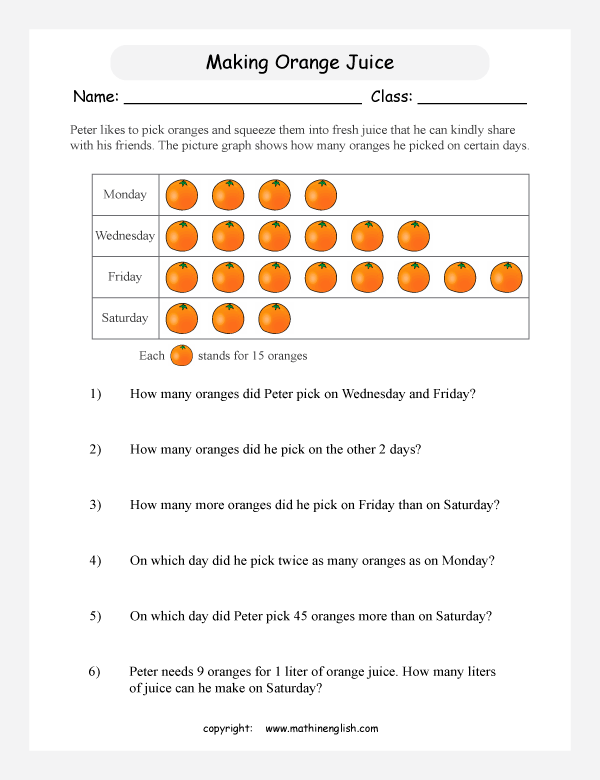
Worksheet Dihybrid Crosses

Understanding Dihybrid Crosses: A Comprehensive Guide
In the realm of genetics, dihybrid crosses play a crucial role in understanding the inheritance of traits. This concept, first introduced by Gregor Mendel, is essential for grasping the fundamental principles of genetics. In this article, we will delve into the world of dihybrid crosses, exploring the concept, its importance, and how to solve dihybrid cross problems.
What are Dihybrid Crosses?
A dihybrid cross is a type of genetic cross that involves the study of two different genes, each with two alleles (forms). This cross is used to investigate how these genes interact and influence the expression of traits in offspring. In a dihybrid cross, two parents are crossed, each contributing one allele for each of the two genes being studied.
Key Concepts in Dihybrid Crosses
Before diving into the world of dihybrid crosses, it’s essential to understand some key concepts:
- Genotype: The genetic makeup of an organism, consisting of the specific set of genes it possesses.
- Phenotype: The physical appearance or trait expressed by an organism, resulting from its genotype.
- Allele: A variant of a gene that occupies a specific location on a chromosome.
- Dominant: An allele that will be expressed if an individual has one or two copies of the allele.
- Recessive: An allele that will only be expressed if an individual has two copies of the allele.
How to Solve Dihybrid Cross Problems
Solving dihybrid cross problems involves several steps:
- Determine the genotype of the parents: Identify the alleles each parent contributes to the cross.
- Determine the possible genotypes of the offspring: Use a Punnett square to predict the possible genotypes of the offspring.
- Determine the phenotype of the offspring: Use the genotype of the offspring to predict their phenotype.
🤔 Note: A Punnett square is a diagram used to predict the probability of different genotypes and phenotypes in offspring.
Example Problem: Solving a Dihybrid Cross
Let’s consider a dihybrid cross between two pea plants. We want to study the inheritance of two genes: one for flower color (R = red, r = white) and one for plant height (T = tall, t = short). The genotype of the parents is:
Parent 1: RrTt Parent 2: rrTt
Using a Punnett square, we can predict the possible genotypes of the offspring:

| R | r | |
|---|---|---|
| T | RT | rT |
| t | Rt | rt |
The possible genotypes of the offspring are: RT, rT, Rt, and rt.
Now, let’s determine the phenotype of the offspring:
- RT: Red, tall
- rT: White, tall
- Rt: Red, short
- rt: White, short
By analyzing the Punnett square and the genotype of the offspring, we can predict the probability of each phenotype.
| Phenotype | Probability |
|---|---|
| Red, tall | 25% |
| White, tall | 25% |
| Red, short | 25% |
| White, short | 25% |
As we can see, each phenotype has a 25% probability of occurring.
Conclusion
Dihybrid crosses are a fundamental concept in genetics, allowing us to understand the inheritance of traits and how genes interact. By following the steps outlined in this article and using tools like Punnett squares, we can solve dihybrid cross problems and predict the probability of different phenotypes in offspring. Whether you’re a student or a researcher, mastering dihybrid crosses will help you grasp the intricacies of genetics and unlock new insights into the fascinating world of life.
What is the purpose of a dihybrid cross?
+A dihybrid cross is used to study the inheritance of two different genes and how they interact to influence the expression of traits in offspring.
What is a Punnett square, and how is it used?
+A Punnett square is a diagram used to predict the probability of different genotypes and phenotypes in offspring. It is used to solve dihybrid cross problems and predict the outcome of genetic crosses.
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
+Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an organism, consisting of the specific set of genes it possesses. Phenotype refers to the physical appearance or trait expressed by an organism, resulting from its genotype.
Related Terms:
- Worksheet dihybrid crosses answer key
- Dihybrid cross Worksheet PDF
- Dihybrid cross exercises with answers