Atoms Basics Worksheet: Explore the Building Blocks of Matter
Atoms: The Indivisible Building Blocks of Matter
Atoms are the fundamental units of matter that make up everything around us, from the air we breathe to the stars in the sky. Understanding atoms is crucial to grasping the basics of chemistry and physics. In this article, we will delve into the world of atoms, exploring their structure, properties, and behaviors.
The Structure of Atoms
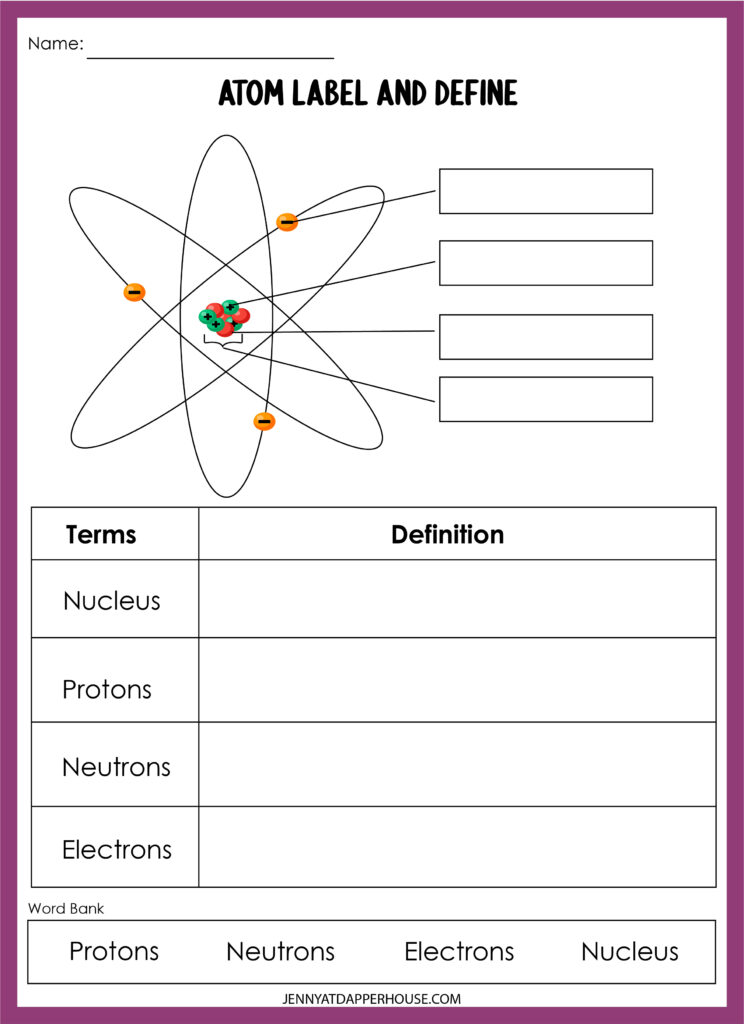
An atom consists of three main parts: protons, neutrons, and electrons.
- Protons: Positively charged particles that reside in the nucleus (center) of the atom. The number of protons in an atom determines the element of an atom.
- Neutrons: Particles with no charge that reside in the nucleus along with protons. The number of neutrons in an atom determines the isotope of an element.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit around the nucleus. The number of electrons in an atom is equal to the number of protons.
The protons and neutrons in the nucleus are known as nucleons, while the electrons in the outermost energy level are called valence electrons.
Atomic Number and Mass Number
- Atomic Number (Z): The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, which determines the element of an atom.
- Mass Number (A): The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus, which determines the mass of an atom.
The atomic number and mass number are used to identify and distinguish between different elements and isotopes.
Isotopes and Ions
- Isotopes: Atoms of the same element with the same number of protons (atomic number) but different numbers of neutrons (mass number).
- Ions: Atoms that have gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge.
Isotopes and ions are crucial in understanding the behavior of atoms in different chemical reactions and environments.
Chemical Bonding
Chemical bonding occurs when atoms share or exchange electrons to form a chemical compound. There are three main types of chemical bonds:
- Ionic Bonding: The transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in the formation of ions with opposite charges.
- Covalent Bonding: The sharing of electrons between atoms, resulting in a strong and stable chemical bond.
- Metallic Bonding: The delocalization of electrons among a lattice of metal atoms, resulting in a strong and conductive material.
Chemical bonding is essential in understanding the properties and behaviors of different materials and substances.
Atomic Radius and Electronegativity
- Atomic Radius: The distance between the nucleus and the outermost energy level of an atom.
- Electronegativity: The ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself.
Atomic radius and electronegativity are important factors in determining the reactivity and chemical behavior of atoms.
Periodic Table
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of elements, organized by their atomic number and chemical properties. The periodic table is a powerful tool for predicting the behavior and properties of different elements and compounds.

| Periodic Table Groups | Description |
|---|---|
| Alkali Metals | Highly reactive metals that readily lose electrons |
| Noble Gases | Unreactive gases that have a full outer energy level |
| Halogens | Highly reactive nonmetals that readily gain electrons |
📝 Note: The periodic table is a powerful tool for predicting the behavior and properties of different elements and compounds. However, it is not a foolproof method and requires careful interpretation.
Conclusion
Atoms are the building blocks of matter, and understanding their structure, properties, and behaviors is crucial for grasping the basics of chemistry and physics. By exploring the world of atoms, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate and complex nature of the universe.
FAQ Section:
What is the difference between atomic number and mass number?
+Atomic number (Z) refers to the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, while mass number (A) refers to the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus.
What is the purpose of the periodic table?
+The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of elements, organized by their atomic number and chemical properties. It is a powerful tool for predicting the behavior and properties of different elements and compounds.
What is the difference between ionic and covalent bonding?
+Ionic bonding involves the transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in the formation of ions with opposite charges. Covalent bonding involves the sharing of electrons between atoms, resulting in a strong and stable chemical bond.