5 Ways to Master Boyle's and Charles' Laws
Understanding the Fundamentals of Gas Laws
Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law are two fundamental principles in chemistry and physics that describe the behavior of gases. Mastering these laws is essential for understanding various natural phenomena and industrial processes. In this article, we will explore five ways to help you grasp these concepts and become proficient in applying them.
1. Visualize the Laws with Diagrams and Graphs
Visual aids are an excellent way to comprehend complex concepts. By creating diagrams and graphs, you can illustrate the relationships between pressure, volume, and temperature, which are the core components of Boyle’s and Charles’ Laws.
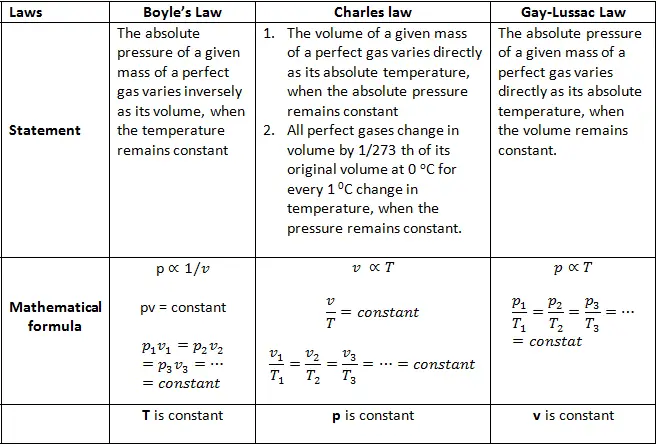
Boyle’s Law
Boyle’s Law states that, at constant temperature, the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to the pressure. Mathematically, this can be expressed as:
P1V1 = P2V2
where P1 and P2 are the initial and final pressures, and V1 and V2 are the initial and final volumes.
Charles’ Law
Charles’ Law states that, at constant pressure, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to the temperature. Mathematically, this can be expressed as:
V1 / T1 = V2 / T2
where V1 and V2 are the initial and final volumes, and T1 and T2 are the initial and final temperatures.
By plotting these relationships on a graph, you can see how changes in pressure and temperature affect the volume of a gas.
📝 Note: Make sure to label your axes correctly and use different colors to distinguish between the two laws.
2. Practice Problems with Real-World Applications
Practice problems are an excellent way to reinforce your understanding of Boyle’s and Charles’ Laws. Try solving problems that involve real-world applications, such as:
- Calculating the pressure of a gas in a container that is being heated or cooled.
- Determining the volume of a gas that is being compressed or expanded.
- Understanding how changes in altitude affect the pressure and volume of a gas.
Example Problem
A scuba diver descends to a depth of 20 meters in the ocean. If the pressure at the surface is 101 kPa, what is the pressure at 20 meters?
Solution
Using Boyle’s Law, we can calculate the pressure at 20 meters:
P1V1 = P2V2
101 kPa x V1 = P2 x V2
Since the volume of the gas decreases with increasing pressure, we can assume that V2 is approximately equal to V1 / 2.
101 kPa x V1 = P2 x V1 / 2
P2 = 2 x 101 kPa = 202 kPa
Therefore, the pressure at 20 meters is approximately 202 kPa.
📝 Note: Make sure to check your units and ensure that you are using the correct formula.
3. Use Online Resources and Simulations
There are many online resources and simulations available that can help you visualize and interact with Boyle’s and Charles’ Laws. Some popular options include:
- PhET Interactive Simulations (University of Colorado Boulder)
- Gas Laws Simulator (ScienceGeeks)
- Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law Calculator (CalculatorSoup)
These resources can help you explore the relationships between pressure, volume, and temperature in a fun and interactive way.
4. Watch Video Tutorials and Lectures
Video tutorials and lectures can provide an excellent overview of Boyle’s and Charles’ Laws. Some popular options include:
- Crash Course Chemistry (YouTube)
- Khan Academy Chemistry (YouTube)
- 3Blue1Brown (YouTube)
These videos can help you understand the underlying concepts and provide examples and practice problems to reinforce your learning.
5. Teach Someone Else
Teaching someone else is an excellent way to reinforce your own understanding of Boyle’s and Charles’ Laws. Try explaining the concepts to a friend or family member, or create a tutorial or video to share with others.
Tips for Teaching
- Use simple language and avoid jargon.
- Use visual aids, such as diagrams and graphs, to illustrate the concepts.
- Provide examples and practice problems to help reinforce understanding.
- Encourage questions and discussion.
By following these five ways to master Boyle’s and Charles’ Laws, you can become proficient in applying these concepts to real-world problems and deepen your understanding of the natural world.
As you practice and apply these laws, you will begin to see the world in a new light. From the way a balloon expands when heated to the way a scuba diver’s body responds to changes in pressure, the principles of Boyle’s and Charles’ Laws are all around us.
What is the difference between Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law?
+Boyle’s Law describes the relationship between pressure and volume at constant temperature, while Charles’ Law describes the relationship between volume and temperature at constant pressure.
How can I apply Boyle’s and Charles’ Laws to real-world problems?
+Boyle’s and Charles’ Laws can be applied to a wide range of real-world problems, including scuba diving, air travel, and industrial processes. By understanding how changes in pressure and temperature affect the volume of a gas, you can make informed decisions and solve complex problems.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when working with Boyle’s and Charles’ Laws?
+Common mistakes to avoid include forgetting to check units, using the wrong formula, and neglecting to consider the assumptions underlying the laws. By being aware of these potential pitfalls, you can ensure accurate and reliable calculations.
Related Terms:
- Boyle's Law Worksheet answer key
- Boyle's Law worksheets



