Waves Worksheet Answer Key Simplified
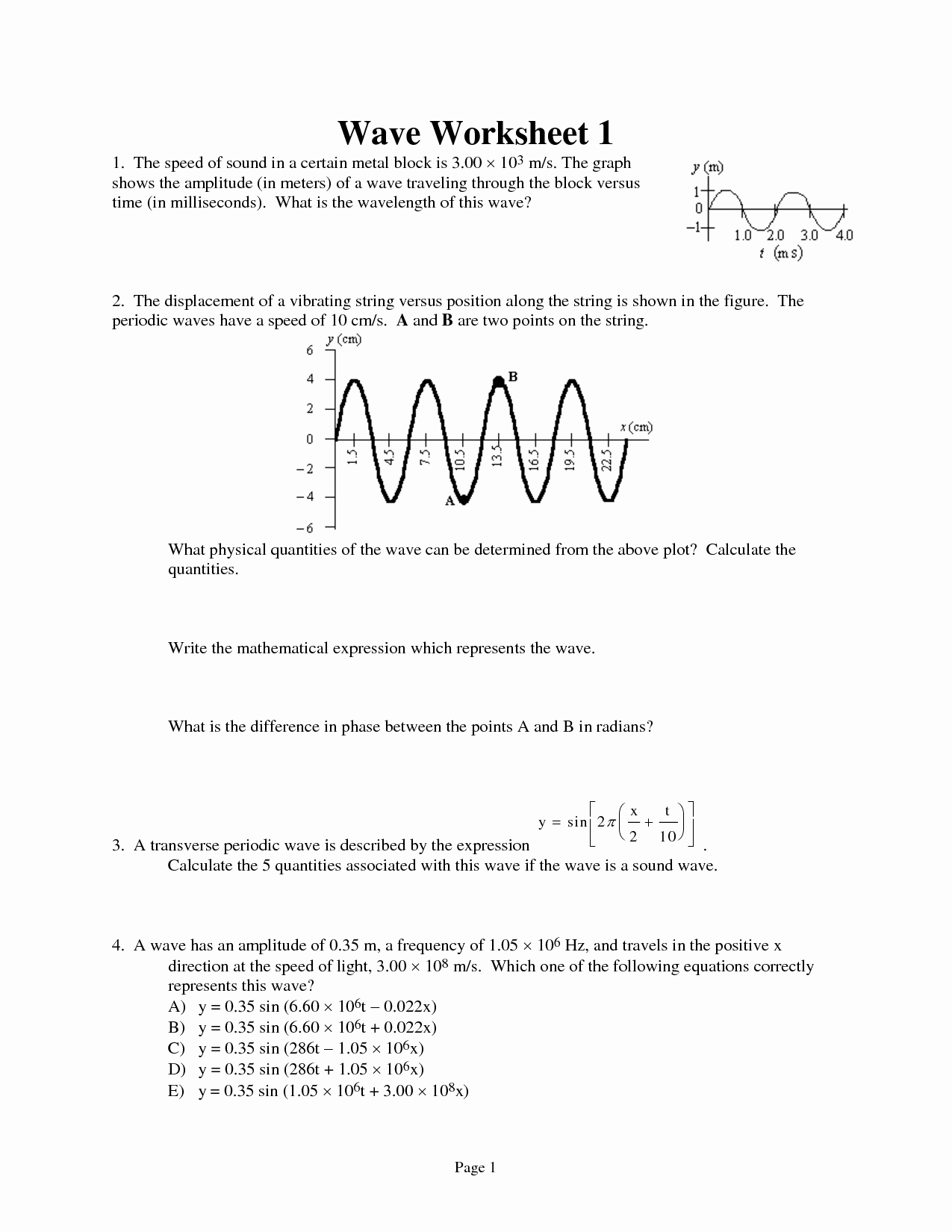
Understanding Waves: A Simplified Guide
Waves are a fundamental concept in physics, and understanding them is crucial for various fields, including physics, engineering, and even music. In this guide, we will delve into the world of waves, exploring their types, characteristics, and behaviors.
What are Waves?
A wave is a disturbance that travels through a medium, transferring energy from one point to another. Waves can be found in various forms, such as water waves, sound waves, and light waves. The key characteristic of a wave is its ability to propagate through a medium, carrying energy with it.
Types of Waves
There are several types of waves, including:
- Mechanical Waves: These waves require a physical medium to propagate, such as water waves or sound waves.
- Electromagnetic Waves: These waves do not require a physical medium and can propagate through a vacuum, such as light waves or radio waves.
- Transverse Waves: These waves oscillate perpendicular to the direction of propagation, such as light waves or water waves.
- Longitudinal Waves: These waves oscillate parallel to the direction of propagation, such as sound waves.
Characteristics of Waves
Waves have several key characteristics, including:
- Amplitude: The maximum displacement of a wave from its equilibrium position.
- Wavelength: The distance between two consecutive peaks or troughs of a wave.
- Frequency: The number of oscillations or cycles of a wave per second.
- Speed: The rate at which a wave propagates through a medium.
Wave Behavior
Waves exhibit various behaviors, including:
- Reflection: The change in direction of a wave when it hits a barrier or surface.
- Refraction: The bending of a wave as it passes from one medium to another.
- Diffraction: The bending of a wave around an obstacle or edge.
- Interference: The interaction between two or more waves, resulting in a new wave pattern.
📝 Note: Waves can also exhibit other behaviors, such as polarization and dispersion, but these are more advanced topics.
Real-World Applications of Waves
Waves have numerous real-world applications, including:
- Communication: Radio waves and light waves are used in communication systems, such as radio broadcasting and fiber optic internet.
- Medical Imaging: Sound waves and electromagnetic waves are used in medical imaging techniques, such as ultrasound and MRI.
- Music: Sound waves are used in music, with different frequencies and amplitudes creating various pitches and volumes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, waves are a fundamental concept in physics, with various types, characteristics, and behaviors. Understanding waves is crucial for various fields, including physics, engineering, and music. By recognizing the different types of waves and their behaviors, we can better appreciate the natural world and harness the power of waves in various applications.
What is the difference between a mechanical wave and an electromagnetic wave?
+A mechanical wave requires a physical medium to propagate, while an electromagnetic wave does not require a medium and can propagate through a vacuum.
What is the relationship between wavelength and frequency?
+The wavelength and frequency of a wave are inversely proportional, meaning that as the wavelength increases, the frequency decreases, and vice versa.
What is an example of wave interference?
+When two sound waves with the same frequency and amplitude meet, they can create a new wave pattern, resulting in an increase or decrease in volume.
Related Terms:
- Aaron Clark
- Dovydas Butka
- Jaxon Olvera
- Stevie Prudholme
- Alex Leiba