance of a series circuit is found by adding the individual resistances of each component.
What is the voltage drop across each resistor in a series circuit?
+The voltage drop across each resistor in a series circuit is found by multiplying the current flowing through the resistor by the resistance of the resistor.
Related Terms:
- Series circuit Worksheet pdf