Valence Electrons and Ions Made Easy for Students
Understanding Valence Electrons and Ions: A Comprehensive Guide for Students
Valence electrons and ions are fundamental concepts in chemistry that can be challenging for students to grasp. However, with a clear understanding of these concepts, students can build a strong foundation in chemistry and excel in their studies. In this article, we will delve into the world of valence electrons and ions, explaining the concepts in a simple and easy-to-understand manner.
What are Valence Electrons?
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom. They are also known as the outer electrons. The number of valence electrons an atom has determines its chemical properties and how it reacts with other atoms.
To understand valence electrons, let’s take a look at the atomic structure. An atom consists of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus, while electrons orbit around the nucleus in energy levels or shells.
The outermost energy level is the valence shell, which contains the valence electrons. The number of valence electrons an atom has depends on the number of electrons in the outermost energy level.
How to Determine the Number of Valence Electrons
To determine the number of valence electrons an atom has, you need to know the atomic number of the element. The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
Here’s a simple method to determine the number of valence electrons:
- Write down the electron configuration of the atom.
- Identify the outermost energy level (valence shell).
- Count the number of electrons in the valence shell.
For example, let’s take the element carbon ©. The atomic number of carbon is 6, and its electron configuration is 1s² 2s² 2p².
The outermost energy level is the second energy level (2s² 2p²), which contains 4 electrons. Therefore, carbon has 4 valence electrons.
What are Ions?
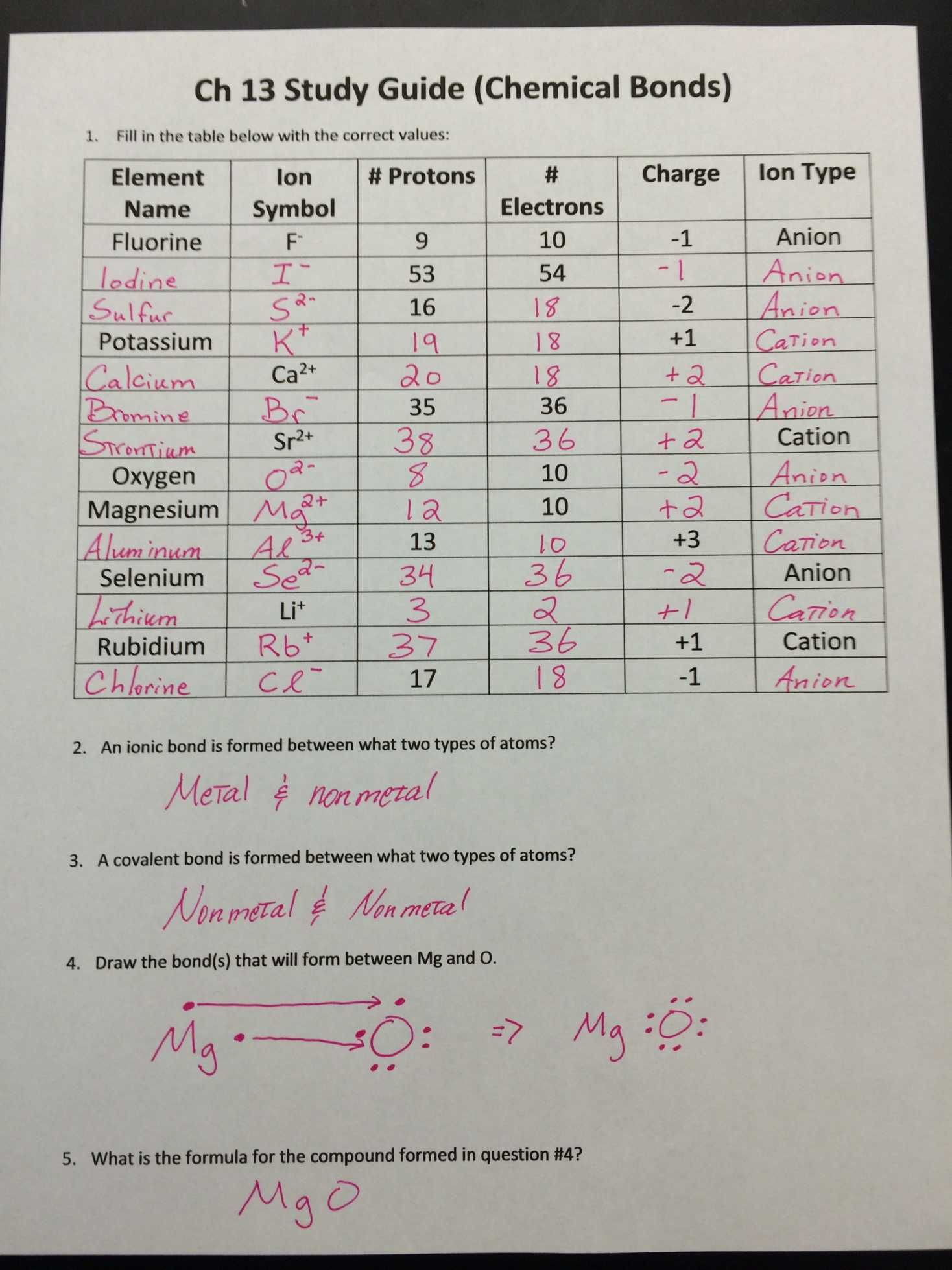
Ions are atoms or molecules that have gained or lost electrons to form a charged particle. When an atom gains or loses electrons, it becomes an ion.
There are two types of ions:
- Cations: These are positively charged ions that are formed when an atom loses one or more electrons.
- Anions: These are negatively charged ions that are formed when an atom gains one or more electrons.
For example, when a sodium atom loses an electron, it becomes a positively charged sodium ion (Na+). When a chlorine atom gains an electron, it becomes a negatively charged chloride ion (Cl-).
How to Form Ions
To form ions, atoms must gain or lose electrons. Here are some simple steps to form ions:
- Identify the atom you want to form an ion from.
- Determine the number of valence electrons the atom has.
- Decide whether you want to form a cation or an anion.
- Add or remove electrons from the atom to form the ion.
For example, let’s say you want to form a sodium ion (Na+). Sodium has 11 electrons, and its electron configuration is 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s¹.
To form a sodium ion, you need to remove one electron from the outermost energy level (3s¹). This leaves the sodium atom with 10 electrons and a positive charge (Na+).
👍 Note: When forming ions, the number of protons in the nucleus remains the same. Only the number of electrons changes.
Types of Chemical Bonds
Chemical bonds are formed when atoms share or exchange electrons to form a stable molecule. There are three main types of chemical bonds:
- Ionic bonds: These are formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another.
- Covalent bonds: These are formed when two or more atoms share one or more pairs of electrons.
- Metallic bonds: These are formed when electrons are delocalized among a lattice of atoms.
Conclusion
Valence electrons and ions are fundamental concepts in chemistry that are essential for understanding chemical bonding and reactions. By understanding the number of valence electrons an atom has and how to form ions, students can build a strong foundation in chemistry and excel in their studies.
In conclusion, valence electrons and ions are not as complicated as they seem. With practice and patience, students can master these concepts and achieve academic success in chemistry.
What is the difference between a cation and an anion?
+A cation is a positively charged ion that is formed when an atom loses one or more electrons. An anion is a negatively charged ion that is formed when an atom gains one or more electrons.
How do you determine the number of valence electrons an atom has?
+To determine the number of valence electrons an atom has, write down the electron configuration of the atom, identify the outermost energy level (valence shell), and count the number of electrons in the valence shell.
What is the purpose of forming ions in chemistry?
+Forming ions is essential in chemistry as it allows atoms to achieve a stable electronic configuration, which is necessary for chemical bonding and reactions to occur.
Related Terms:
- Ion formation Worksheet pdf
- Charges of Ions Worksheet pdf
- Cation and anion Worksheet PDF
- Atoms vs ions worksheet