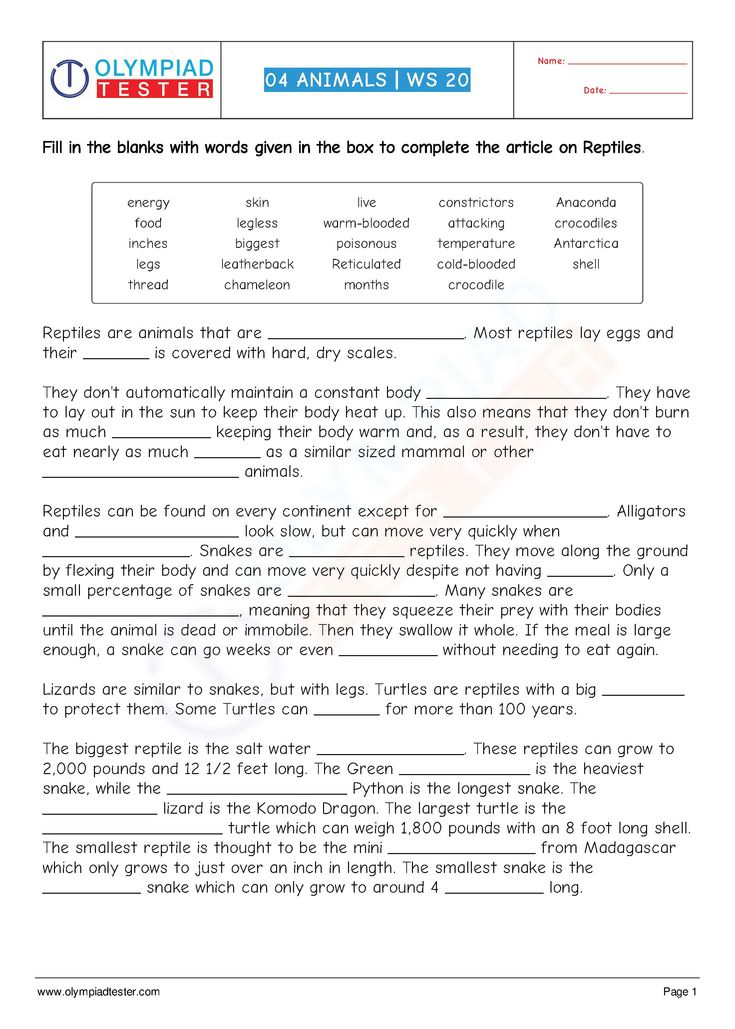
6 Types of Chemical Reactions Worksheet Answers

Understanding the 6 Types of Chemical Reactions
Chemical reactions are the processes by which atoms are rearranged to form new substances. These reactions are fundamental to understanding chemistry and are classified into several types based on the changes that occur during the reaction. There are six main types of chemical reactions: synthesis, decomposition, single displacement, double displacement, combustion, and acid-base neutralization. Each type of reaction has distinct characteristics that help us identify and predict the outcomes of chemical changes.
1. Synthesis Reactions
Synthesis reactions involve the combination of two or more substances to form a new compound. This type of reaction is also known as a direct combination reaction. The general formula for a synthesis reaction is:
A + B → AB
Where A and B are the reactants, and AB is the product.
Example: 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O
In this example, hydrogen gas (H₂) reacts with oxygen gas (O₂) to form water (H₂O).
🔍 Note: Synthesis reactions often involve the formation of a covalent bond between the reactants.
2. Decomposition Reactions
Decomposition reactions involve the breakdown of a single compound into two or more simpler substances. This type of reaction is also known as a direct decomposition reaction. The general formula for a decomposition reaction is:
AB → A + B
Where AB is the reactant, and A and B are the products.
Example: 2H₂O → 2H₂ + O₂
In this example, water (H₂O) decomposes into hydrogen gas (H₂) and oxygen gas (O₂).
🔍 Note: Decomposition reactions often involve the breaking of a covalent bond within the reactant.
3. Single Displacement Reactions
Single displacement reactions involve the displacement of one element by another element from a compound. This type of reaction is also known as a substitution reaction. The general formula for a single displacement reaction is:
A + BC → AC + B
Where A is the displacing element, BC is the reactant compound, AC is the product compound, and B is the displaced element.
Example: Zn + CuSO₄ → ZnSO₄ + Cu
In this example, zinc (Zn) displaces copper (Cu) from copper(II) sulfate (CuSO₄) to form zinc sulfate (ZnSO₄) and copper (Cu).
🔍 Note: Single displacement reactions often involve the formation of a new compound and the release of a different element.
4. Double Displacement Reactions
Double displacement reactions involve the displacement of two elements from two different compounds. This type of reaction is also known as a metathesis reaction. The general formula for a double displacement reaction is:
AB + CD → AD + CB
Where AB and CD are the reactant compounds, and AD and CB are the product compounds.
Example: NaCl + AgNO₃ → NaNO₃ + AgCl
In this example, sodium chloride (NaCl) reacts with silver nitrate (AgNO₃) to form sodium nitrate (NaNO₃) and silver chloride (AgCl).
🔍 Note: Double displacement reactions often involve the formation of two new compounds.
5. Combustion Reactions
Combustion reactions involve the reaction of a substance with oxygen to produce heat and light. This type of reaction is also known as a burning reaction. The general formula for a combustion reaction is:
A + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O
Where A is the reactant, O₂ is oxygen, CO₂ is carbon dioxide, and H₂O is water.
Example: CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O
In this example, methane (CH₄) reacts with oxygen (O₂) to produce carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O).
🔍 Note: Combustion reactions often involve the release of heat and light energy.
6. Acid-Base Neutralization Reactions
Acid-base neutralization reactions involve the reaction of an acid with a base to produce a salt and water. This type of reaction is also known as a neutralization reaction. The general formula for an acid-base neutralization reaction is:
HA + BOH → BA + H₂O
Where HA is the acid, BOH is the base, BA is the salt, and H₂O is water.
Example: HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂O
In this example, hydrochloric acid (HCl) reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to produce sodium chloride (NaCl) and water (H₂O).
🔍 Note: Acid-base neutralization reactions often involve the formation of a salt and water.
In conclusion, the six types of chemical reactions are essential to understanding chemistry and predicting the outcomes of chemical changes. Each type of reaction has distinct characteristics that help us identify and classify the reaction. By understanding these types of reactions, we can better appreciate the complexities of chemical reactions and their importance in our daily lives.
What is the difference between a synthesis reaction and a decomposition reaction?
+A synthesis reaction involves the combination of two or more substances to form a new compound, whereas a decomposition reaction involves the breakdown of a single compound into two or more simpler substances.
What is the general formula for a single displacement reaction?
+A + BC → AC + B
What is the general formula for a combustion reaction?
+A + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O