Chemical Bonding: Ionic and Covalent Explained
Understanding Chemical Bonding: Ionic and Covalent Explained
Chemical bonding is a fundamental concept in chemistry that explains how atoms share or exchange electrons to form molecules. It is a crucial aspect of chemistry that helps us understand the properties and behavior of molecules. In this article, we will delve into the two main types of chemical bonds: ionic and covalent bonds.
What are Ionic Bonds?
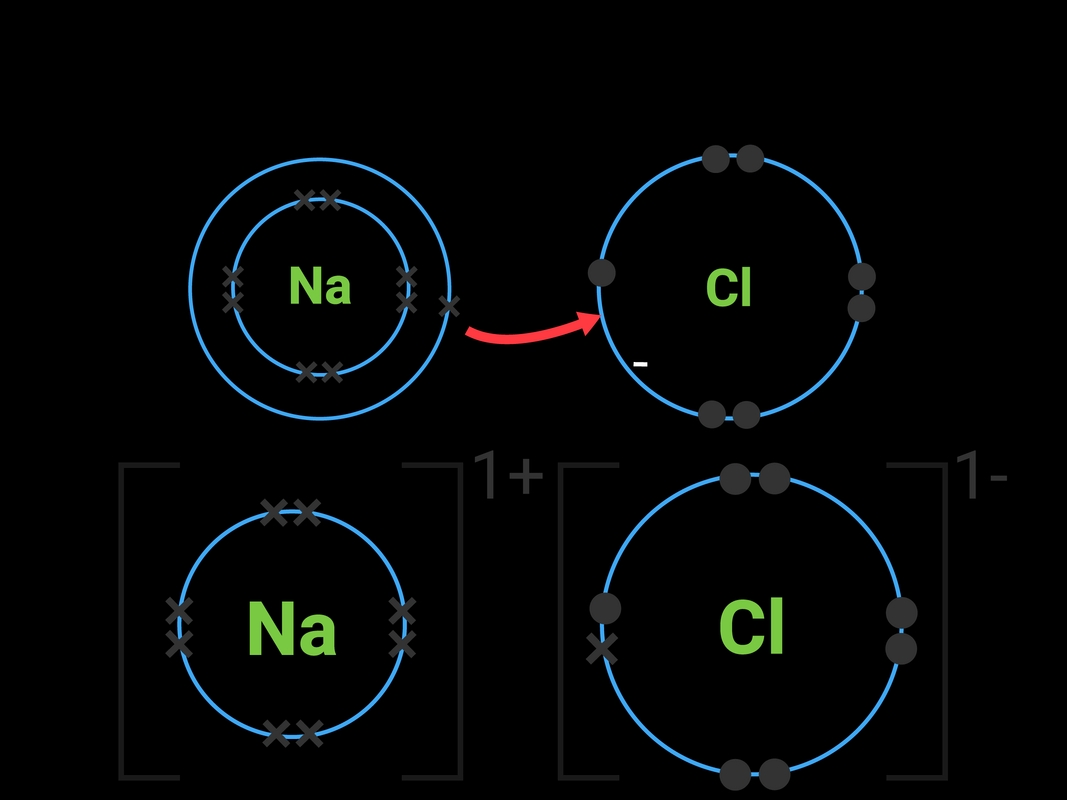
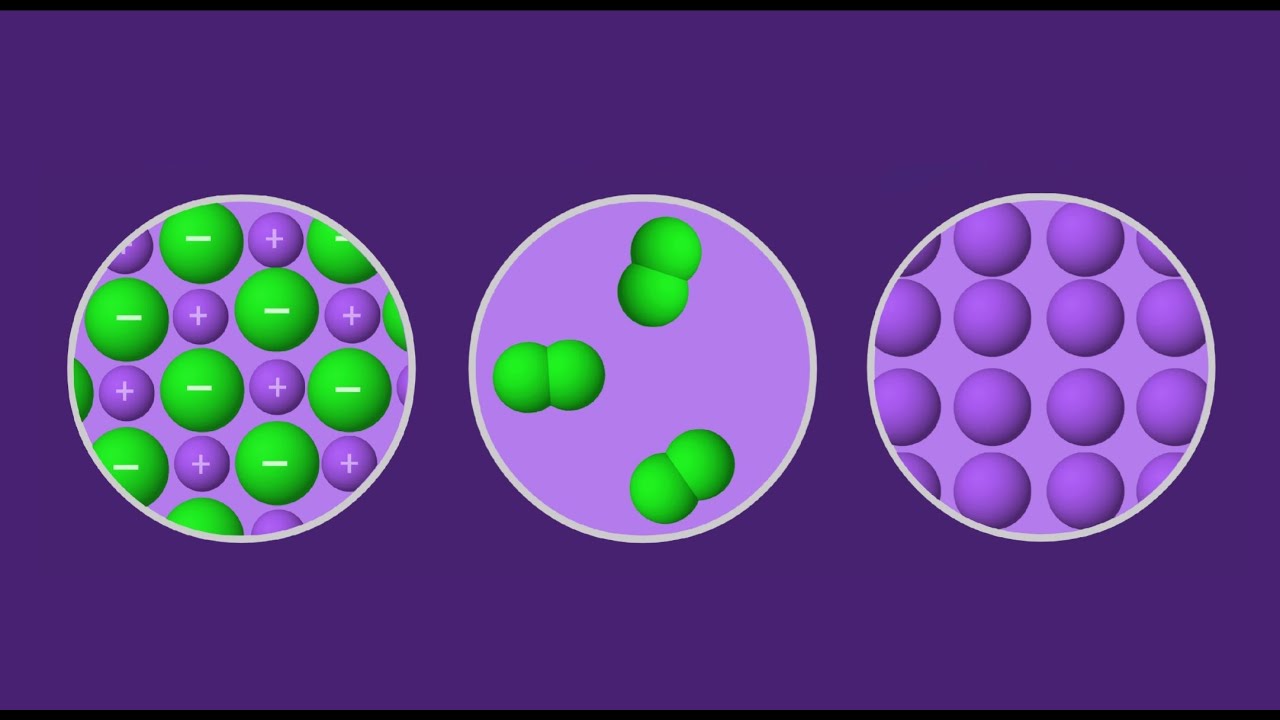
Ionic bonds are formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of ions with opposite charges. This type of bond typically occurs between a metal atom and a non-metal atom. The metal atom loses one or more electrons to form a positively charged ion, known as a cation, while the non-metal atom gains one or more electrons to form a negatively charged ion, known as an anion.
The electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions holds them together, forming a strong bond. Ionic bonds are typically found in salts, such as sodium chloride (NaCl) and calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
Characteristics of Ionic Bonds
- Ionic bonds are typically strong and rigid.
- They have high melting and boiling points.
- Ionic compounds are usually soluble in water.
- They can conduct electricity when dissolved in water.
What are Covalent Bonds?
Covalent bonds are formed when two or more atoms share one or more pairs of electrons to form a molecule. This type of bond typically occurs between non-metal atoms. The shared electrons are attracted to the nuclei of both atoms, holding them together.
Covalent bonds can be further classified into two types: polar covalent bonds and non-polar covalent bonds. Polar covalent bonds are formed when the shared electrons are not equally shared between the atoms, resulting in a molecule with a slightly positive and negative end. Non-polar covalent bonds are formed when the shared electrons are equally shared between the atoms.
Characteristics of Covalent Bonds
- Covalent bonds are typically weaker than ionic bonds.
- They have lower melting and boiling points.
- Covalent compounds are usually insoluble in water.
- They do not conduct electricity.
Examples of Covalent Bonds
- Water (H2O) is a polar covalent compound.
- Methane (CH4) is a non-polar covalent compound.
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a polar covalent compound.
Comparison of Ionic and Covalent Bonds
| Ionic Bonds | Covalent Bonds | |
|---|---|---|
| Formation | Transfer of electrons | Sharing of electrons |
| Type of Atoms | Typically between metal and non-metal atoms | Typically between non-metal atoms |
| Strength | Strong and rigid | Weaker than ionic bonds |
| Melting and Boiling Points | High | Low |
| Solubility in Water | Soluble | Insoluble |
| Conductivity | Conduct electricity | Do not conduct electricity |
🔥 Note: Ionic bonds are typically stronger than covalent bonds, but they can also be more brittle.
Real-Life Applications of Ionic and Covalent Bonds
- Ionic bonds are used in the manufacture of ceramics, glass, and cement.
- Covalent bonds are used in the manufacture of plastics, fibers, and fuels.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ionic and covalent bonds are two fundamental types of chemical bonds that play a crucial role in the formation of molecules. Understanding the characteristics and properties of these bonds is essential in chemistry and has numerous real-life applications.
Chemical bonding is a complex and fascinating topic that continues to be studied and researched by scientists. By understanding the principles of ionic and covalent bonds, we can gain a deeper insight into the world of chemistry and its applications.
What is the main difference between ionic and covalent bonds?
+The main difference between ionic and covalent bonds is the way in which the atoms share or exchange electrons. Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons, while covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons.
Which type of bond is stronger, ionic or covalent?
+Ionic bonds are typically stronger than covalent bonds.
What are some examples of covalent compounds?
+Examples of covalent compounds include water (H2O), methane (CH4), and carbon dioxide (CO2).