Mastering Subject and Predicate with Our Free Worksheet
Understanding the Basics of Subject and Predicate
The subject and predicate are the two fundamental components of a sentence in English grammar. A thorough comprehension of these elements is essential for effective communication and sentence construction. In this article, we will delve into the world of subjects and predicates, exploring their definitions, types, and relationships.
What is a Subject?
The subject of a sentence is the noun or pronoun that performs the action described by the verb. It is the “doer” of the action, and it typically appears before the verb in a sentence. For example:
- In the sentence “The dog runs quickly,” “the dog” is the subject because it is the one performing the action of running.
- In the sentence “She eats breakfast every morning,” “she” is the subject because it is the one performing the action of eating.
What is a Predicate?
The predicate of a sentence is the verb or verb phrase that describes the action or state of being of the subject. It is the “action” or “state” that the subject is performing or experiencing. For example:
- In the sentence “The dog runs quickly,” “runs quickly” is the predicate because it describes the action of the subject (the dog).
- In the sentence “She eats breakfast every morning,” “eats breakfast every morning” is the predicate because it describes the action of the subject (she).
Types of Subjects
There are several types of subjects, including:
- Simple Subject: A simple subject is a single noun or pronoun that functions as the subject of a sentence. For example: “The dog” in the sentence “The dog runs quickly.”
- Compound Subject: A compound subject is two or more nouns or pronouns that function together as the subject of a sentence. For example: “The dog and the cat” in the sentence “The dog and the cat are sleeping.”
- Collective Subject: A collective subject is a group of people, animals, or things that function together as the subject of a sentence. For example: “The team” in the sentence “The team is winning the game.”
Types of Predicates
There are also several types of predicates, including:
- Simple Predicate: A simple predicate is a single verb that functions as the predicate of a sentence. For example: “runs” in the sentence “The dog runs quickly.”
- Compound Predicate: A compound predicate is two or more verbs that function together as the predicate of a sentence. For example: “eats and drinks” in the sentence “She eats and drinks every morning.”
- Complete Predicate: A complete predicate is a predicate that includes a verb and all the necessary information to complete its meaning. For example: “eats breakfast every morning” in the sentence “She eats breakfast every morning.”
📝 Note: A predicate can also include additional information such as adverbs, adjectives, and prepositional phrases.
Relationship Between Subject and Predicate
The subject and predicate are closely related in a sentence, as they work together to convey meaning. The subject performs the action described by the predicate, and the predicate describes the action or state of being of the subject. A sentence cannot exist without both a subject and a predicate.
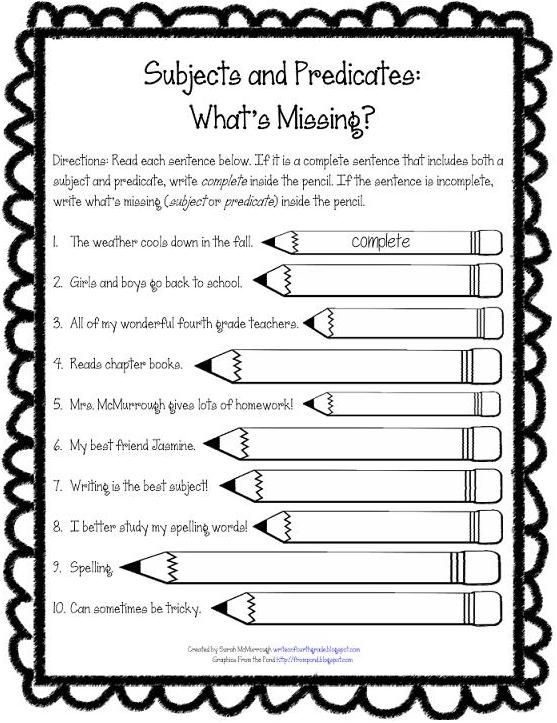
Free Worksheet: Mastering Subject and Predicate
To help you practice identifying subjects and predicates, we have created a free worksheet that includes a variety of exercises and activities. This worksheet is perfect for students, teachers, and language learners who want to improve their understanding of sentence structure and grammar.

| Exercise | Example Sentence | Subject | Predicate |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Identify the subject and predicate in the following sentence: | The teacher is writing on the board. | The teacher | is writing on the board |
| 2. Identify the subject and predicate in the following sentence: | The students are studying for their exam. | The students | are studying for their exam |
📝 Note: Answers can be found at the end of the worksheet.
Mastering the subject and predicate is an essential skill for effective communication and sentence construction. By understanding the definitions, types, and relationships between subjects and predicates, you can improve your writing and speaking skills. Don’t forget to practice with our free worksheet to reinforce your knowledge!
In summary, the subject and predicate are the two fundamental components of a sentence, working together to convey meaning and describe the action or state of being of the subject. Understanding the different types of subjects and predicates, as well as their relationships, is crucial for effective communication and sentence construction.
What is the difference between a simple subject and a compound subject?
+A simple subject is a single noun or pronoun that functions as the subject of a sentence, while a compound subject is two or more nouns or pronouns that function together as the subject of a sentence.
What is a complete predicate?
+A complete predicate is a predicate that includes a verb and all the necessary information to complete its meaning.
Why is it important to understand the subject and predicate in a sentence?
+Understanding the subject and predicate is essential for effective communication and sentence construction, as it helps to convey meaning and describe the action or state of being of the subject.