Worksheet Dna Replication
Understanding DNA Replication: A Comprehensive Guide
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an exact copy of its DNA before cell division. This process is crucial for the transmission of genetic information from one generation of cells to the next. In this article, we will delve into the world of DNA replication, exploring the key steps, enzymes, and mechanisms involved.
The Importance of DNA Replication
DNA replication is essential for the survival and propagation of living organisms. Without it, cells would not be able to divide, and the genetic information necessary for the development and function of organisms would be lost. DNA replication ensures that the genetic material is duplicated accurately, allowing cells to maintain their genetic integrity.
The DNA Replication Process
The DNA replication process involves several key steps:
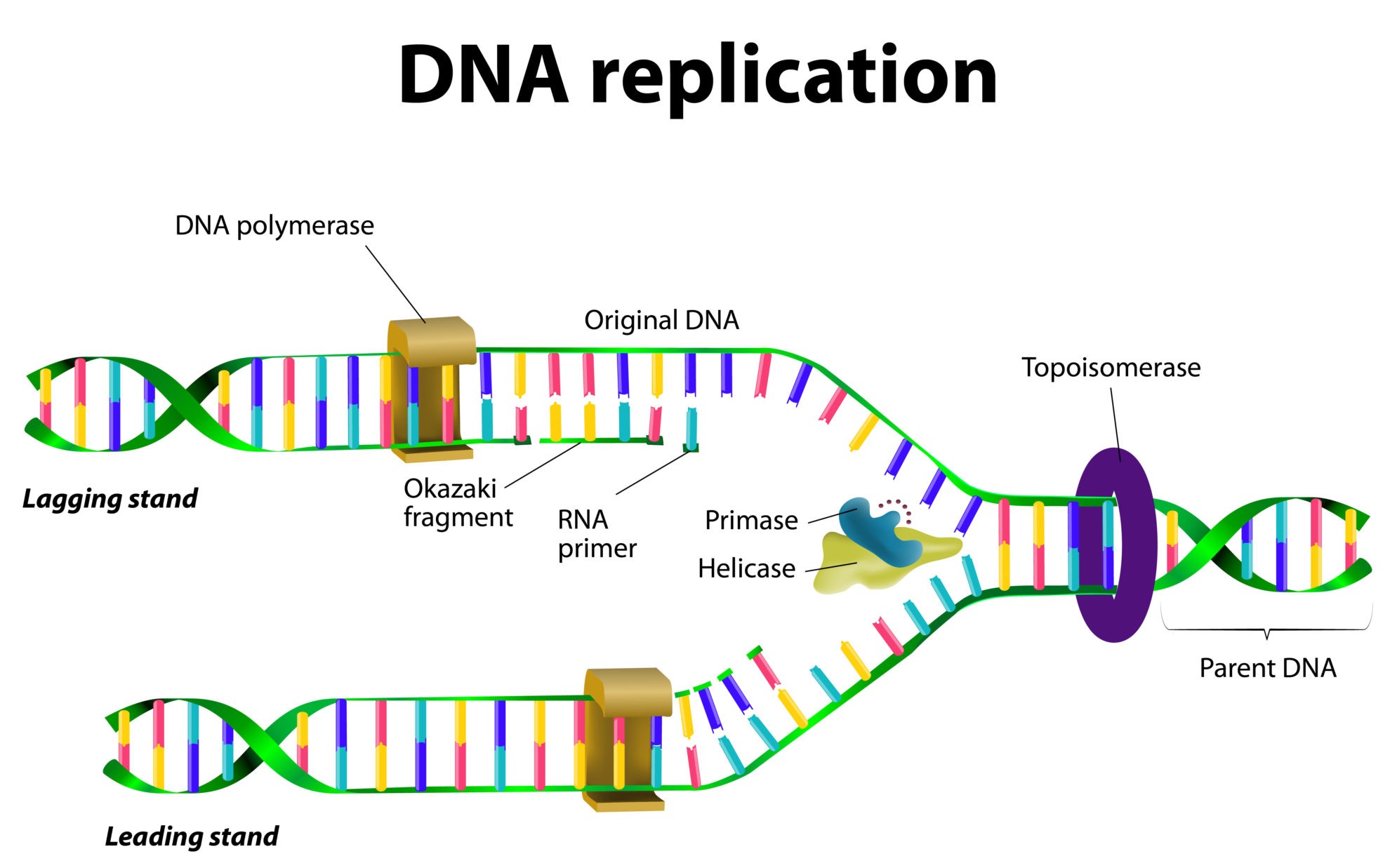
- Initiation: The process of DNA replication begins with the unwinding of the double helix structure of DNA. This is achieved by an enzyme called helicase, which breaks the hydrogen bonds between the two strands of DNA.
- Unwinding: As the DNA is unwound, another enzyme called topoisomerase relaxes the tension in the DNA molecule by cutting and rejoining it.
- Synthesis: The synthesis of new DNA strands occurs simultaneously on both the leading and lagging strands. The leading strand is synthesized continuously, while the lagging strand is synthesized in short, discontinuous segments called Okazaki fragments.
- Elongation: The elongation phase involves the addition of nucleotides to the growing DNA strands. This is carried out by an enzyme called DNA polymerase, which matches the incoming nucleotides to the base pairing rules (A-T and G-C).
- Ligation: Once the Okazaki fragments are synthesized, they are joined together by an enzyme called DNA ligase to form a continuous strand.
Key Enzymes Involved in DNA Replication
Several key enzymes play crucial roles in the DNA replication process:
- Helicase: Unwinds the double helix structure of DNA.
- Topoisomerase: Relaxes the tension in the DNA molecule by cutting and rejoining it.
- DNA polymerase: Synthesizes new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to the growing strands.
- DNA ligase: Joins Okazaki fragments together to form a continuous strand.
Mechanisms of DNA Replication
The mechanisms of DNA replication involve the coordination of multiple enzymes and proteins. Some of the key mechanisms include:
- Semiconservative replication: The process of DNA replication results in two daughter DNA molecules, each consisting of one old strand (the template strand) and one newly synthesized strand.
- Leading strand synthesis: The leading strand is synthesized continuously, while the lagging strand is synthesized in short, discontinuous segments.
- Okazaki fragment synthesis: The lagging strand is synthesized in short segments called Okazaki fragments, which are later joined together by DNA ligase.
| Enzyme | Function |
|---|---|
| Helicase | Unwinds the double helix structure of DNA |
| Topoisomerase | Relaxes the tension in the DNA molecule by cutting and rejoining it |
| DNA polymerase | Synthesizes new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to the growing strands |
| DNA ligase | Joins Okazaki fragments together to form a continuous strand |
💡 Note: The DNA replication process is a complex and highly regulated process that involves the coordination of multiple enzymes and proteins.
As we have seen, DNA replication is a crucial process that ensures the transmission of genetic information from one generation of cells to the next. Understanding the key steps, enzymes, and mechanisms involved in DNA replication is essential for appreciating the complexity and beauty of this process.
What is the purpose of DNA replication?
+The purpose of DNA replication is to create an exact copy of the cell’s DNA before cell division, ensuring that the genetic information is transmitted accurately to the daughter cells.
What is the role of helicase in DNA replication?
+Helicase is an enzyme that unwinds the double helix structure of DNA, creating a replication fork that allows the replication process to begin.
What is the difference between the leading strand and the lagging strand?
+The leading strand is synthesized continuously, while the lagging strand is synthesized in short, discontinuous segments called Okazaki fragments.