5 Ways to Master Water, Carbon, and Nitrogen Cycles

Understanding the Building Blocks of Life: Mastering the Water, Carbon, and Nitrogen Cycles
The water, carbon, and nitrogen cycles are three essential processes that sustain life on Earth. These cycles are intricately connected and play a crucial role in maintaining the health of our planet. In this article, we will explore the five ways to master these cycles, enabling you to better understand the delicate balance of our ecosystem.
1. Water Cycle: The Source of Life
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle, is the continuous process of water movement on, above, and below the surface of the Earth. It involves the movement of water in three phases: liquid, solid (ice), and gas (water vapor). To master the water cycle, it’s essential to understand the different stages involved:
- Evaporation: Water from the oceans, lakes, rivers, and the ground surface evaporates into the atmosphere, forming water vapor.
- Condensation: Water vapor in the atmosphere cools and condenses into clouds, fog, or dew.
- Precipitation: Water droplets in clouds become too heavy to remain suspended, falling to the ground as precipitation (rain, snow, sleet, or hail).
- Runoff: Precipitation that flows over the land surface, eventually returning to bodies of water.
- Infiltration: Precipitation that seeps into the soil, recharging groundwater.
2. Carbon Cycle: The Backbone of Life
The carbon cycle is the process by which carbon is exchanged between the atmosphere, oceans, land, and living organisms. It’s a vital component of life on Earth, as it supports the growth and development of all living organisms. To master the carbon cycle, it’s crucial to understand the different stages involved:
- Photosynthesis: Plants, algae, and some bacteria convert carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere into organic compounds, releasing oxygen (O2) as a byproduct.
- Respiration: Living organisms break down organic compounds, releasing CO2 into the atmosphere.
- Decomposition: Microorganisms break down dead organic matter, releasing CO2 into the atmosphere.
- Fossil Fuel Formation: Over millions of years, plant and animal remains are compressed and transformed into fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas.
3. Nitrogen Cycle: The Essential Nutrient
The nitrogen cycle is the process by which nitrogen is converted between its various forms in the environment. Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for plant growth, and its availability can limit the productivity of ecosystems. To master the nitrogen cycle, it’s vital to understand the different stages involved:
- Nitrogen Fixation: Certain bacteria, such as those found in legume roots, convert atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into a usable form, such as ammonia (NH3) or nitrate (NO3-).
- Assimilation: Plants absorb nitrogen from the soil, using it to build proteins, nucleic acids, and other biomolecules.
- Ammonification: Microorganisms break down organic matter, releasing ammonia (NH3) into the soil.
- Nitrification: Microorganisms convert ammonia (NH3) into nitrite (NO2-) and then nitrate (NO3-), making nitrogen available to plants.
4. Interconnections Between Cycles
The water, carbon, and nitrogen cycles are interconnected, with each cycle influencing the others. For example:
- Water Cycle and Carbon Cycle: Evaporation and precipitation play a crucial role in the global carbon cycle, as they help regulate the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere.
- Carbon Cycle and Nitrogen Cycle: The availability of nitrogen in the soil affects the rate of photosynthesis, which in turn affects the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere.
- Water Cycle and Nitrogen Cycle: The movement of water through the environment affects the availability of nitrogen in the soil, as nitrogen is often transported in water.
5. Human Impact on the Cycles
Human activities can significantly impact the water, carbon, and nitrogen cycles, leading to changes in the environment and ecosystems. Some examples include:
- Climate Change: Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, contribute to climate change, which affects the water cycle, carbon cycle, and nitrogen cycle.
- Pollution: Human activities, such as industrial processes and agricultural runoff, release pollutants into the environment, affecting the water cycle, carbon cycle, and nitrogen cycle.
- Land Use Changes: Human activities, such as deforestation and urbanization, alter the natural habitats and ecosystems, affecting the water cycle, carbon cycle, and nitrogen cycle.
🌎 Note: Understanding the interconnectedness of the water, carbon, and nitrogen cycles is crucial for mitigating the impact of human activities on the environment.
In conclusion, mastering the water, carbon, and nitrogen cycles requires a deep understanding of the complex interactions between these cycles and the environment. By recognizing the importance of these cycles and the impact of human activities on them, we can work towards creating a more sustainable future for our planet.
What is the importance of the water cycle?
+The water cycle is essential for life on Earth, as it supports the growth and development of all living organisms. It also regulates the Earth’s climate and weather patterns.
How do human activities affect the carbon cycle?
+Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, release CO2 into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change and affecting the carbon cycle.
What is the role of nitrogen in the environment?
+Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for plant growth, and its availability can limit the productivity of ecosystems. It’s also a critical component of amino acids, nucleotides, and chlorophyll.
Related Terms:
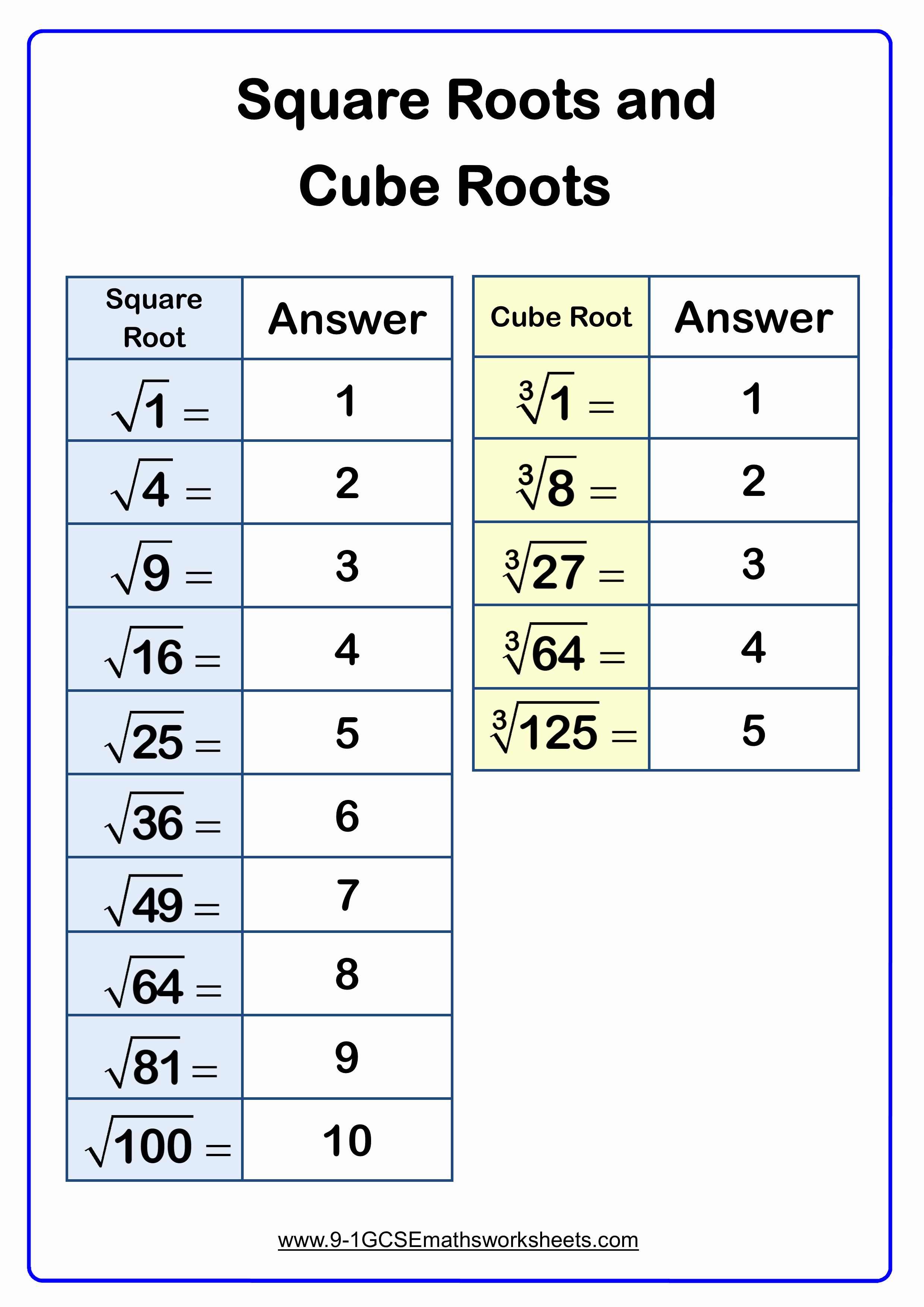
- Nitrogen cycle Worksheet answers PDF
- Nitrogen cycle Worksheet PDF
- Carbon and oxygen cycle worksheet
- Biogeochemical cycles worksheet answer key