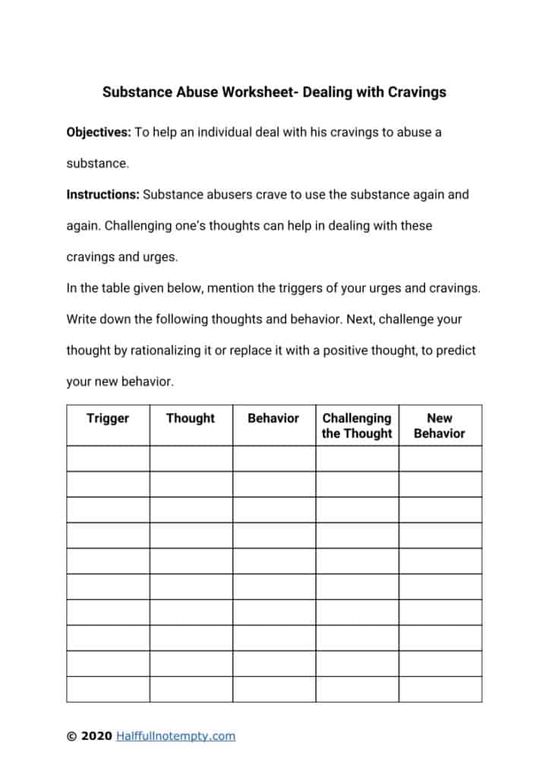
Substance Abuse Worksheet
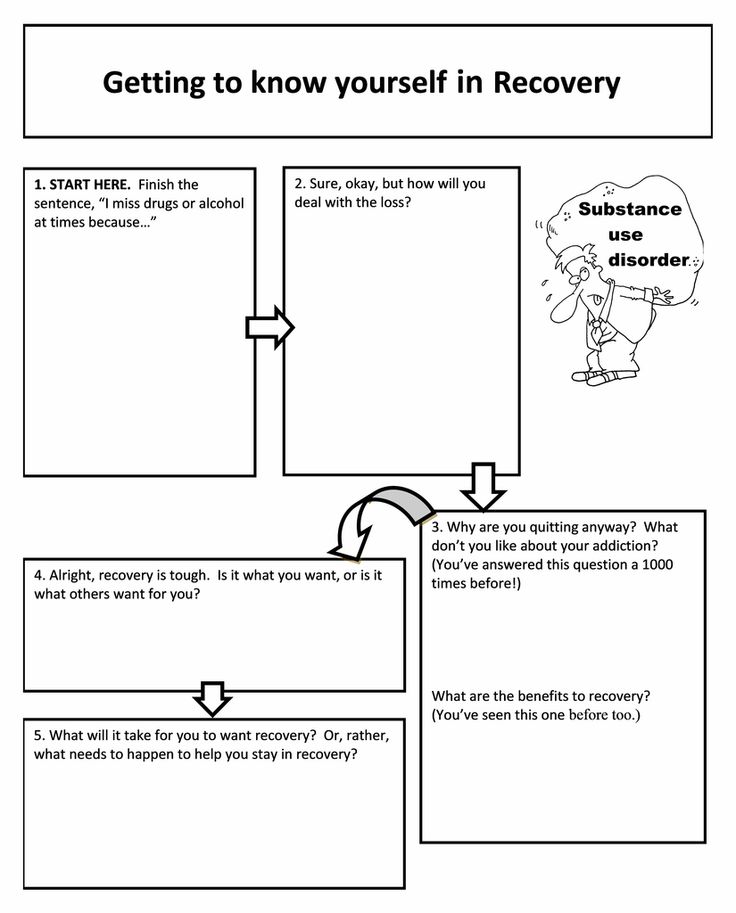
Understanding Substance Abuse: A Comprehensive Guide
Substance abuse is a serious issue that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a complex problem that can have severe consequences on an individual’s physical and mental health, relationships, and overall well-being. In this article, we will delve into the world of substance abuse, exploring its causes, symptoms, effects, and treatment options.
What is Substance Abuse?
Substance abuse, also known as drug abuse or addiction, refers to the excessive and compulsive use of substances despite the negative consequences. These substances can include:
- Illicit drugs: such as heroin, cocaine, and methamphetamine
- Prescription medications: such as opioids, benzodiazepines, and stimulants
- Alcohol: including beer, wine, and liquor
- Tobacco: including cigarettes, cigars, and chewing tobacco
Substance abuse can be characterized by:
- Loss of control: using more of the substance than intended or using it for longer than intended
- Neglect of responsibilities: neglecting work, school, or family responsibilities due to substance use
- Continued use despite negative consequences: using the substance despite physical or mental health problems, relationship problems, or other negative consequences
Causes of Substance Abuse
Substance abuse is a complex issue with multiple causes. Some of the most common causes include:
- Genetics: individuals with a family history of substance abuse are more likely to develop an addiction
- Environmental factors: exposure to substance use at a young age, peer pressure, and stress can contribute to substance abuse
- Mental health: individuals with mental health disorders, such as depression or anxiety, may turn to substance use as a coping mechanism
- Trauma: individuals who have experienced trauma, such as physical or emotional abuse, may be more likely to develop an addiction
Symptoms of Substance Abuse
The symptoms of substance abuse can vary depending on the substance being used and the individual’s overall health. Some common symptoms include:
- Physical symptoms:
- Changes in appetite or sleep patterns
- Weight loss or gain
- Bloodshot eyes or dilated pupils
- Slurred speech or stumbling
- Behavioral symptoms:
- Secrecy or hiding substance use
- Lying about substance use
- Neglecting responsibilities
- Engaging in risky behaviors
- Psychological symptoms:
- Mood swings or irritability
- Anxiety or depression
- Loss of interest in activities
- Suicidal thoughts or behaviors
Effects of Substance Abuse
Substance abuse can have severe consequences on an individual’s physical and mental health, relationships, and overall well-being. Some of the effects of substance abuse include:
- Physical health problems: such as liver disease, heart problems, and respiratory issues
- Mental health problems: such as depression, anxiety, and psychosis
- Relationship problems: such as divorce, family conflict, and social isolation
- Cognitive problems: such as memory loss, attention deficits, and decision-making difficulties
Treatment Options for Substance Abuse
Fortunately, there are many effective treatment options for substance abuse. Some of the most common treatment options include:
- Medication-assisted treatment: such as methadone or buprenorphine for opioid addiction
- Behavioral therapy: such as cognitive-behavioral therapy or contingency management
- Support groups: such as 12-step programs or SMART Recovery
- Inpatient or outpatient treatment: such as residential treatment programs or intensive outpatient programs
💡 Note: Treatment for substance abuse should be tailored to the individual's specific needs and circumstances. A mental health professional can help determine the best course of treatment.
Recovery from Substance Abuse
Recovery from substance abuse is a lifelong process that requires commitment, support, and self-care. Some tips for maintaining recovery include:
- Attend support groups: regularly attending support groups can help individuals stay connected and motivated
- Engage in self-care: practicing self-care activities, such as exercise or meditation, can help individuals manage stress and cravings
- Build a support network: surrounding oneself with supportive family and friends can help individuals stay accountable and motivated
- Seek professional help: regularly seeing a mental health professional can help individuals stay on track and address any challenges that arise
| Substance | Abuse Symptoms | Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|
| Alcohol | Increased tolerance, withdrawal symptoms, secretive drinking | Medication-assisted treatment, behavioral therapy, support groups |
| Opioids | Constipation, drowsiness, pinpoint pupils | Medication-assisted treatment, behavioral therapy, support groups |
| Cocaine | Increased energy, anxiety, paranoia | Behavioral therapy, support groups, contingency management |
In summary, substance abuse is a complex issue that requires comprehensive treatment and support. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and effects of substance abuse, individuals can take the first steps towards recovery.
What is the difference between substance abuse and addiction?
+Substance abuse refers to the excessive and compulsive use of substances despite the negative consequences. Addiction, on the other hand, refers to the physical and psychological dependence on a substance. While substance abuse can be a symptom of addiction, not everyone who abuses substances is addicted.
How can I help a loved one with substance abuse?
+Helping a loved one with substance abuse can be challenging, but there are many ways to provide support. Some tips include: encouraging treatment, attending support groups, and setting boundaries. It’s also important to seek professional help and support for yourself, as substance abuse can affect the entire family.
What are some common relapse triggers?
+Some common relapse triggers include: stress, anxiety, and depression; social pressures and peer influence; and exposure to substance-related cues, such as seeing a substance or smelling a certain smell. It’s essential to identify personal triggers and develop a plan to manage them.