Electrons in Atoms Worksheet Answer Key

Understanding Electrons in Atoms
Atoms, the basic building blocks of matter, consist of three main parts: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus, which is the center of the atom, while electrons orbit around the nucleus. In this post, we will delve into the world of electrons in atoms, exploring their behavior, arrangement, and importance in understanding chemistry.
What are Electrons?
Electrons are tiny, negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus of an atom. They are a fundamental part of an atom and play a crucial role in determining the chemical properties of an element. Electrons are attracted to the positively charged protons in the nucleus and are held in their orbits by the electrostatic force of attraction.
Energy Levels and Electron Shells
Electrons in an atom are arranged in energy levels or electron shells. These energy levels are also known as electron configurations. Each energy level can hold a specific number of electrons, and electrons in each level have a specific amount of energy. The energy levels are arranged in the following order: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, and so on.
The first energy level, or 1s orbital, can hold up to 2 electrons. The second energy level, which includes the 2s and 2p orbitals, can hold up to 8 electrons. The third energy level, which includes the 3s, 3p, and 3d orbitals, can hold up to 18 electrons.
Electron Configuration
Electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons in an atom. It is a way of describing the energy levels and orbitals that electrons occupy. Electron configuration is written in a specific notation, with the energy level and orbital type written first, followed by the number of electrons in that orbital.
For example, the electron configuration of carbon is 1s² 2s² 2p². This means that carbon has two electrons in the 1s orbital, two electrons in the 2s orbital, and two electrons in the 2p orbital.
Valence Electrons
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom. They are the electrons that participate in chemical bonding and determine the chemical properties of an element. Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest energy level, and they are the most reactive.
Electron Groups
Electron groups are the number of electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom. They are also known as valence electron groups. Electron groups are used to predict the chemical properties of an element and to determine the type of bond that an atom will form.
Electron Worksheet Answer Key
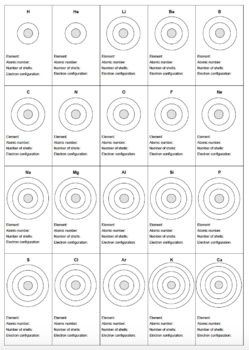
| Element | Electron Configuration | Valence Electrons | Electron Group |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 1s¹ | 1 | 1 |
| Helium | 1s² | 2 | 2 |
| Carbon | 1s² 2s² 2p² | 4 | 4 |
| Nitrogen | 1s² 2s² 2p³ | 5 | 5 |
| Oxygen | 1s² 2s² 2p⁴ | 6 | 6 |
📝 Note: The electron worksheet answer key provides a summary of the electron configuration, valence electrons, and electron group for each element listed.
Importance of Electrons in Atoms
Electrons play a crucial role in determining the chemical properties of an element. They participate in chemical bonding and determine the type of bond that an atom will form. Electrons also determine the reactivity of an element and the type of compounds that it can form.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electrons are an essential part of an atom, and understanding their behavior and arrangement is crucial in chemistry. Electron configuration, valence electrons, and electron groups are all important concepts that help us understand the chemical properties of an element.
What is the purpose of electrons in an atom?
+
Electrons participate in chemical bonding and determine the type of bond that an atom will form.
What is the difference between valence electrons and electron groups?
+
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom, while electron groups are the number of electrons in the outermost energy level.
How do electrons determine the chemical properties of an element?
+
Electrons participate in chemical bonding and determine the type of bond that an atom will form, which in turn determines the chemical properties of an element.