Periodic Table Worksheet Answers and Study Guide
Unlocking the Secrets of the Periodic Table
The periodic table is a powerful tool in chemistry that helps us understand the properties and behavior of elements. In this worksheet and study guide, we will delve into the world of the periodic table and explore its secrets.
Understanding the Periodic Table
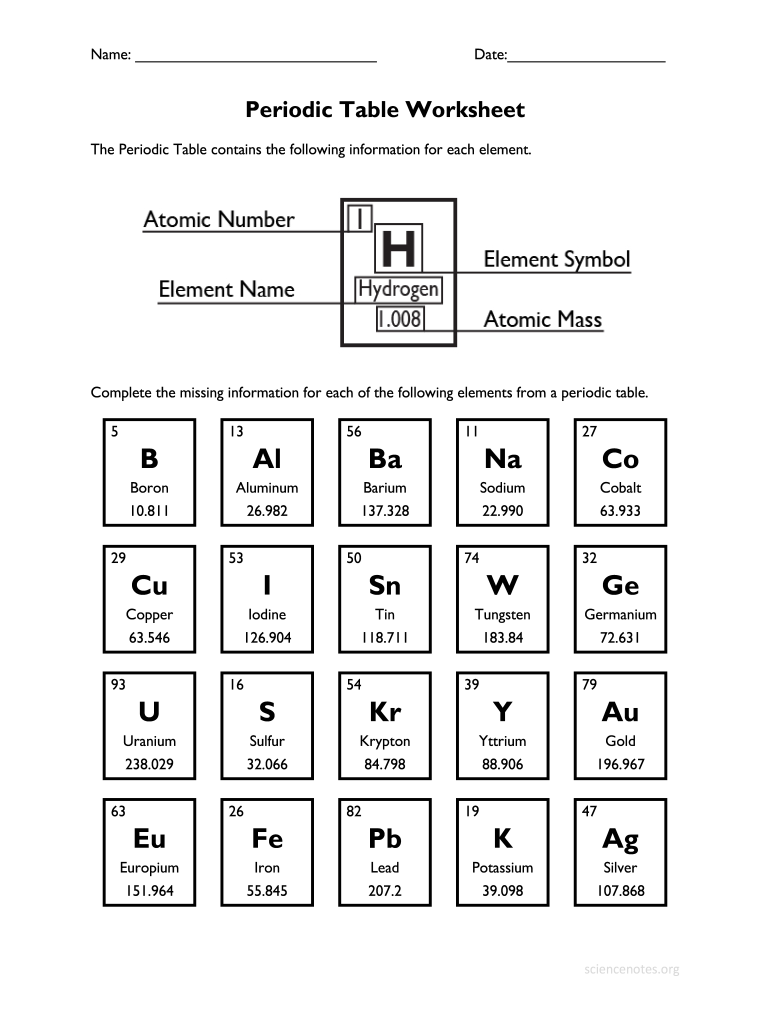
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of elements, organized by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. The elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus) and are grouped into rows called periods and columns called groups or families.
Periods
- The horizontal rows of the periodic table are called periods.
- The elements in a period have the same number of electron shells.
- As you move from left to right in a period, the elements become less metallic and more nonmetallic.
Groups or Families
- The vertical columns of the periodic table are called groups or families.
- The elements in a group have similar chemical properties due to the same number of electrons in their outermost energy level.
- The elements in a group are arranged in order of increasing atomic number.
Blocks of the Periodic Table
The periodic table can be divided into four blocks: s, p, d, and f.
- s-block: The elements in the s-block are in the first two columns of the periodic table. They have one or two electrons in their outermost energy level and are highly reactive.
- p-block: The elements in the p-block are in the last six columns of the periodic table. They have three or more electrons in their outermost energy level and are less reactive than the s-block elements.
- d-block: The elements in the d-block are in the middle of the periodic table. They have five or more electrons in their outermost energy level and are less reactive than the s-block and p-block elements.
- f-block: The elements in the f-block are at the bottom of the periodic table. They have seven or more electrons in their outermost energy level and are the least reactive of all the blocks.
Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids
- Metals: The elements on the left side of the periodic table are metals. They are shiny, malleable, and good conductors of electricity.
- Nonmetals: The elements on the right side of the periodic table are nonmetals. They are dull, brittle, and poor conductors of electricity.
- Metalloids: The elements on the border between the metals and nonmetals are metalloids. They have some properties of metals and some properties of nonmetals.
Periodic Trends
As you move from left to right in a period, the following trends are observed:
- Atomic radius decreases
- Electronegativity increases
- Ionization energy increases
- Electron affinity increases
As you move down a group, the following trends are observed:
- Atomic radius increases
- Electronegativity decreases
- Ionization energy decreases
- Electron affinity decreases
Conclusion
In conclusion, the periodic table is a powerful tool in chemistry that helps us understand the properties and behavior of elements. By understanding the periods, groups, blocks, and periodic trends, we can predict the properties of elements and make connections between them.
💡 Note: The periodic table is a complex and multifaceted tool. This study guide provides a general overview of the periodic table, but there is always more to learn.
What is the periodic table?
+The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of elements, organized by their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties.
What are the blocks of the periodic table?
+The periodic table can be divided into four blocks: s, p, d, and f.
What are the periodic trends?
+As you move from left to right in a period, the following trends are observed: atomic radius decreases, electronegativity increases, ionization energy increases, and electron affinity increases.
Related Terms:
- Periodic table Worksheet pdf
- Periodic table puzzle worksheet